The Causes, Symptoms And Treatment Of Malaria
4. Symptoms Of Severe Malaria
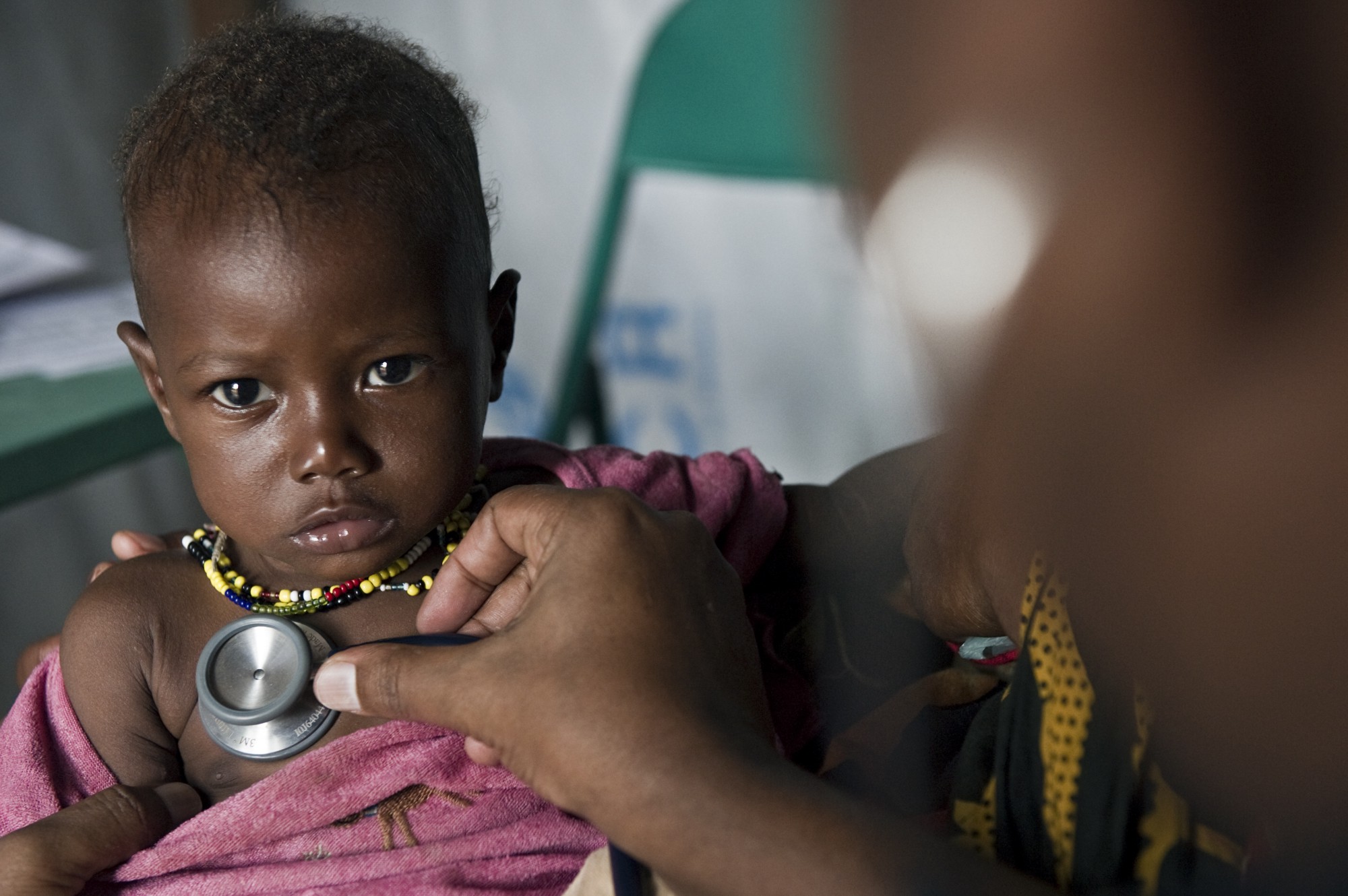
Clinical symptoms of severe or complicated malaria include generalized weakness such as the inability to sit, stand or walk without assistance, impaired consciousness including a coma, convulsions lasting more than two episodes within a twenty-four hour period, respiratory distress, deep breathing, acute kidney injury, shock, systolic blood pressure, jaundice, abnormal bleeding and other signs of vital organ dysfunction. Severe malaria can also mimic other diseases such as pneumonia, typhoid fever, central nervous system infections, and gastroenteritis.
