What Are The Symptoms Of Gallstones?
Dark Urine Or Clay-Colored Stool
A healthy individual's stool gets its dark color from the bile used in the process of digestion. A small amount of bile in the intestine is absorbed to be re-used, while the remainder is secreted in the stool. Bile is used in the digestive system to enable the breakdown of fats into molecules the intestine can absorb. Fats are the component of food that is the most difficult for the body to digest and takes the longest to digest. An individual with gallstones may experience symptoms related to the absence of bile when the gallstones obstruct the ducts that deliver the bile to the intestine. With a bile duct blockage, no bile can come through to aid in digestion and fats in the food an affected individual consumes are not broken down. These undigested fats remain in the stool until it is excreted. The stool is pale because there is no bile in it, and often has a foul odor as a result of undigested lipids. Darker urine may manifest if bile builds up behind the gallstone blocking it from reaching the intestine.
Fever And Shivering
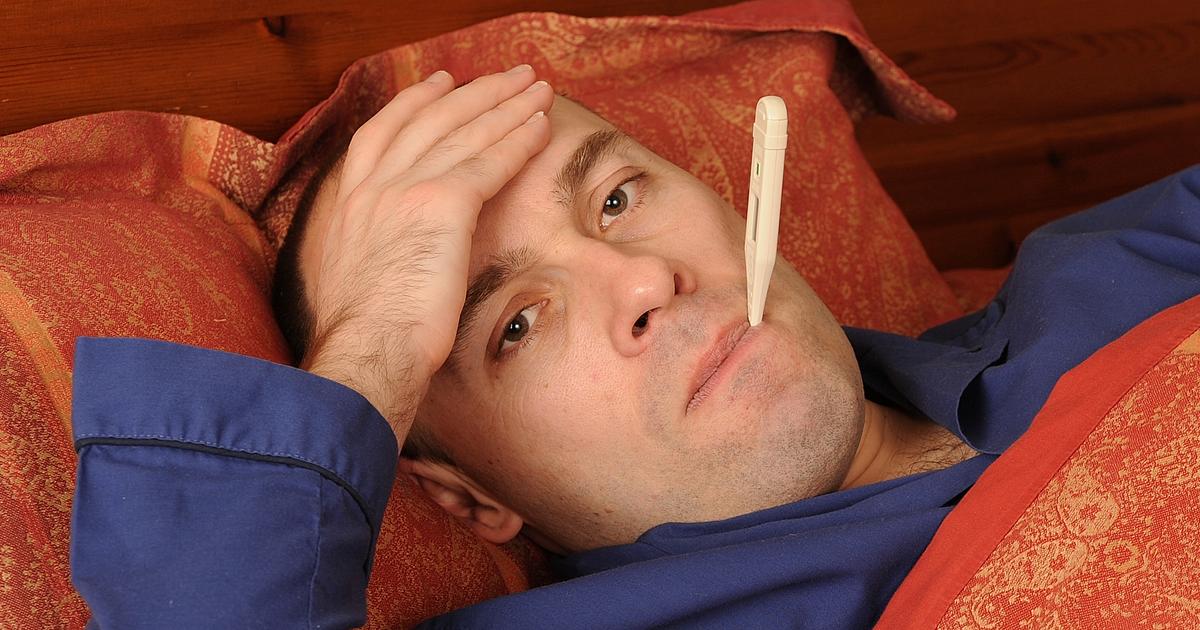

A fever and shivering can occur if individuals develop cholecystitis, gallbladder inflammation, as a result of the gallstone. This can be a very serious complication with life-threatening consequences. If patients suddenly develop a high fever and chills, it's important to see a doctor. High fevers are often a sign of an infection or inflammation. A fever is typically considered high if it reaches 103 degrees Fahrenheit or higher. Inflammation due to gallstones is typically the result of the gallstone blocking the tube that leads out of the gallbladder. If patients don't get the condition treated, they might suffer a gallbladder rupture, which could be fatal. The most common treatment for cholecystitis is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Patients should talk to their doctor immediately if they have worrying signs of gallstones accompanied by a fever and chills.
