The Basics Of Chronic Kidney Disease
Causes Of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease is the result of another medical condition or other factor impairs the function of an individual's kidneys and causes kidney damage to worsen over an extended period. There are many potential conditions and other factors that contribute to this, including a urinary tract infection that becomes a kidney infection that further develops into kidney disease. Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, such as through kidney stones, some forms of cancer, and an enlarged prostate in men, can also result in chronic kidney disease. Another major factor is pyelonephritis, which refers to recurrent kidney infections.
Medical Risk Factors For Chronic Kidney Disease
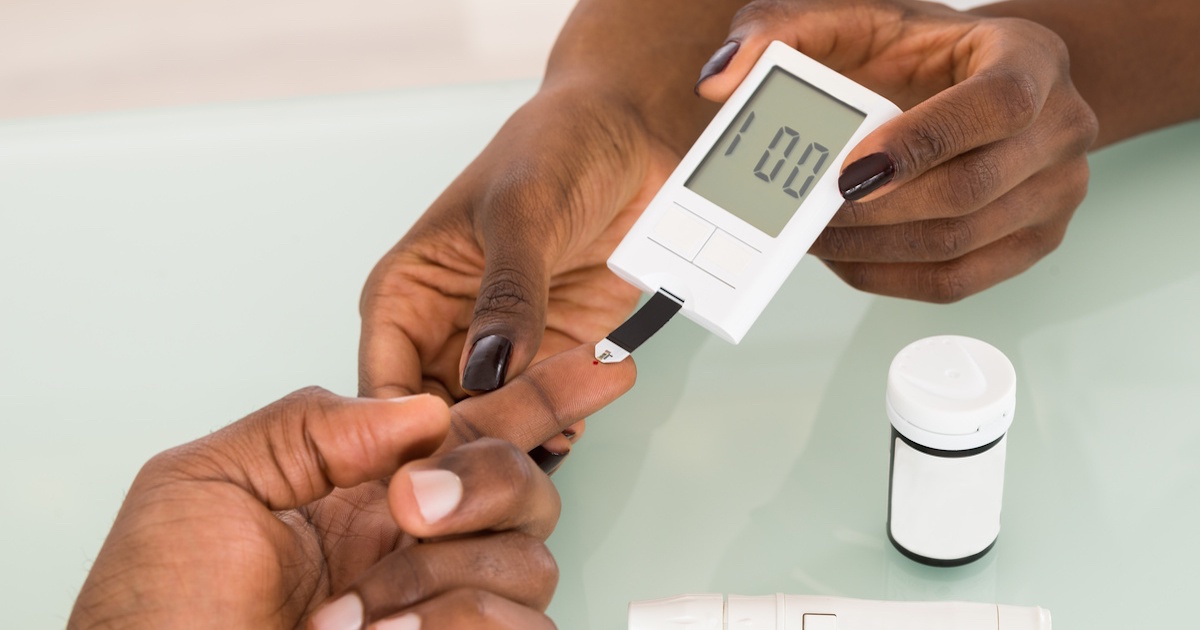

Two of the most significant medical risk factors of chronic kidney disease include diabetes and high blood pressure. Diabetes is a disease where a patient's body cannot appropriately manage its blood sugar levels. Individuals affected by diabetes often have high blood sugar, which causes damage to the small blood vessels inside of their kidneys. The kidneys are not able to properly filter the blood without these healthy vessels, causing a decrease in function.
On the other hand, long-term hypertension causes an affected individual's renal arteries to become hardened, narrowed, or weakened. This malfunction results in reduced blood delivery to the tissues of the kidneys, reducing their function. Other less common medical risk factors for chronic kidney disease include glomerulonephritis or irritation of the small filters in the kidneys, interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the kidney's tubules and structures), injury to the kidney, vesicoureteral reflux (where urine backs up in the kidneys), lupus, IgA nephropathy, and polycystic kidney disease.