3. Other Signs Of Malaria
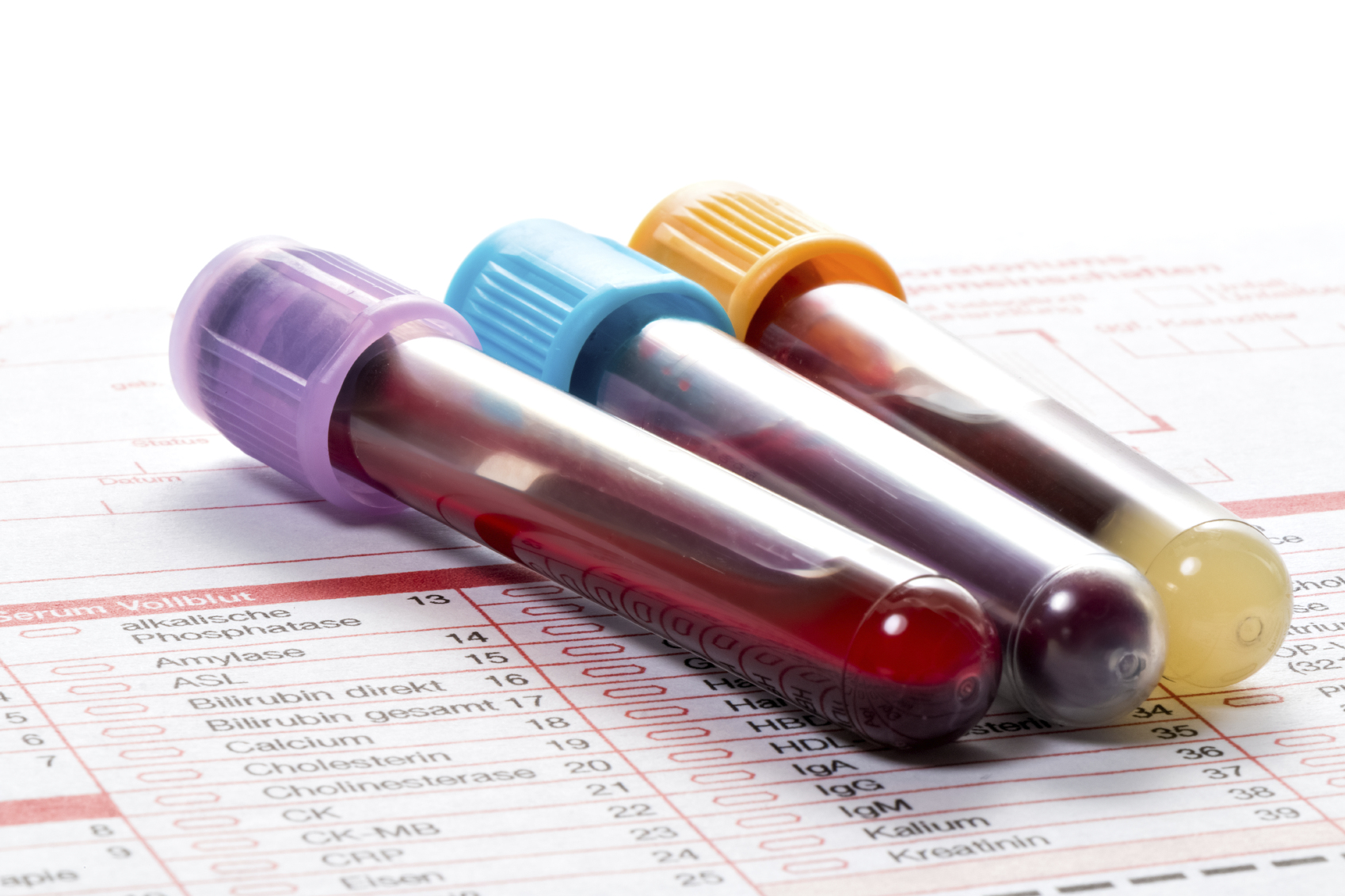
Severe malaria may cause anemia, which occurs when the body carries a small amount of red blood cells. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin that is needed to carry oxygen throughout the body. Polymorphonuclear leukocytosis, or an increase of white blood cells, is also common. People with malaria may have higher blood levels of liver and muscle enzymes, urea, and creatinine, which is a chemical waste that passes through the kidneys and is eliminated via the urine. Malaria also causes acidity in the blood, which occurs when there is an imbalance in pH levels.
