Common Cooking Habits That Could Be Ruining Your Nutrients
7. Sautéing: Quick and Nutritious
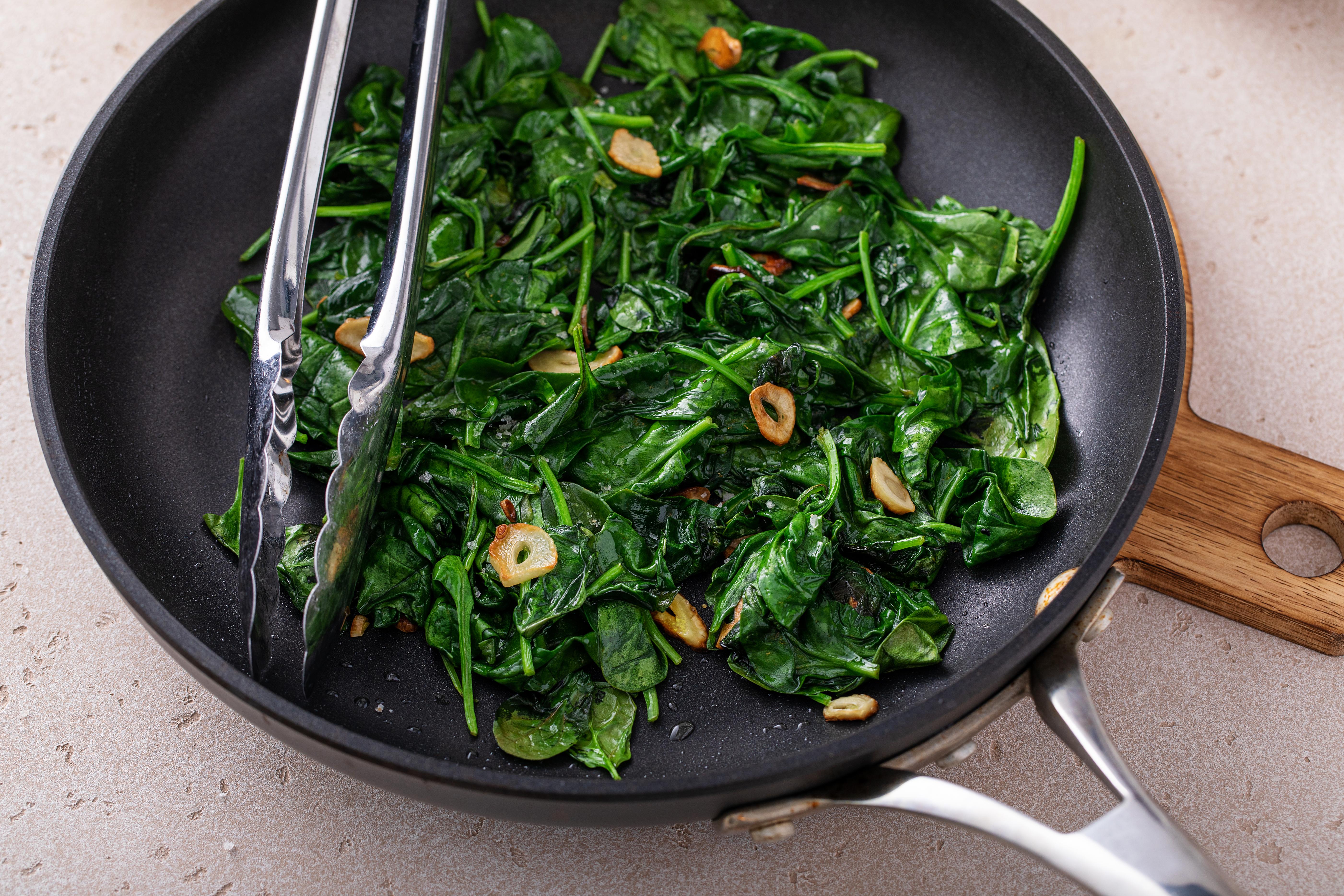

Sautéing is a quick cooking method that uses a small amount of oil to cook food over high heat. This technique is effective for preserving nutrients because it involves short cooking times and minimal water. However, the type of oil used can influence the nutritional outcome. Oils high in unsaturated fats, such as olive oil, can enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. To further boost nutrient retention, avoid overcrowding the pan, which can lead to uneven cooking and nutrient loss. Instead, cook in batches if necessary, and keep the food moving with frequent stirring to ensure even heat distribution.
