Common Warning Signs Of Vasculitis
Blood Clots
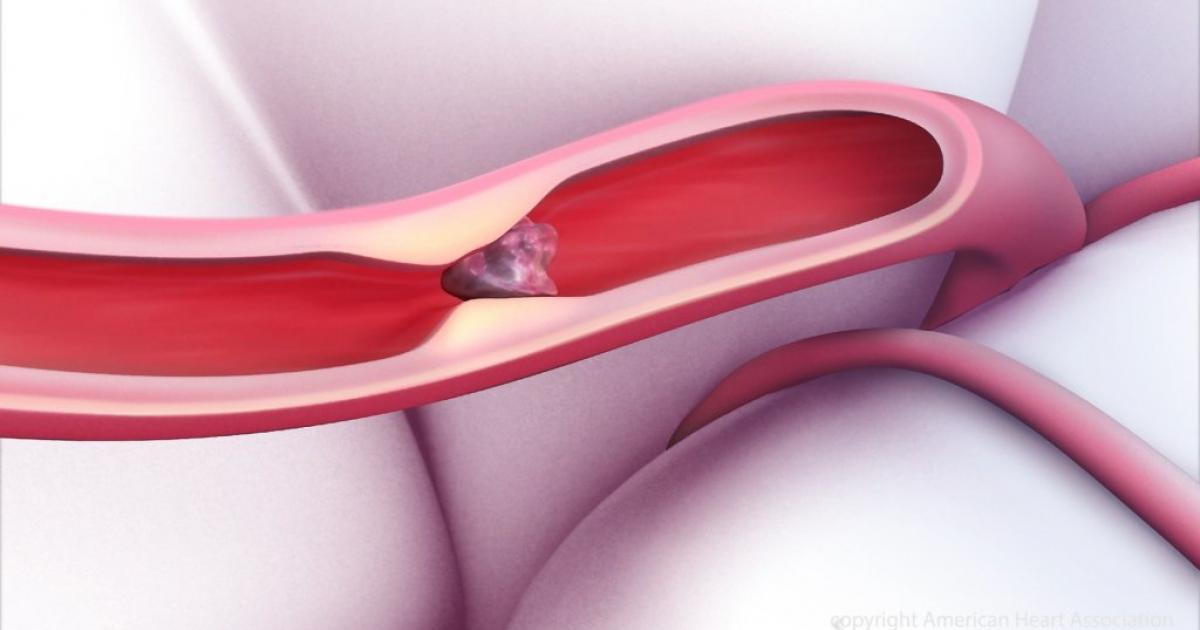
The formation of blood clots can be a symptom indicative of vasculitis. The mechanism behind this occurrence is thought to be associated with the close relationship between the immune system and coagulation processes in the body. Inflammation has a modulating influence on thrombotic responses through several mechanisms. It upregulates procoagulant or stimulates inactive protein synthesis into a clotting enzyme. Inflammation also suppresses fibrinolysis or stops the breakdown process of fibrin in clots no longer needed in the body.
Furthermore, inflammatory responses downregulate anticoagulants or naturally occurring proteins in the body responsible for stopping the formation of inappropriate blood clots and inhibiting the extension of existing clots. Because vasculitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, the inflammatory components are in direct contact with coagulation components. This mechanism may result in the inappropriate formation of clots, the extension of existing clots, and stop the breakdown of clots that are no longer needed. All of these processes can cause blood clots to float freely around the body in the vessels that can become lodged.
Blurred Or Double Vision

Blurred or double vision are symptoms that may occur in individuals affected by vasculitis. Inflammation and swelling of certain blood vessels in an individual's head as a result of vasculitis can cause a blood flow obstruction to the nerves responsible for keeping the eyes aligned properly. When these nerves do not tell certain muscles to move the eyes, they do not report the same image to the brain. This malfunction called cranial nerve palsy results in what is known as double vision. Inflammation of the blood vessels in the retina (retinal vasculitis) is a common mechanism in vasculitis that results in vision loss or blurry vision. Blurry vision can also be caused by uveitis.
The bundle of nerve fibers responsible for transmitting visual information from the eyes to the brain (the optic nerve) is supplied by numerous small blood vessels that intertwine with it. Vasculitis can cause these blood vessels to become swollen and inflamed, resulting in reduced blood flow to the optic nerve. When the optic nerve does not receive an adequate amount of blood with nutrients and oxygen, it cannot perform its function correctly. This process results in inflammation of the optic nerve fibers, vision loss, and blurry vision.
