Overview Of The Warning Signs Of Gallbladder Problems
Nausea And Vomiting
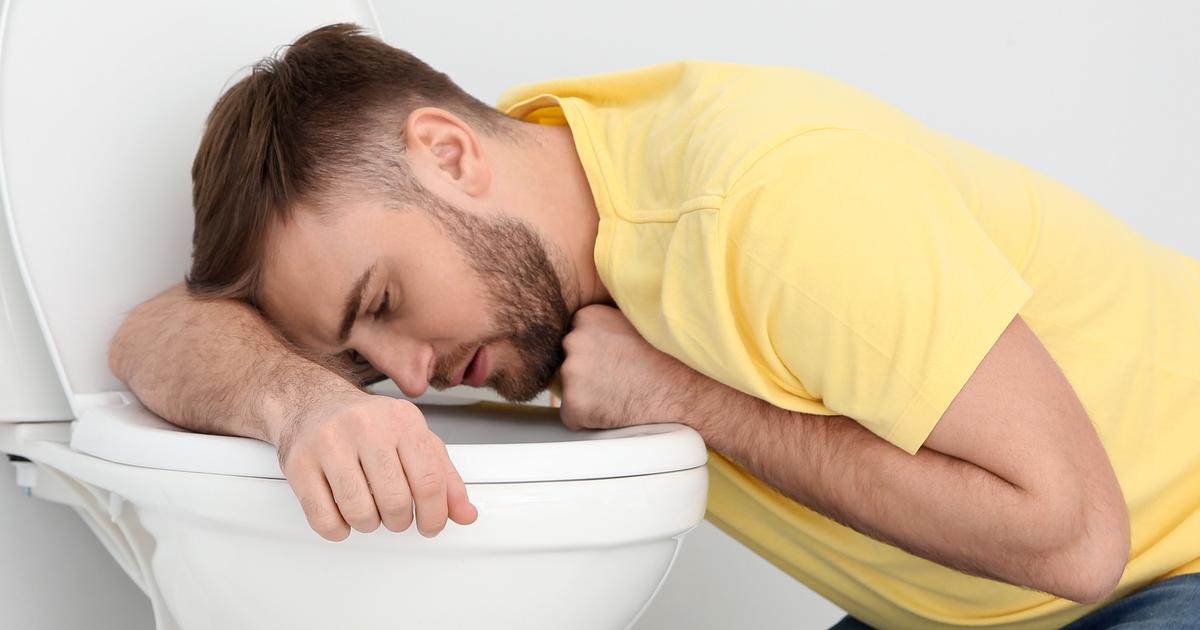

Nausea and vomiting can occur with any gallbladder issue, though they are common in a variety of other conditions as well. When the symptoms occur after eating a fatty or exceptionally large meal, they are more likely to be related to the gallbladder. This can be an indication of infection or inflammation. If individuals do not treat the inflammation, they may experience these symptoms long-term until their gallbladder is removed. They may also develop an infection. If individuals have ongoing digestive issues like gas and acid reflux, it may be a sign of chronic disease.
These symptoms do not indicate inflammation, but instead indicate that the individual's body is systematically losing its ability to digest the material. This is often related to the reduced amount of bile in their intestines. Some patients also experience issues with digestion following gallbladder surgery. There are typically ways to treat this by ensuring that the body can digest food. This may involve a specialized diet, eating at certain times of day, or taking medication to balance symptoms.
Jaundice
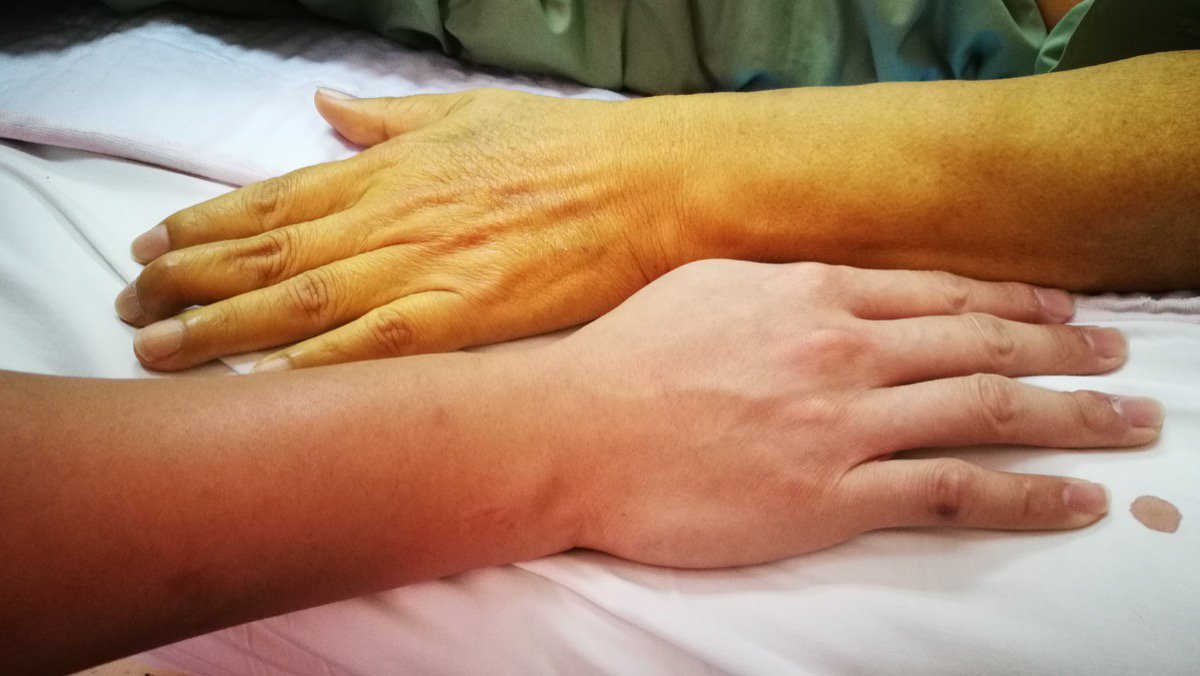
Jaundice is best known as a liver issue, but it can also indicate gallbladder problems. Patients may develop a yellow tint to their skin when their bile duct becomes obstructed. Oftentimes, this happens due to gallstones. The bile duct allows bile to flow from the gallbladder into the small intestine so that individuals can digest food. If the duct is partially or fully blocked, bile will build up. Jaundice causes yellowing of the eyes and skin because bilirubin levels become high. This bile has a yellowish-orange tint. Bilirubin forms when the body breaks down red blood cells in the liver.
Jaundice can be caused before and during bilirubin production, but it is typically gallstone-related when it occurs afterward. Individuals may also have an inflamed gallbladder blocking their bile duct without gallstones. Some patients may develop gallbladder cancer. A cancerous mass of cells may obstruct the duct and create the blockage. In adults, jaundice does not always need treatment. However, if individuals develop jaundice suddenly, they must determine the cause to make sure it is not serious.
