What Are The Most Common Lung Diseases?
Pulmonary Embolism
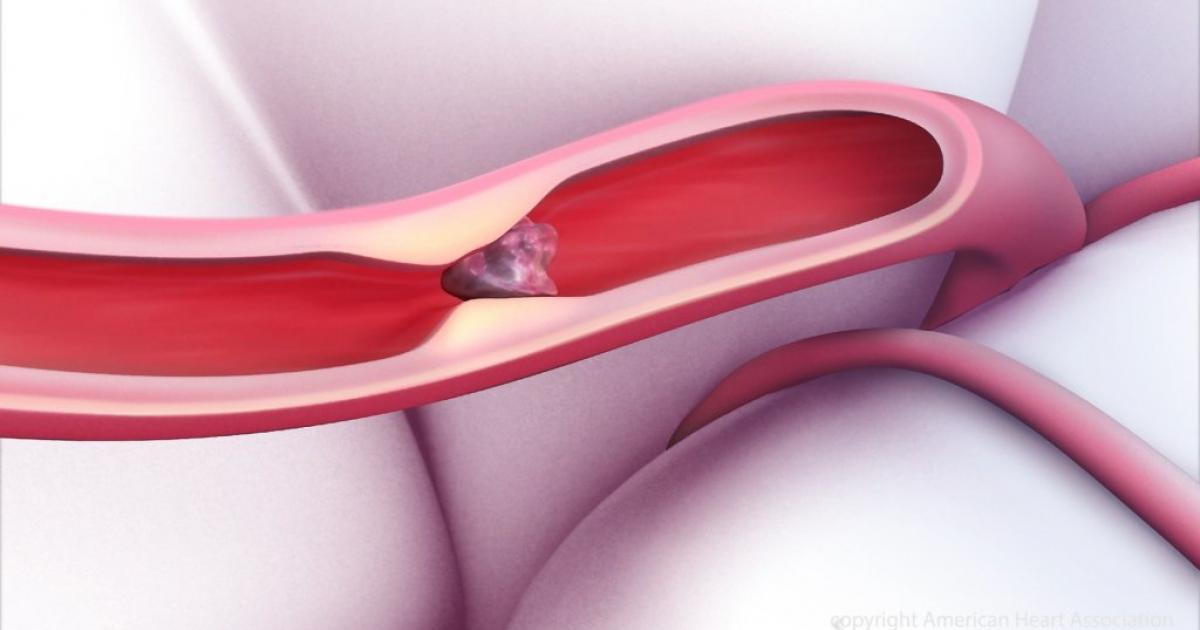
Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening condition where a blood clot becomes lodged in the lung tissues. A blood clot in the lung tissues can cause tissue damage as a result of the deprivation of blood. Pulmonary embolism can cause oxygen levels in the patient's blood to become too low, which can cause damage to other vital organs in the body from the insufficient oxygen supply. Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include shortness of breath, productive or unproductive cough, chest pain, back pain, more sweating than usual, lightheadedness, syncope, and blue tint in the lips or nails. A diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is made through physical examination, ultrasound of the lungs, x-rays of the lungs, blood tests, computed tomographic angiography, ventilation/perfusion scan, pulmonary angiography, MRI scans, and echocardiogram. Treatment includes the short or long term administration of anticoagulants to help prevent the body from forming new blood clots inappropriately, such as warfarin, heparin, dalteparin, enoxaparin, and tinzaparin.
Lung Cancer
The lungs are the two delicate organs in the chest cavity that facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood before it is pumped by the heart back to the tissues in the rest of the body. Lung cancer is a common lung disease, leading the United States in most deaths attributed to cancer. Most cases of lung cancer are caused by smoking cigarettes and exposure to other carcinogens commonly found in certain occupations. A small percentage of lung cancer cases occur in individuals who do not smoke because of genetic factors and a general predisposition to developing cancer. Symptoms of lung cancer include a productive cough that will not go away, hoarseness, unintentional weight loss, headaches, bone pain, chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood in small or large amounts. A diagnosis of lung cancer is made with the use of sputum cytology, x-ray imaging, CT scans, and lung tissue biopsy. Treatment options include surgery, radiosurgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care.
