Blood-Test Breakdowns That Could Make You The Sherlock Holmes of Hematology
3. Blood Enzyme Test

A blood enzyme test can be a vital diagnostic tool during a medical emergency. Cardiac enzyme tests are used to determine if a patient has had or is currently having a heart attack. The test may also be administered for individuals who have artery blockage symptoms. These include chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness and tiredness, dizziness, cool and clammy skin, sweating, and nausea or vomiting. When the heart undergoes severe stress, the muscle can become damaged. The damaged muscle releases enzymes into the bloodstream. Following a heart attack, these enzymes can reach high levels. If a doctor finds high enzyme levels in the patient's blood, they know there is a serious issue. Cardiac tests often measure the enzyme troponin. Even after the other released enzymes return to normal, troponin will continue to be in high concentrations in the blood. The results from these tests tend to come in quickly since they are a response to an urgent medical condition. Doctors may repeat the test a few times to monitor how the patient's enzyme levels change.
4. Blood Glucose Test
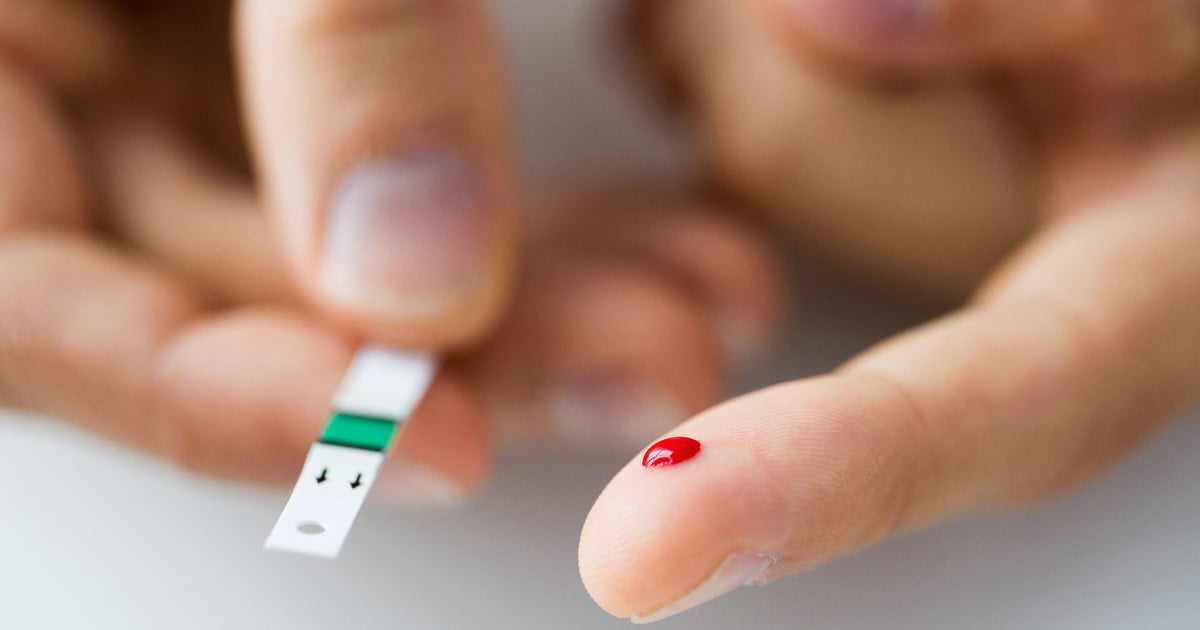
Blood glucose tests measure the glucose levels in the blood. Glucose is a simple sugar that cells use for energy. When individuals eat carbohydrates, their body converts them into glucose. These tests are most commonly ordered for individuals with a form of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes, type 1 diabetes, and type 2 diabetes. The test may also be used to diagnose or check for the presence of diabetes. Diabetes causes high blood glucose levels, which can damage a patient's internal organs and cause death if untreated. The body controls blood sugar with the hormone insulin. With diabetes, the patient's body either does not create enough insulin or does not create properly working insulin. Since the insulin is not converting carbohydrates to usable energy, they build up in the blood and cause toxic reactions. Some patients may also have a blood glucose test done to determine if they have hypoglycemia, which occurs when their blood glucose is low. After a diabetes diagnosis, patients may have regular glucose tests to monitor their blood sugar and make sure their treatment is working.
