Comprehensive Overview Of Heart Cancer
Causes And Complications Of Heart Cancer

The exact causes of heart cancer development in some individuals but not others is not known. However, certain factors and circumstances make an individual more likely to get heart cancer. Some types of heart tumors are more common in children, while others occur more often in adults. Some inherited genetic factors like mutations or deletions in certain genes can increase an individual's risk of developing a malignancy in their heart. Some genetic cancer syndromes are known to increase an individual's risk of forming heart cancer, such as tubular sclerosis.
Individuals who have an immune system that has been damaged or compromised are at a higher risk of developing heart cancer. Any individual who has had or currently has cancer in any other region of the body is more likely to develop heart cancer. Complications that occur in heart cancer patients include failure of the heart, tumor metastasis, and tumor emboli, which are fragments that have broken off and made their way into circulation.
How It Is Diagnosed
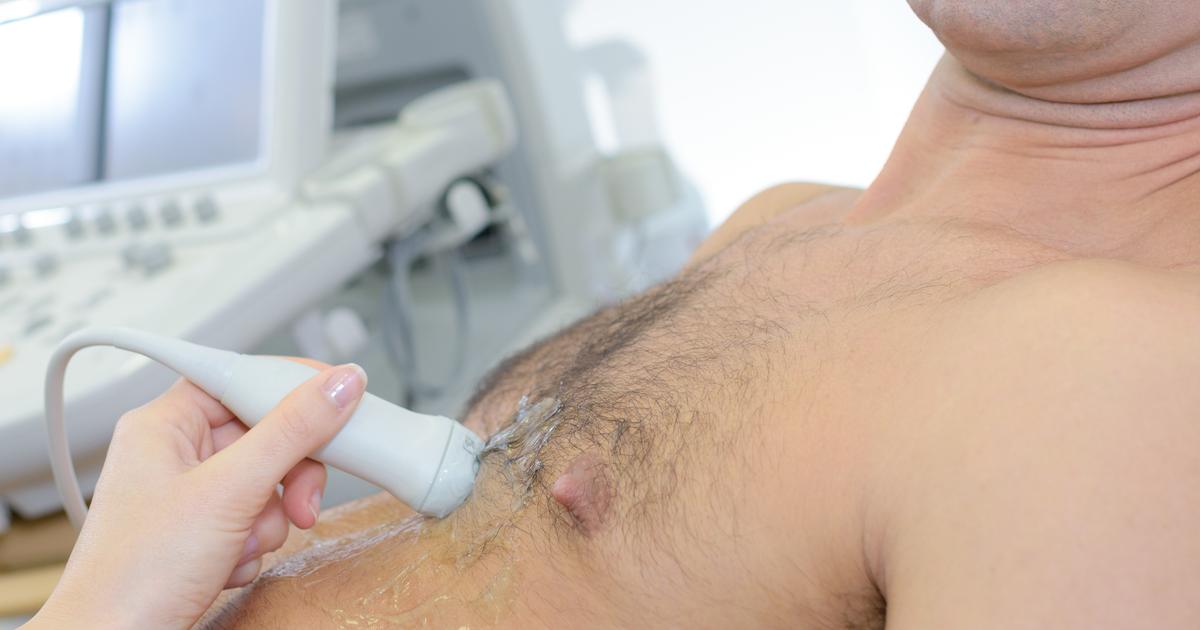
The diagnosis of malignant tumors in the heart has a high reliance on an extensive combination of diagnostic imaging techniques. Cardiac computed tomography scans, echocardiography or heart ultrasound, positron emission tomography, and cardiovascular magnetic resonance are used to aid in the diagnosis of heart cancer. These forms of diagnostic imaging technology help physicians determine the exact size of a patient's intracardiac mass, the amount of growth and metastasis of the mass, the degree of invasion the mass has in the myocardial tissue, and the location of the cardiac chamber that contains the intracardiac tumor.
In patients who have exceptionally rare cases of heart cancer, a definitive tissue biopsy may be performed when the diagnostic imaging methods are unable to provide an accurate characterization of the malignant mass in the heart. There can be challenges in overcoming the safety of performing a heart tissue biopsy on some patients, which complicates the diagnostic process significantly in such cases.
