Symptoms Of Scleroderma
Joint And Muscle Aches
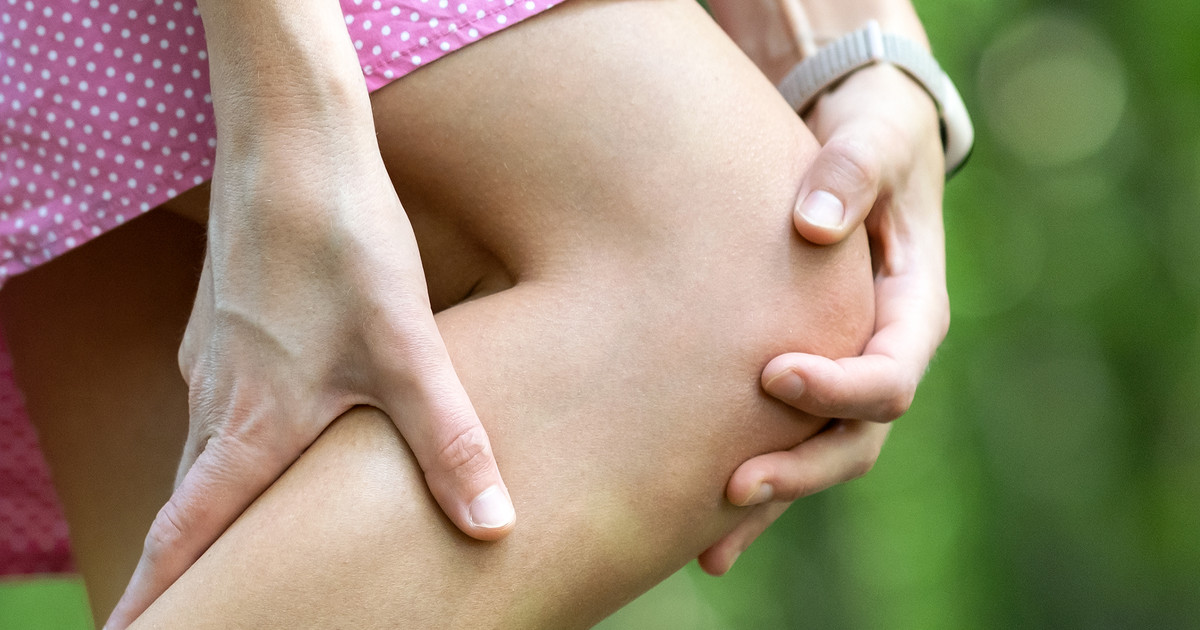

Joint and muscle aches are common symptoms that occur in individuals with scleroderma. There are numerous ways scleroderma can cause pain in an affected individual's joints and muscles. Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease because the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing an overproduction of collagen and scar tissue. Rheumatoid arthritis is also an autoimmune disease that is associated with scleroderma that causes the bones of a joint to become severely inflamed. The muscle aches may originate from thick and stiff blood vessels that are unable to provide muscle fibers with adequate amounts of oxygenated blood.
Muscle pain may also arise from a buildup of scar tissue caused by the abnormal autoimmune actions taken by the immune system of scleroderma-affected individuals. Scar tissue is more dense and fibrous than healthy muscle tissue, and it also cannot stretch the same way as healthy muscle tissue. Scar tissue can cause injury and damage to surrounding healthy muscle tissue when the individual attempts to utilize the affected muscle.
Irregular Heartbeat
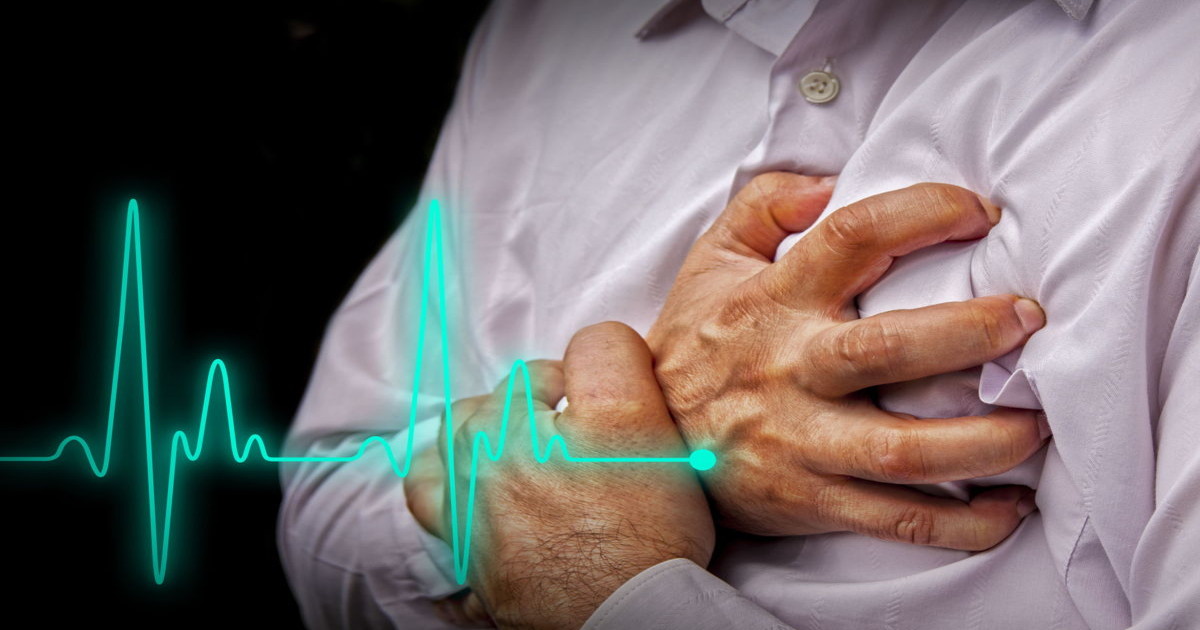
An irregular heartbeat can be indicative of the presence of scleroderma in an individual. A healthy individual's heart has its own electrical system responsible for the careful timing coordination of the contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle. Nodes are located throughout the heart muscle that sends and receives electrical impulses that trigger the movement of different chambers of the heart. In order for an individual's heart to beat in a normal rhythm, the electrical impulses have to travel without interruption on a pathway that passes through the nodes.
Scleroderma causes excess scar tissue to develop in connective tissues around the body. Because the heart is a muscle, scleroderma can affect it. When the immune system of individuals with scleroderma attacks the muscle tissues of the heart, scarring can form in areas involved in its electrical pathways. When dense fibrous scar tissue disrupts the heart's electrical pathway between or at the site of the nodes, an abnormal heart rhythm can result.
