Causes Of Tinnitus To Look Out For
Acoustic Neuroma

An acoustic neuroma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that slowly grows along the vestibular nerve, one of the major nerves connecting the inner ear to the brain. Patients with this tumor often have very subtle symptoms that take years to develop. Symptoms associated with an acoustic neuroma normally include tinnitus in the ear affected by the tumor and gradual hearing loss. Dizziness, balance problems, and facial numbness have been reported, and some individuals with this tumor might experience weakness or an inability to move certain muscles. To perform an assessment for an acoustic neuroma, a physician will examine the ear with an otoscope, and a hearing test with an audiologist may be performed. MRI scans are ideal for detecting acoustic neuromas, and these scans are capable of detecting tumors as small as one millimeter in diameter. If an acoustic neuroma is detected, doctors may recommend regular monitoring for some patients, particularly for individuals who have no symptoms and who have small tumors. Surgical removal is an option for many acoustic neuromas, and stereotactic radiosurgery may also be considered.
Uncover another cause of tinnitus now.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
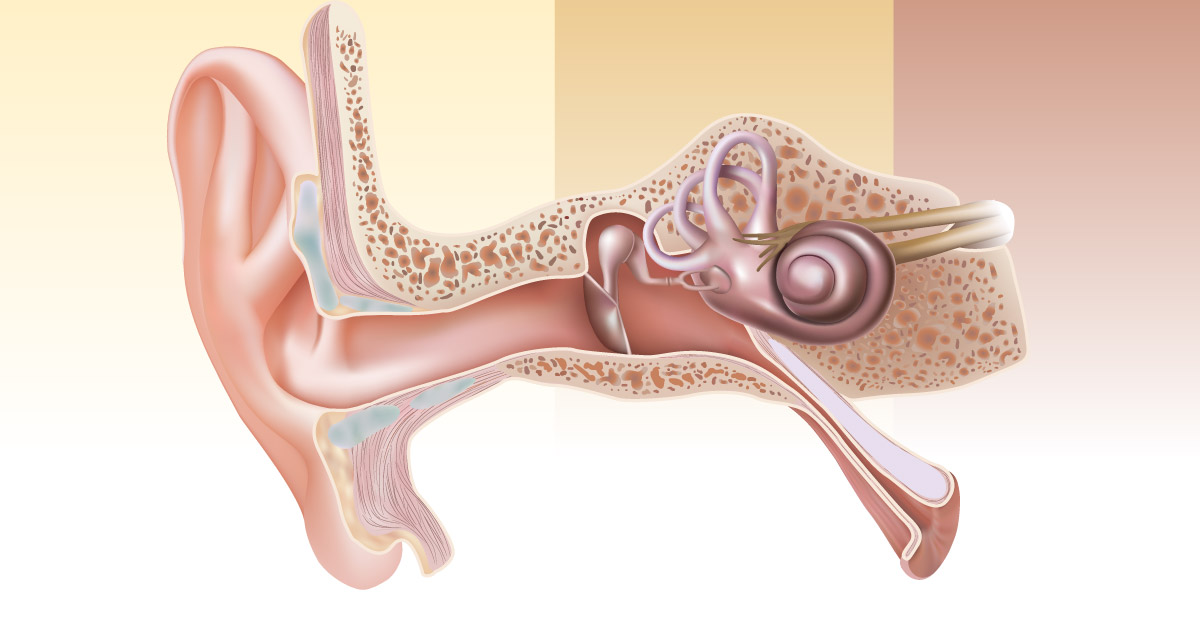
Eustachian tube dysfunction is a common condition that typically resolves with home treatment. Patients with this condition generally experience clicking or popping sensations in the ear, and a feeling of fullness in the ears is frequently observed. Sometimes, individuals with Eustachian tube dysfunction may have ear pain or a feeling their ear is being tickled. Allergies, colds, and altitude changes are some of the most common causes of this ailment, and children are at an increased risk of the condition since they have smaller Eustachian tubes than adults. Eustachian tube issues are routinely diagnosed with a physical exam of the ear. The doctor may also need to check the patient's throat and nose to rule out other ailments. Treatment options for this condition include saline nasal sprays, antibiotic ear drops, and over the counter pain relievers. Ear candles should not be used to treat Eustachian tube problems. For the majority of patients, the condition resolves within two weeks.
