The Essential Overview Of Fatty Liver Disease
Diagnosing Fatty Liver Disease
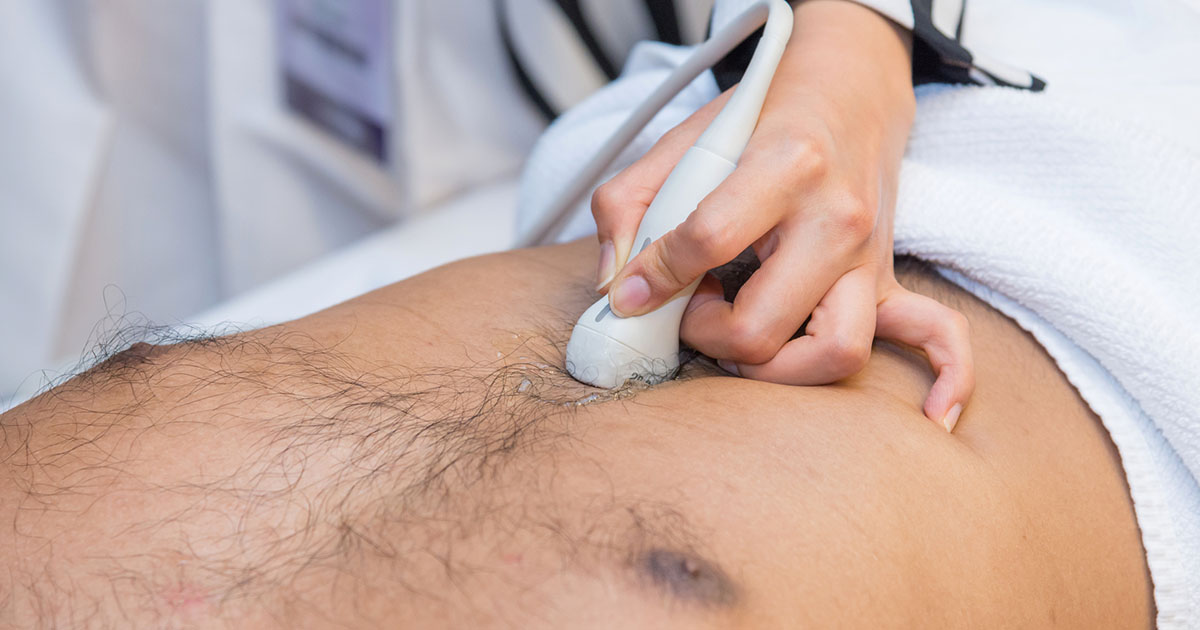
Since symptoms may take years to onset, fatty liver disease is often discovered when doing tests for other reasons. Some methods used to diagnose fatty liver disease include blood tests, ultrasounds, computerized tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), transient elastography, and magnetic resonance elastography. If all other test results are inconclusive, a liver biopsy may be implemented to remove a sample of liver tissue. The tissue sample is then examined for signs of inflammation and cirrhosis. The liver biopsy may be painful and can have some small risks.
Treatment Of Fatty Liver Disease
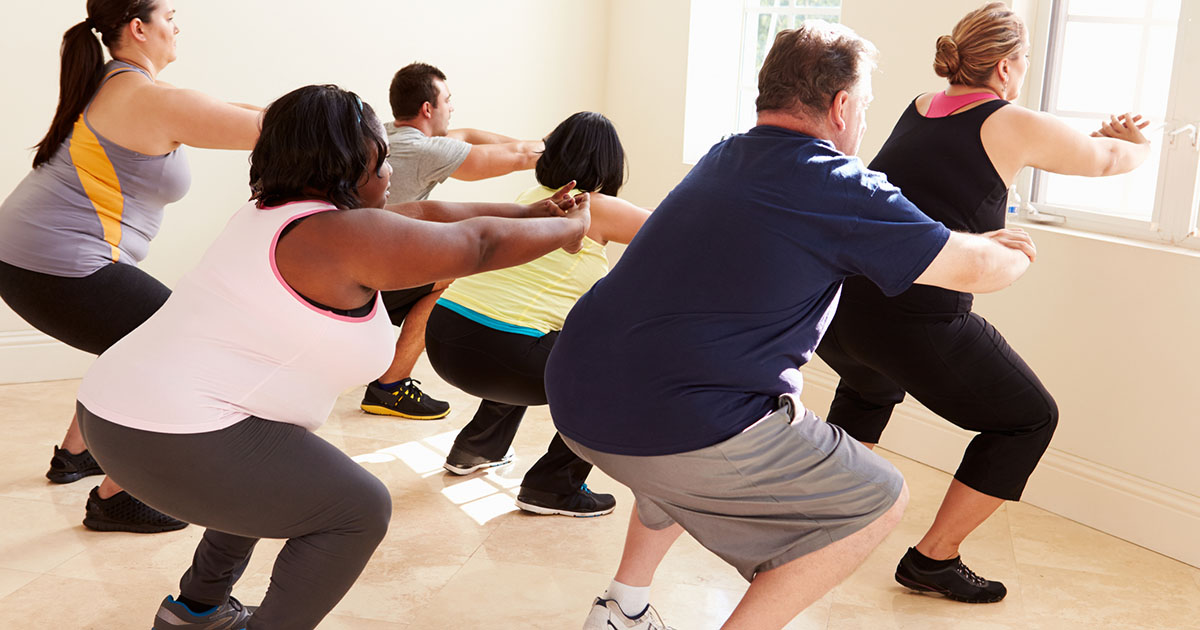

Beginning treatment for fatty liver disease begins with weight loss through a combination of changing to a healthier diet and getting more exercise. If suffering from ALD, the consumption of alcohol must cease immediately, and even with NAFLD, alcohol consumption should be limited, if any is consumed at all. An ideal amount of weight to lose is ten percent of total body weight, but improvements will become apparent after losing three to five percent of starting weight. Some other possible treatments include vaccines for hepatitis A and B to prevent further liver damage, and possibly a liver transplant for patients with cirrhosis.