8. Roasting: Flavorful, Yet Risky
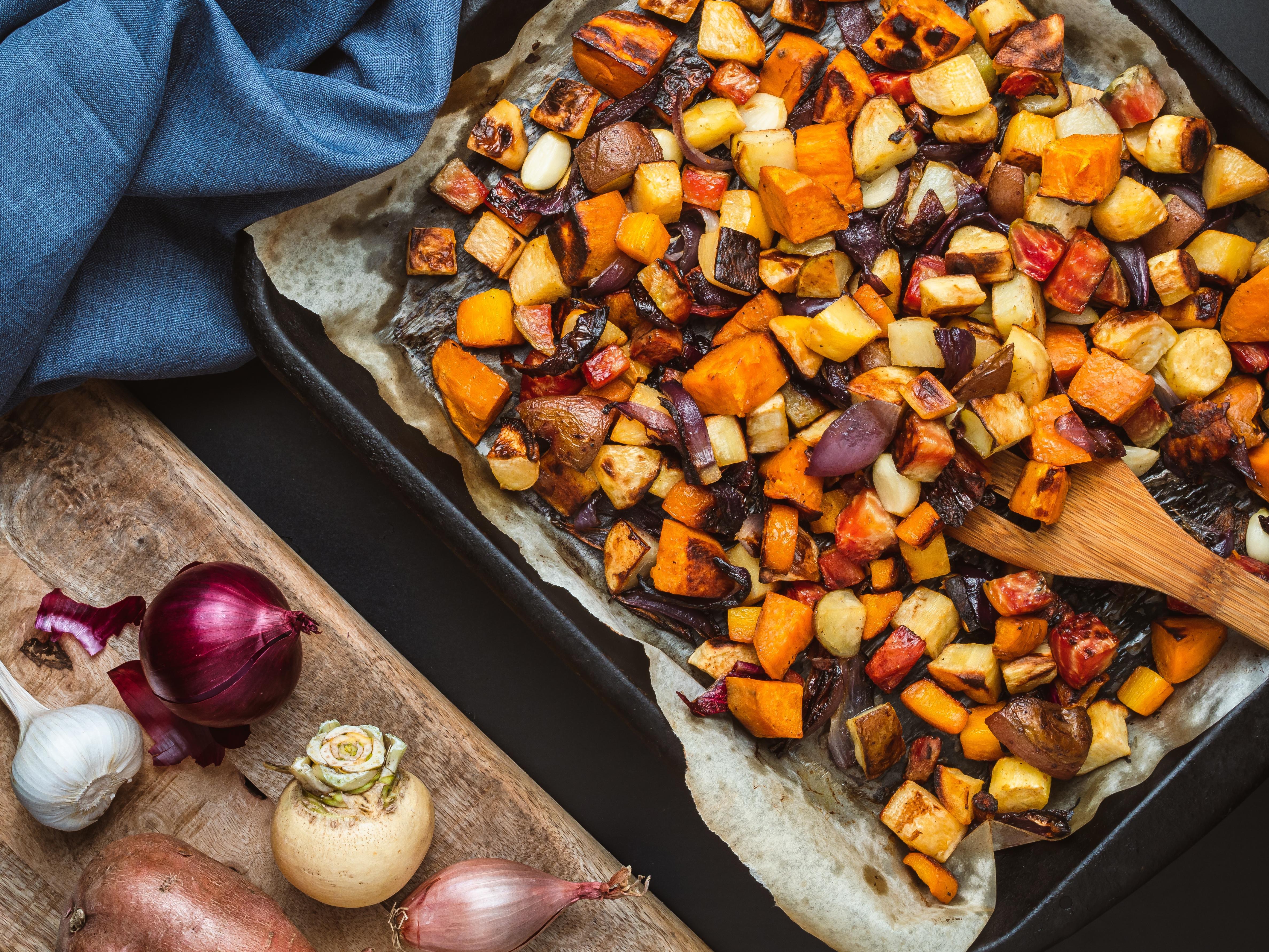
Roasting enhances the natural sweetness and flavor of foods, especially vegetables and meats, through caramelization and Maillard reactions. However, the high temperatures involved can lead to nutrient degradation, particularly of vitamins C and B. To mitigate nutrient loss, consider roasting at lower temperatures for longer periods, which can help preserve more nutrients while still achieving a desirable texture and flavor. Additionally, using a roasting rack can allow fat to drip away from meats, reducing the formation of harmful compounds. Pairing roasted dishes with fresh, raw vegetables or a nutrient-rich salad can also help balance the meal.
