Causes And Risk Factors Of Age Spots
Previously Believed To Be Caused By Liver Problems
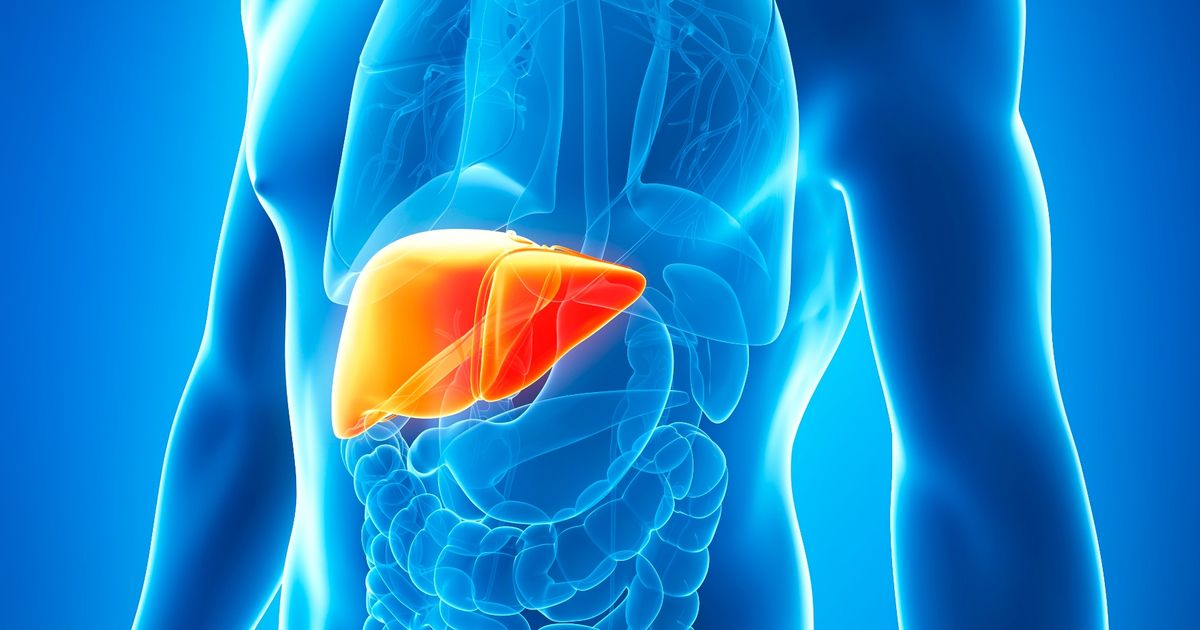
Age spots were previously believed to be caused by liver problems, which is why some referred to them as liver spots. However, scientists now recognize these spots have absolutely nothing to do with the liver at all, and they are not indicative of any liver concerns. Known as lentigines, the spots are simply localized concentrations or clumps of a pigment called melanin. As mentioned, patients who have light skin and red hair are believed to be at a greater risk of developing lentigines, and individuals who have previously been sunburned are also at an increased risk.
To prevent these spots, doctors recommend patients stay out of the sun as much as possible, and tanning beds should not be used. Sunscreen should be worn at all times when outdoors, even if it is a cloudy day, and patients may wish to wear clothing specially treated to provide built-in sun protection. Dermatologists recommend that patients avoid sun exposure during the afternoon hours as the sun's rays are particularly intense during this time. Age spots can be lightened with prescription retinol products, and laser treatments, chemical peels, freezing procedures, and surgical options are available to remove the spots entirely.
Learn more about age spots now.
Location And Appearance
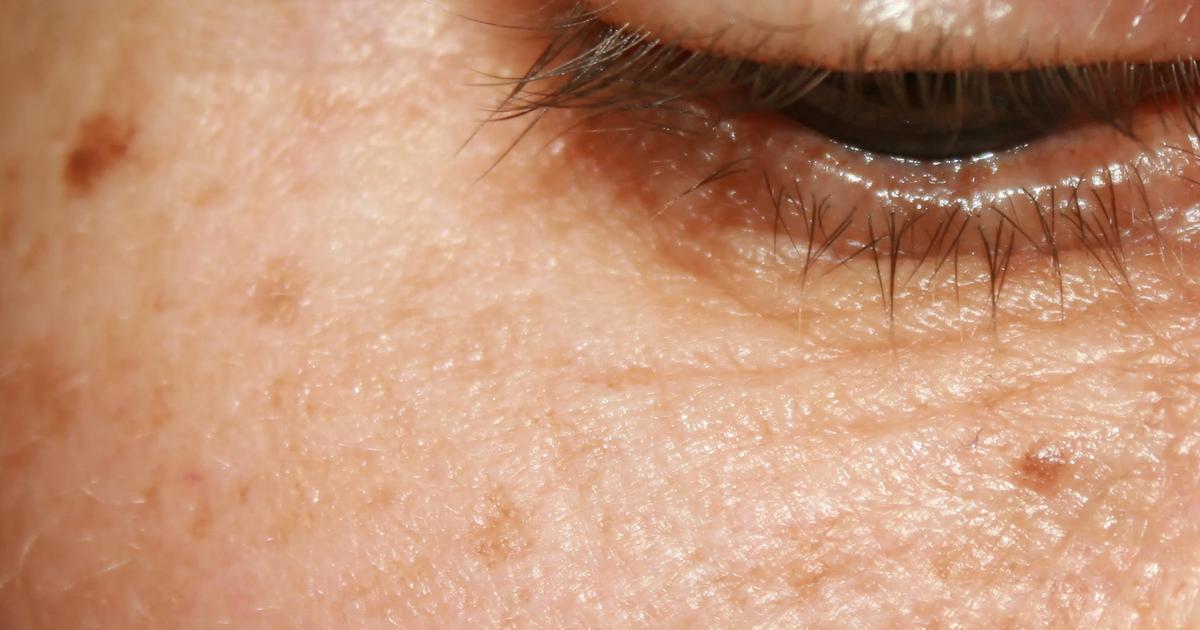
Age spots may develop anywhere on the body, though they appear most frequently in areas that have experienced the highest amounts of sun exposure, including the face, feet, shoulders, and upper back. Patients may also develop them on the backs of the hands and on the forearms, and they could appear on the upper chest as well. It is common for clusters of several small age spots to appear on the skin. These spots tend to be tan, brown, or black, and they might sometimes be gray. These spots are universally flat and round or oval in appearance; they are never elevated (raised above the surface of the skin). In terms of texture, the spots will almost always have an identical texture to the surrounding skin. At times, they may be slightly rough. The average size of an age spot ranges from 0.2 centimeters to two centimeters in diameter. Patients should monitor their skin for any new spots. If a new or existing spot bleeds, changes color, elevates above the skin, or increases in size, an evaluation should be conducted by a dermatologist. Any spot that is flaky, red, itchy, or painful warrants a medical examination too.
