Uncommon Autoimmune Diseases Everyone Should Be Aware Of
Risk Factors & Treatment For Vitiligo

Common factors for developing vitiligo include a family history of the disorder and other autoimmune diseases such as alopecia areata, hyperthyroidism, and pernicious anemia. Diagnosis can be confirmed with a tissue biopsy, but also by holding an ultraviolet light over the affected area which will appear lighter than the patient's skin color. There is no cure for vitiligo, although it can be treated and managed with sunscreen and makeup for lighter-skinned individuals, as well as steroid creams or phototherapy to darken lighter patches, hydroquinone to lighten unaffected areas, as well as surgery if other methods do not work.
However, a combination of treatments generally provides a patient with a better outcome and counseling for emotional support is also recommended for some. Globally, males and females are equally affected by vitiligo, making up approximately one percent of individuals with a majority of patients developing the condition before age forty.
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis?
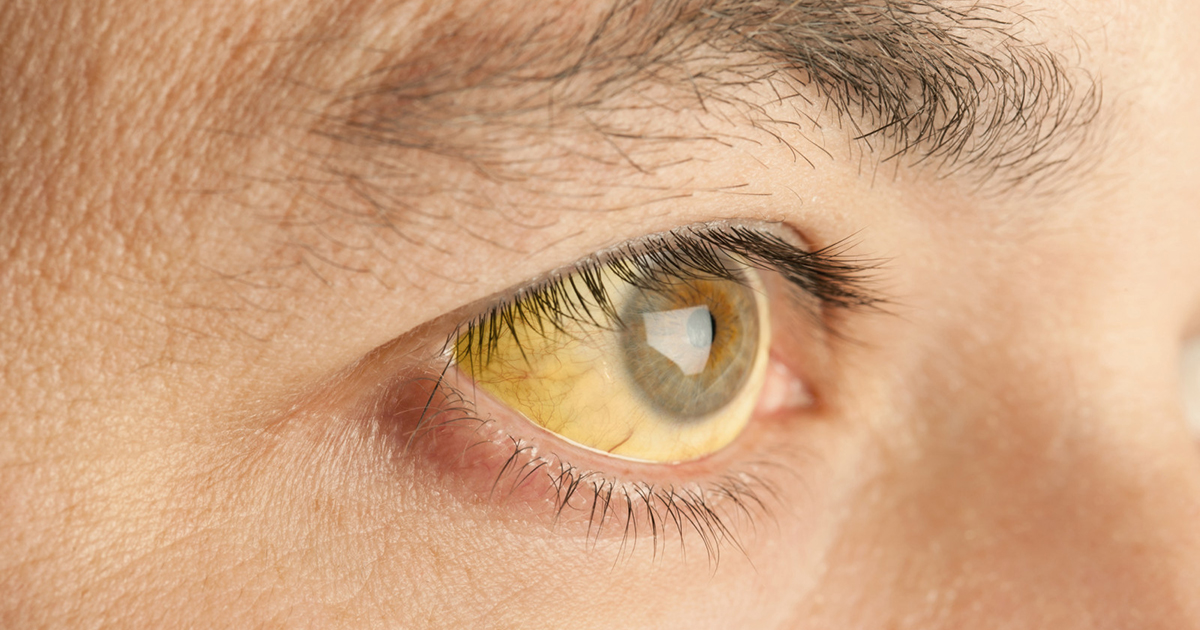
Lupoid hepatitis - now commonly known as autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) - is a chronic autoimmune disease that targets the liver and occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, resulting in liver inflammation. Common symptoms include fatigue, muscle aches, or signs of acute liver inflammation including fever, jaundice, and upper right abdominal pain. Patients usually show no initial symptoms of the condition, and abnormal liver function tests usually detect it. Inflammation of the liver can lead to further symptoms and result in complications such as fatigue, cirrhosis of the liver, and liver failure.
