How To Diagnose And Treat Liver Cysts
Also known as hepatic cysts, liver cysts are believed to affect approximately five percent of individuals in the United States. The cysts are small sacs of fluid that form on the liver, and the majority of patients will have only a single cyst. Most liver cysts produce no symptoms and require no treatment. If symptoms do develop, these may include abdominal fullness or pain. If bleeding into the liver cyst occurs, patients could experience severe pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, and this pain may radiate to the shoulder. Hepatic cysts cause no issues with liver function. In cases where treatment is necessary, doctors normally recommend removal of the cysts or cyst wall. Medications known as somatostatin analogs are currently being researched as a nonsurgical treatment option.
The major methods of diagnosis and treatment for liver cysts are outlined below.
Ultrasound
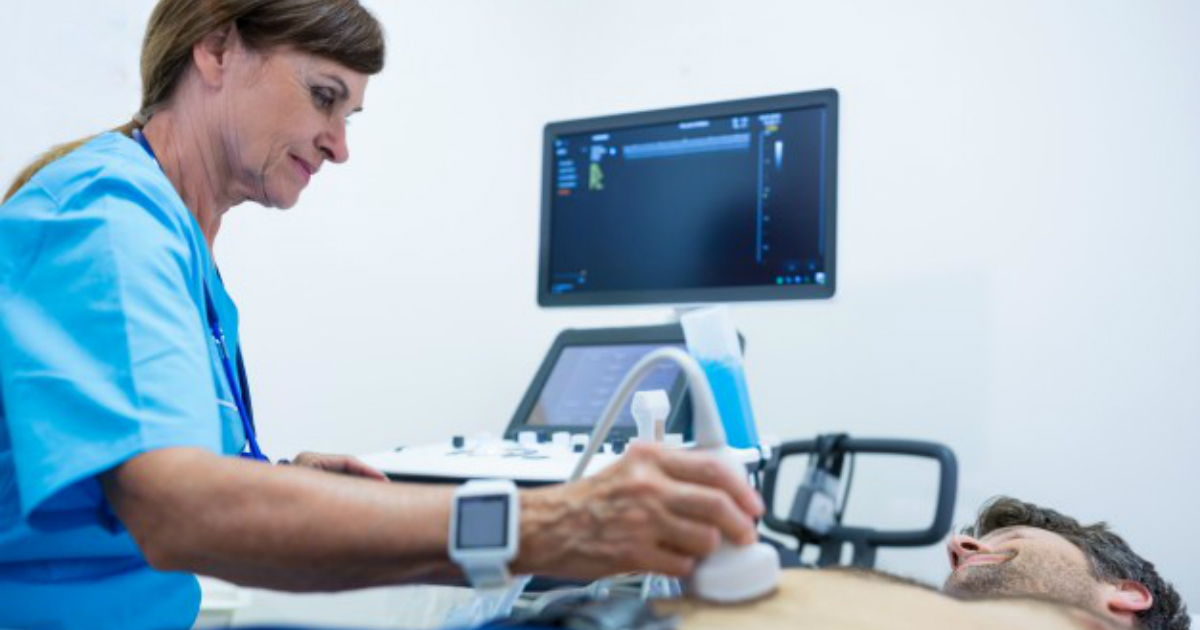

Ultrasound scans are a primary method for detecting liver cysts. These painless scans use high-frequency sound waves to produce images, and there is no radiation involved. To create an ultrasound image of the liver, the sonographer will place a gel on the patient's skin, and a transducer (wand) is then placed on the skin over the liver itself. Ultrasounds can be performed in clinics and hospitals, and they normally take around twenty to sixty minutes. Patients having an ultrasound of the liver may be asked to fast for a few hours before their appointment; this will help produce a clearer image. Individuals allergic to latex should tell the provider about this allergy so a non-latex cover can be used for the transducer. A few days after the scan is complete, a radiologist or other specialist will explain the results to the patient.
Keep reading to learn more about diagnosing and treating liver cysts now.
CT Scans
CT scans take multiple x-rays from several angles, and computer processing is then used to create cross-sectional images, also known as slices. These slices can help doctors diagnose cysts and other liver diseases, and they are also useful in planning treatment and mapping out potential surgical intervention. Before having a CT scan, the patient will need to change into a hospital gown. If the physician has ordered contrast to be used to improve the quality of the images, the patient may be given an oral solution to drink containing a dye that will appear white on the images. This dye could be administered via injection instead. Sometimes, patients might be asked to fast in preparation for the scan. CT scans normally take roughly thirty minutes in all, and this time includes positioning the patient in the scanner and the scanning process itself. To help doctors obtain clear images, the radiologist may ask the patient to hold their breath for a few moments during the scan. If contrast was used, special instructions will be provided on what to expect after the procedure. It can be helpful to drink plenty of fluids to promote the removal of the dye from the body through urination.
Uncover more options when it comes to the diagnosis and treatment of liver cysts now.
