Causes And Risk Factors Of Monkeypox
Consumption Of Meat From Infected Animals
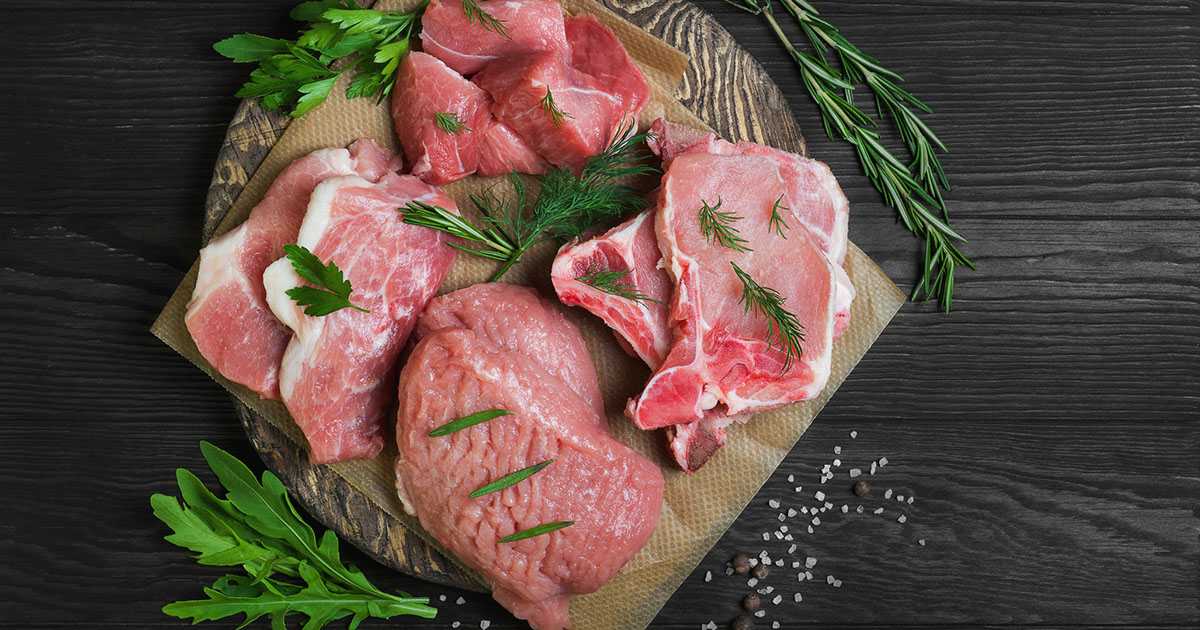

A risk factor for monkeypox is the consumption of meat from infected animals. It appears only the consumption of inadequately cooked meat can pass the virus to a human. Many of the animals known to harbor monkeypox are native to Africa where the consumption of bushmeat can cause monkeypox in humans. Bushmeat is the meat of non-domesticated animals of Africa, and its consumption has been linked to numerous outbreaks of diseases such as monkeypox and Ebola. In Central Africa, bushmeat accounts for about eighty percent of individuals' protein intake. Bushmeat that may cause monkeypox can include Gambian pouched rats, monkeys, and rope squirrel. The movement of bushmeat out of Africa is believed to be a driver for outbreaks of the virus across the world.
The best way to mitigate this risk is wearing gloves and protective clothing while handling animals and during slaughtering and cooking meat thoroughly.
Keep going to get to know more risk factors and causes of monkeypox.
Direct Contact With Patients
It is possible to catch monkeypox through direct contact with patients who have the disease, but it is less infectious than smallpox. The disease can spread through direct contact with lesions or bodily fluids of someone who is infected or through respiratory droplets during face-to-face contact. It's even possible to catch the virus through contact with clothing, bedding, or other objects recently contaminated with the bodily fluids of someone with monkeypox.
Person-to-person transmission of monkeypox is uncommon. Most cases of monkeypox are transmitted from animals, especially rodents, to individuals through direct contact, and person-to-person transmission is infrequent.
Learn about another factor in monkeypox.
