Benefits Of Using A Pulse Oximeter
A pulse oximeter is a device that monitors the amount of oxygen (oxygen saturation) in the blood. The readings from pulse oximeters help doctors assess how well oxygen is being transported from the patient's heart to the extremities. In addition to measuring oxygen levels, pulse oximeters provide continuous monitoring of the patient's heart rate and produce a waveform that indicates the strength of the pulse. Pulse oximeters are used in clinics and hospitals and are also available for home use. The devices are small clips worn on the patient's finger, toe, or earlobe. Patients who have asthma, heart disease, or other chronic conditions may be advised to purchase a pulse oximeter to use at home. Some pulse oximeters have recording capabilities and can send readings directly to doctor's offices. Pulse oximetry is entirely non-invasive and painless. For the most accurate readings, nails must be free of nail polish, and fingers must be clean.
In particular, regular use of a pulse oximeter can help with the steps and conditions described below.
Monitoring Oxygen Saturation Over Time
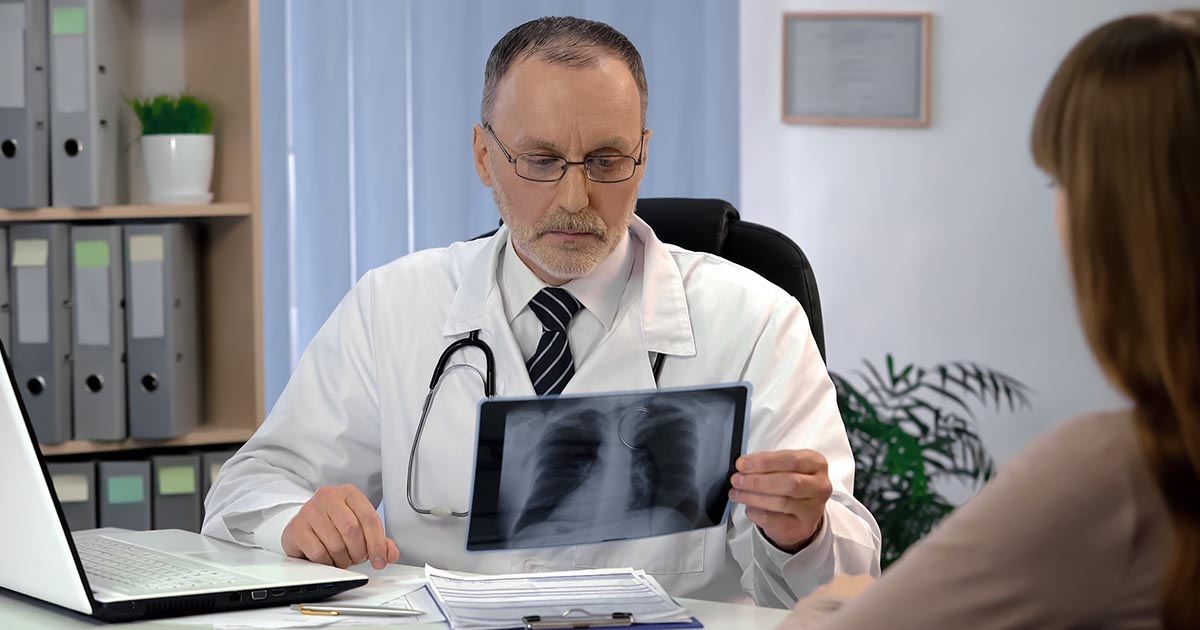
Pulse oximetry is perhaps most beneficial for monitoring oxygen saturation over time. When worn, pulse oximeters provide continuous monitoring of changes in oxygen saturation. Oxygen saturation readings are frequently taken by pulmonologists (lung specialists), and oxygen saturation is sometimes measured at routine physical examinations. Crucially, the devices can alert patients and doctors to changes that may need medical intervention such as additional oxygen, ventilation, or medication. For this reason, patients in the hospital routinely wear a pulse oximeter at all times. Since the oximeter contains a small red light that can generate heat, clinicians should move the probe to another finger or toe every two to four hours for patient comfort.
