Why Do My Knees Hurt? The Top 12 Culprits To Watch For
3. Rheumatoid Arthritis – An Autoimmune Assault
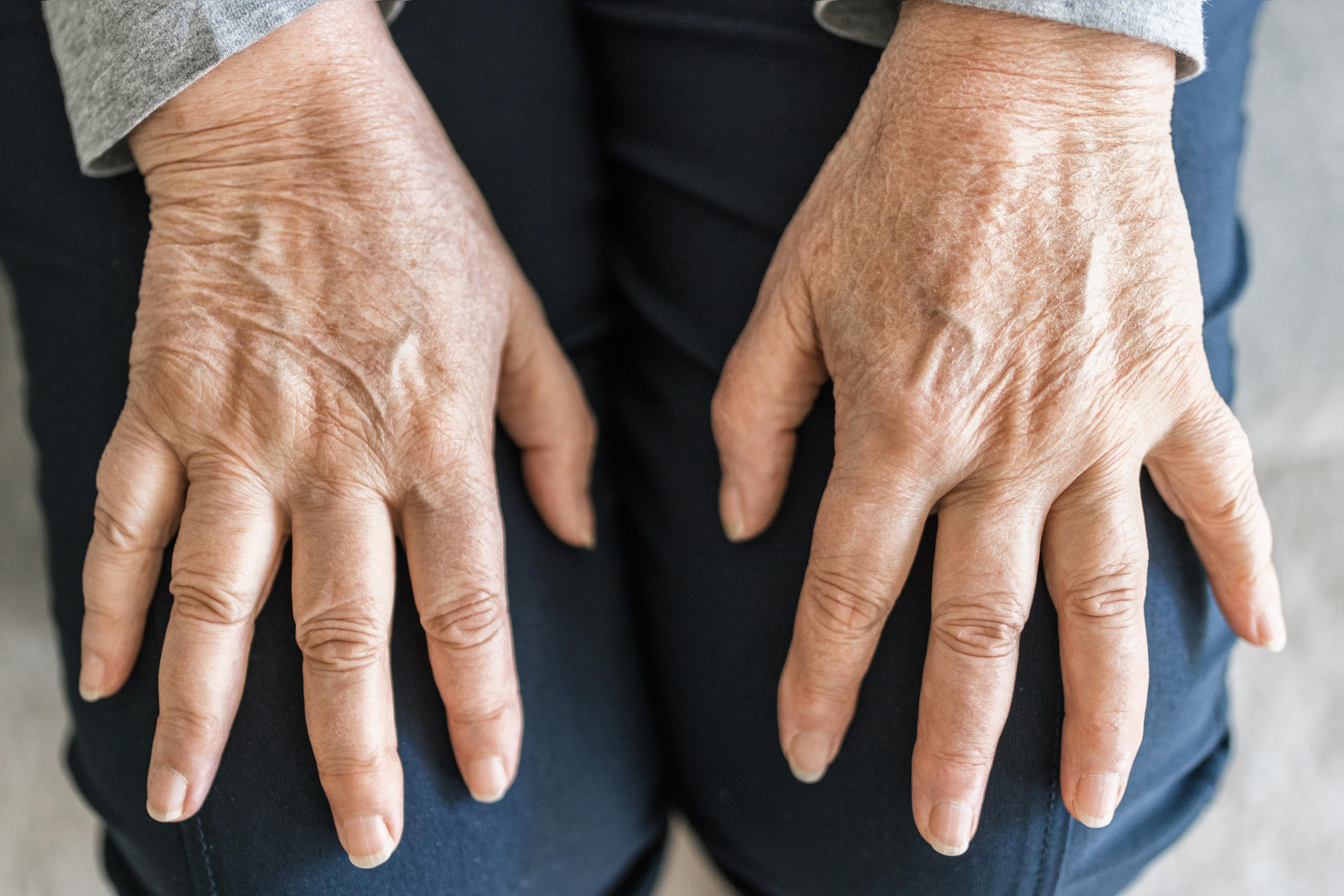
Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation and pain. RA can affect any joint, but the knees are often involved, leading to significant discomfort and disability. The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Symptoms include swelling, redness, and warmth in the joints, along with stiffness and pain. Treatment for RA focuses on reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression through medications such as DMARDs and biologics. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing RA effectively and preventing joint damage.
4. Bursitis – The Inflammation of Cushions
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint, reducing friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. When these sacs become inflamed, a condition known as bursitis occurs, leading to pain and swelling around the knee. Bursitis can result from repetitive motion, prolonged kneeling, or direct trauma to the knee. It is commonly seen in athletes and individuals whose occupations require frequent kneeling, such as carpenters and gardeners. Treatment for bursitis includes rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medications. In some cases, aspiration of the bursa fluid or corticosteroid injections may be necessary. Understanding bursitis's role in knee pain helps in identifying appropriate preventive and therapeutic measures.
