Beyond the Scale: A Dietitian's Guide to Understanding Body Composition and Metabolism
In the world of health and nutrition, the scale has long been the ultimate judge of success. However, a growing body of evidence suggests that this singular focus on weight can be misleading. Understanding body composition and metabolism offers a more comprehensive picture of health. Body composition refers to the percentages of fat, bone, water, and muscle in human bodies, while metabolism encompasses the biochemical processes that occur within a living organism to maintain life. This guide delves into the intricacies of these concepts, offering insights into how they relate to overall health and well-being. By shifting focus from sheer weight loss to a more nuanced understanding of body composition and metabolism, individuals can achieve more sustainable health outcomes.
The Science of Body Composition

Body composition analysis provides a deeper understanding of an individual's health beyond what the scale can reveal. It differentiates between fat mass and lean mass, which includes muscle, bone, and water. This distinction is crucial because two individuals with the same weight may have vastly different body compositions, leading to different health outcomes. Methods such as Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and skinfold measurements are commonly used to assess body composition. Understanding the balance between fat and lean mass can help in designing personalized nutrition and exercise plans that cater to individual needs, ultimately promoting better health and physical performance.
Metabolism: The Engine of Life
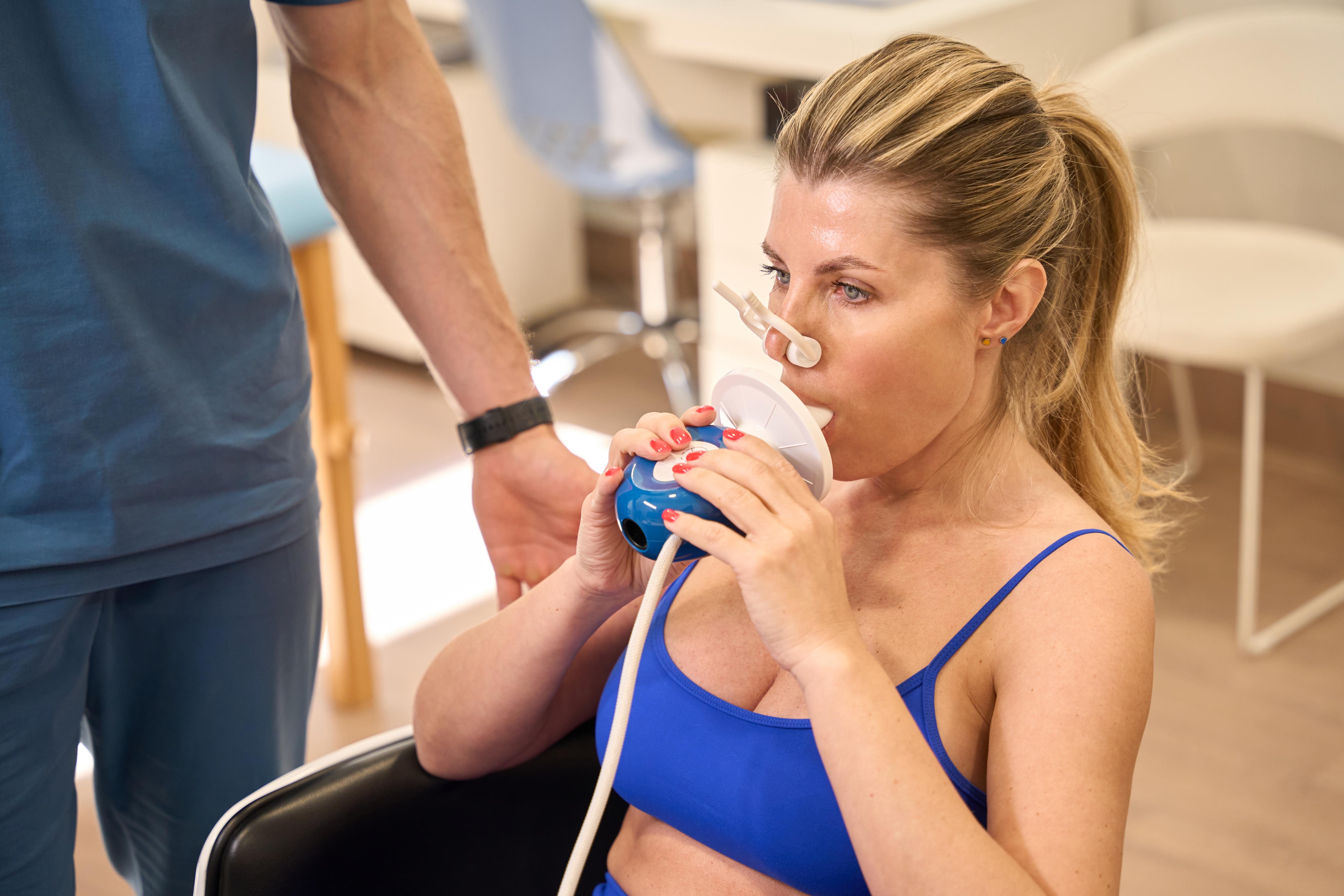
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body that keep it alive and functioning. It can be divided into two categories: catabolism, the breakdown of molecules to obtain energy, and anabolism, the synthesis of all compounds needed by the cells. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is a key component, representing the number of calories the body needs to perform basic life-sustaining functions. Factors such as age, sex, muscle mass, and hormonal balance significantly influence metabolism. Understanding one's metabolic rate can aid in tailoring dietary and exercise regimens to enhance energy expenditure and support weight management goals.
