Beyond the Itch: The Infection Risks You Face When You Over-Scratch Bug Bites
Common Infections Resulting from Over-Scratching
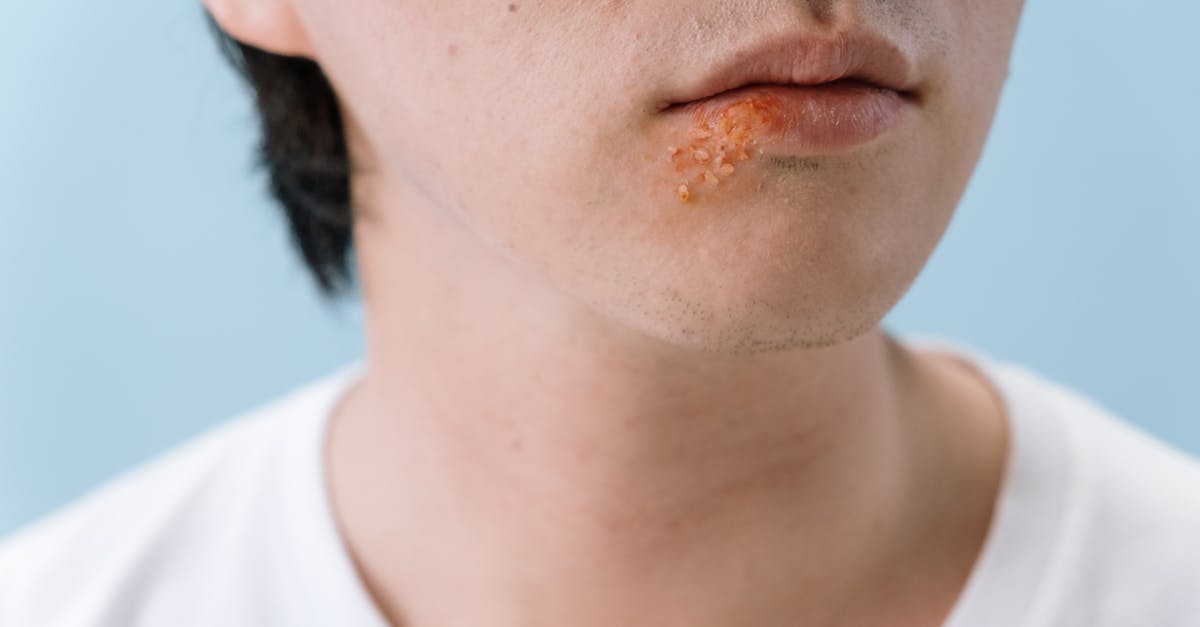
When the skin barrier is breached due to over-scratching, it opens the door to a range of infections. Bacterial infections are the most common, with impetigo being a frequent consequence of broken skin. This contagious infection results in red sores that can ooze and crust over, often requiring antibiotic treatment. In severe cases, cellulitis can develop, characterized by swollen, red, and tender areas that spread rapidly. Fungal infections, such as ringworm, can also exploit the compromised skin. Understanding these potential outcomes underscores the importance of treating bug bites with care and avoiding the temptation to scratch.
The Role of Hygiene in Preventing Infections

Maintaining good hygiene is a critical factor in preventing infections from bug bites. Thoroughly cleaning the affected area with soap and water can help remove irritants and reduce the risk of bacterial invasion. Applying antiseptic creams or ointments can further protect the skin and promote healing. Additionally, keeping fingernails short and clean minimizes the chance of transferring bacteria during scratching. These simple yet effective hygiene practices are essential in safeguarding against infections and maintaining skin health, emphasizing the role of personal care in infection prevention strategies.