Patients with asthma and other respiratory conditions who are monitoring their oxygen saturation at home can observe patterns in their readings and share these with their doctors. For example, patients with certain lung conditions may experience a drop in oxygen saturation during the night. Reporting this can help patients receive the most effective treatment for their condition, and doctors may recommend additional therapies or more advanced treatments based on these readings. During surgery, anesthesia can reduce oxygen saturation levels. Pulse oximetry readings enable anesthesiologists to provide the safest level of anesthesia for each patient and to start oxygen therapy or make changes during the operation if necessary.
Reveal more on the benefits of using a pulse oximeter now.
Assess Need For Supplemental Oxygen
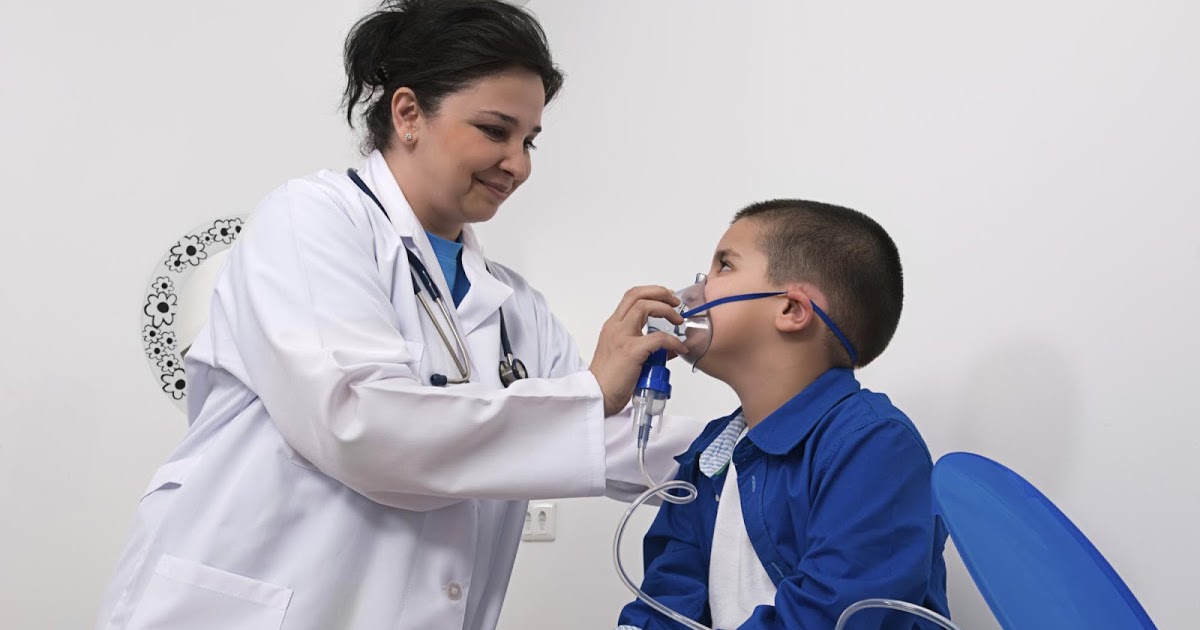
Pulse oximetry readings can help doctors assess the need for supplemental oxygen in patients known to have or who are suspected of having a lung condition or other condition that may reduce the oxygen in the blood. A normal oxygen saturation reading with a pulse oximeter is between ninety-five and one hundred percent. Most doctors recommend starting supplemental oxygen if pulse oximeter readings are consistently at eighty-eight percent or lower. Supplemental oxygen is used at home and is covered by most insurance plans.
Patients most often receive oxygen through a nasal cannula (nasal prongs), and it can also be administered through an oxygen mask that covers the mouth and nose. Oxygen for home use is available in metal tanks or as liquid oxygen. Most patients who use supplemental oxygen do so overnight. Depending on their condition's severity, patients may also need to use it during the day. In homes where supplemental oxygen is present, patients should avoid open flames and flammable materials.
Get the details on the next benefit of using a pulse oximeter now.
