A Comprehensive Guide To Sickle Cell Anemia
How Is It Diagnosed?
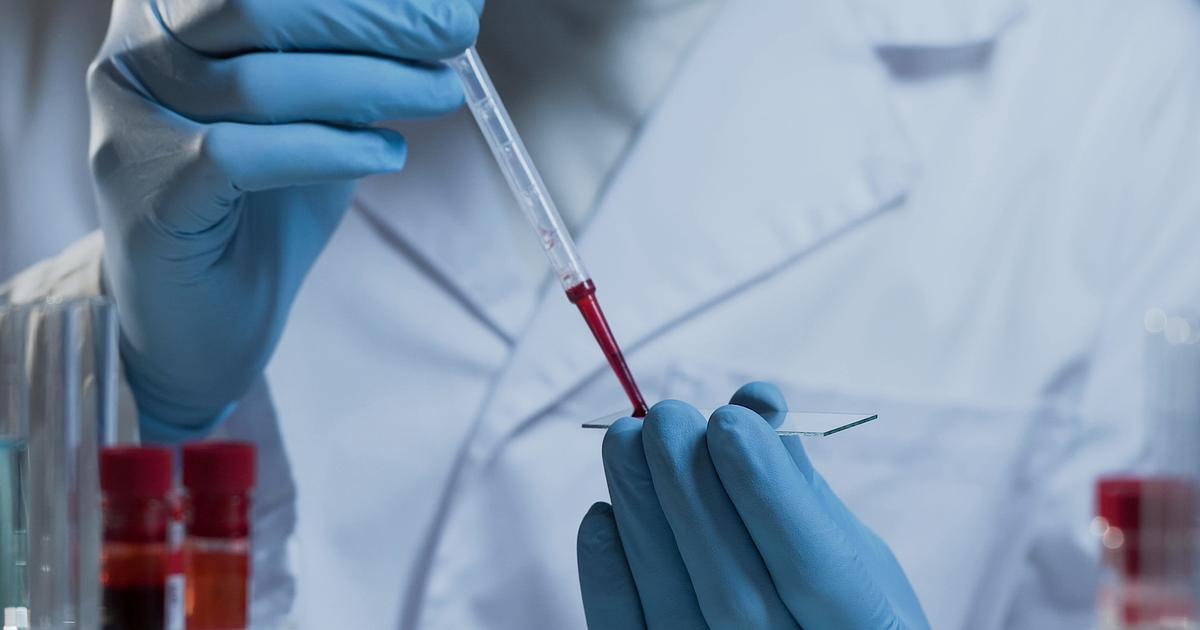
Sickle cell anemia can be diagnosed in a few different ways. One way is the abnormal sickle-shaped cells in the blood can be identified under a microscope, where a smear of blood is extracted and tested using a special low-oxygen preparation known as a sickle prep. Other prep tests can also identify the abnormal hemoglobin in the blood, including solubility tests performed on vials of blood solutions. The disease can be determined by quantifying the types of hemoglobin present using hemoglobin electrophoresis, which precisely identifies the hemoglobins in the blood by separating them. This is made possible due to the unique electrical charges each hemoglobin has on their protein surfaces. Prenatal diagnosis can also occur before birth if the mother suffers from sickle cell anemia, or is at least a carrier, by using amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. The sample obtained from the womb is then tested for DNA analysis of the fetal cells.
Keep reading to unearth the variety of treatment options available to patients dealing with the disease.
Available Treatment Options
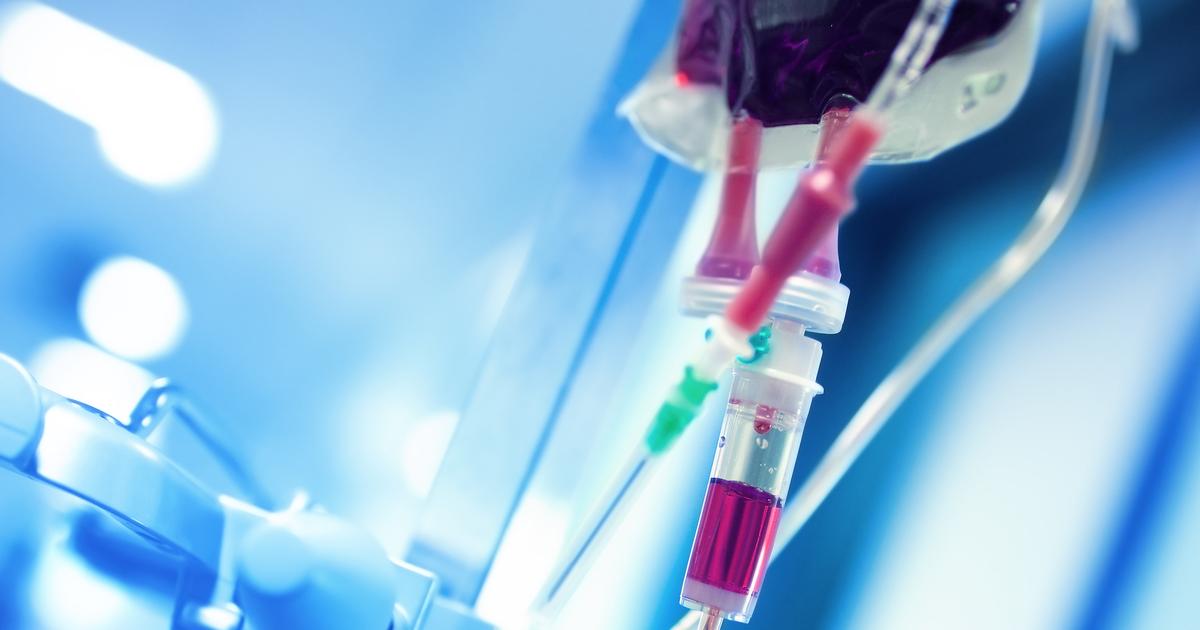
There is no cure for sickle cell anemia, but there are numerous treatment options that can manage and prevent the condition based on the individual features of the illness present. Treatments are directed at the management and prevention of the red blood cells from stacking on top of each other, which forms blood clots. It is essential for affected individuals to have a profound understanding of the disease and to communicate with medical professionals to ensure they are receiving the proper care for the symptoms they exhibit. However, sickle cell anemia tends to become stable without specific treatments over time. Treatment options also depend on the degree of anemia the patient has, which is defined by their blood hemoglobin level.
One treatment option is a blood transfusion, which is required when a severe drop in hemoglobin occurs to correct the anemia and also for patients who are dealing with other complications such as pneumonia, lung infarction, stroke, leg ulcers, or late pregnancy. A transfusion can remove some of the sickle blood cells and replace them with healthy blood cells. Hydroxyurea is a medication that can also be used for adults and children who suffer from severe pain associated with the illness, as well as for individuals who have recurrent strokes and frequent transfusions. The drug increases the amount of fetal hemoglobin in the blood, a form of the molecule resistant to the sickling of the red blood cells found in infants right after birth.
Understand the role of stem cell transplants in sickle cell anemia treatment next.
