Guide To Endocrine System Diseases
Turner Syndrome

Turner syndrome is a genetic condition that occurs in girls, and it develops when one of the X chromosomes is partially or entirely absent. Patients with Turner syndrome may have heart and kidney abnormalities before birth, and these can be detected with a prenatal ultrasound. The ultrasound might also show abnormal fluid collection at the back of the neck. Other symptoms may become apparent at birth or during infancy. For example, patients could have a wide neck, swollen hands or feet, delayed growth, short fingers and toes, and low-set ears. In childhood and into adulthood, the patient might attain a height that is significantly less than other females in the family, and sexual development may begin late or stall during the teenage years. Turner syndrome patients often need fertility treatment to become pregnant. Turner syndrome may be diagnosed prenatally with amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. Treatment options include estrogen therapy and growth hormone therapy, and patients will need regular checkups throughout their lives.
Learn more about the different endocrine system diseases now.
Prolactinoma
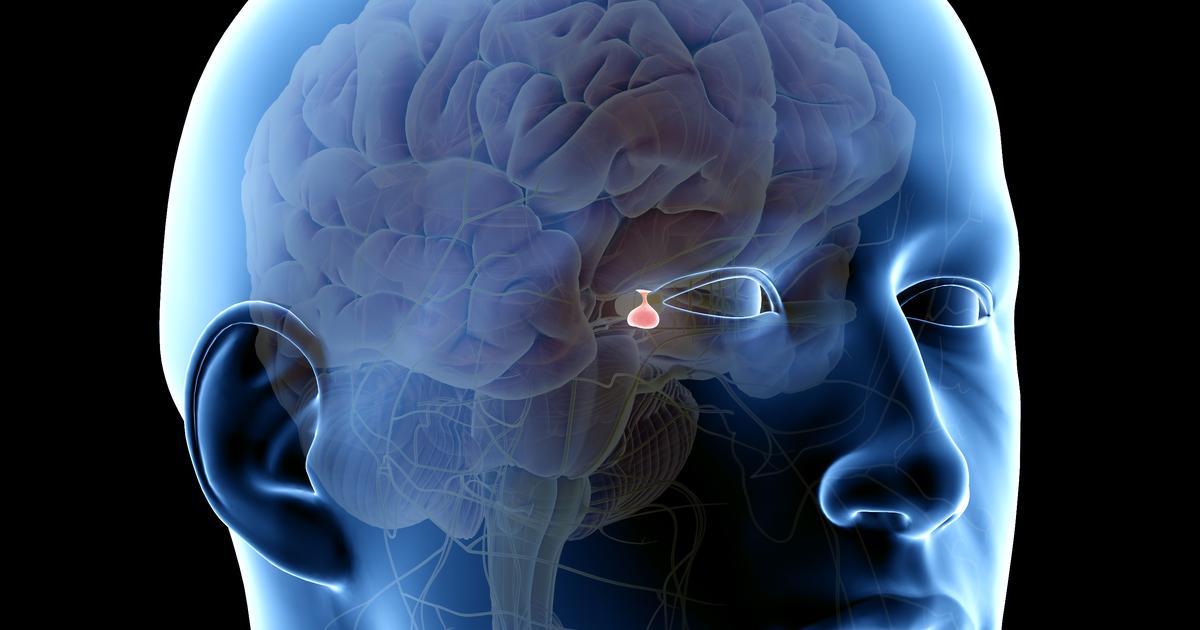
A prolactinoma is a type of benign pituitary gland tumor, and it causes the gland to produce too much of a hormone called prolactin. The overproduction of this hormone reduces estrogen in women and testosterone in men. Although patients with this condition might be asymptomatic, prolactinomas can trigger a range of symptoms if they grow large enough to press on surrounding tissues or if they cause excessive prolactin in the blood. Females may have irregular or absent menstrual periods, and a milky discharge from the breasts might occur in women who are not currently pregnant or breastfeeding. Prolactinomas might cause vaginal dryness that could make sex painful, and women could also notice excessive hair growth on the face and body. In males, prolactinomas might cause enlarged breasts, decreased facial and body hair, and erectile dysfunction. Male and female patients could notice headaches and visual disturbances, and low bone density and infertility might occur. To diagnose a prolactinoma, doctors perform blood tests to check prolactin levels, and MRI scans of the brain are done to detect potential tumors on the pituitary gland. Long-term treatment with dopamine agonists is recommended to decrease the production of prolactin and reduce tumor size. Patients may need to have transcranial or transsphenoidal surgery to remove the tumor.
