How To Treat Tinnitus Effectively
Hearing Aids
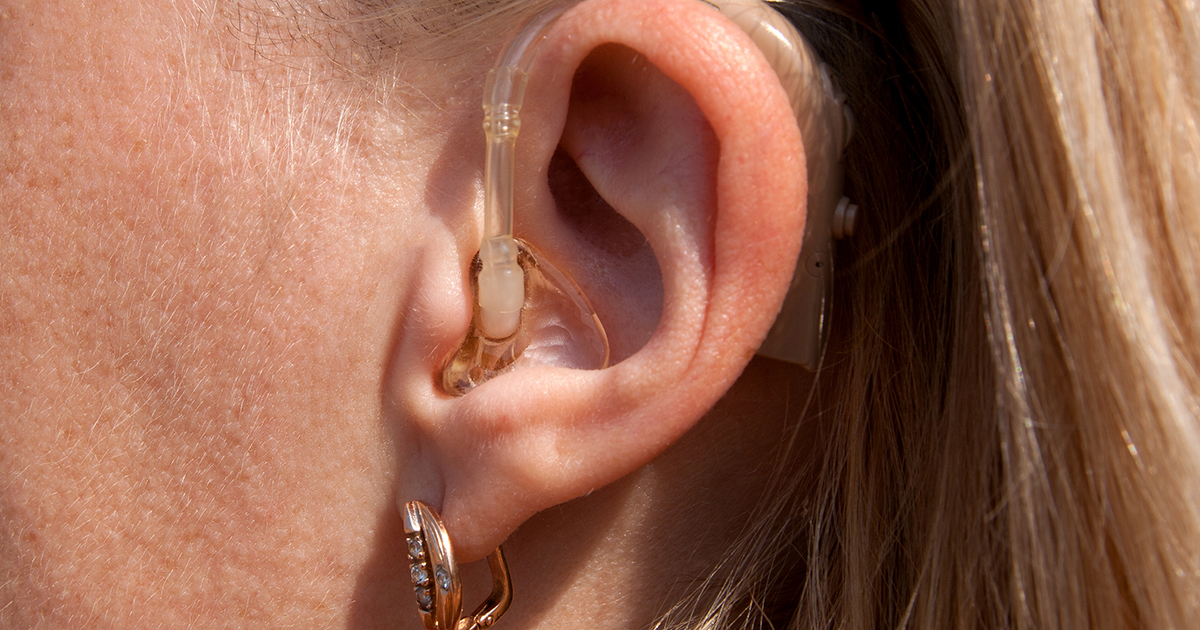
Because tinnitus is overwhelmingly related to some degree of hearing loss, the augmentation of receiving and perceiving of external noise frequently provides relief from the interior sound of the condition. Most patients find themselves developing tinnitus as a symptom of loss of hearing, whether by long-term hearing damage, age, or the auditory system experiencing acute trauma.
The consensus of the scientific community is when hearing loss is causing limited external noise stimuli to the brain, that organ responds by undergoing neuroplastic changes in the way it processes various sound frequencies. Tinnitus results from these maladaptive changes. Because of this, hearing aids, as well as other sound amplification devices, may offer relief from tinnitus. These are little electronic devices the patient wears in or behind the ear. They use a microphone, speaker, and amplifier to supplement outside noise's volume and increase the sheer amount of received and processed sound stimuli.
Noise Suppression Techniques
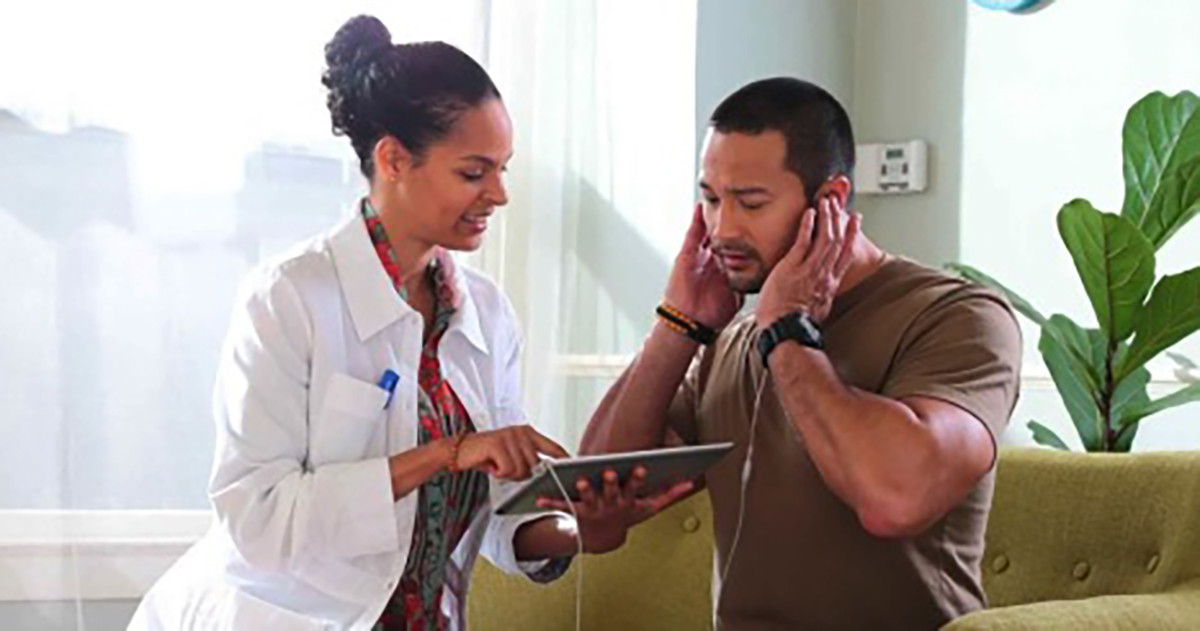

Tinnitus is an internal, non-auditory sound, but patients can make use of real, external noise to counteract the perception of and reaction to the condition. Sound masking and noise suppression can cover the illusory sounds of tinnitus. There are four different types of sound therapy, or noise suppression techniques. Masking exposes the patient to noise at high enough volumes to either completely or partially cover the sound. Distraction uses sounds to divert attention. Habituation helps the brain reclassify the internal sounds to unimportant sounds the mind can ignore with practice.
Neuromodulation is the practice of specialized sound use in the minimization of neural hyperactivity which is widely thought to be tinnitus's underlying cause. Traditional sound maskers are bedside or table-top devices with a few pre-set sound options. Almost any device that produces sound can be used for masking purposes, however, ranging from phones, radios, computers, and televisions to table fountains and electric fans. Unfortunately, sound masking in this way is generally only effective while in use or immediately after.
