Effective Treatment Options For Urticaria Pigmentosa
Urticaria pigmentosa is a skin condition that typically affects infants and children. Individuals with this condition develop a reddish-brown rash that may be either flat or slightly elevated from the skin's surface. Although the rash is not painful, patients usually experience extreme itching. Urticaria pigmentosa most often occurs on the torso, and though it is also frequently found on the face, scalp, arms, and legs. Other symptoms associated with this condition include a rapid heartbeat, headache, and diarrhea. In some patients, the face may become red very quickly, and fainting has been reported as well. To diagnose urticaria pigmentosa, doctors will examine the skin and may perform a skin biopsy. Blood and urine tests may also be completed. More than half of patients with urticaria pigmentosa experience a complete resolution of their condition by the time they reach puberty. Even for patients whose symptoms do not completely disappear, symptoms normally reduce substantially by puberty.
Antihistamines To Control Allergic Reactions
Since the rash associated with urticaria pigmentosa can produce extreme itching, akin to allergic reactions, doctors will often prescribe antihistamines. These medications are taken orally or as a nasal spray, and they work by decreasing the release of histamine from the body. In addition to reducing the itchiness of the rash, antihistamines may reduce facial flushing and redness that can occur with urticaria pigmentosa. During treatment with antihistamines, the patient will be monitored closely. Potential side effects from antihistamines include drowsiness, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, trouble with urination, restlessness, dizziness, and irritability. If patients are on an antihistamine that causes drowsiness, they may be able to be switched to another form without this side effect. Any worrying or persistent side effects should be reported to medical staff. Patients taking antihistamines should not take acetylsalicylic acid, codeine, or opiates, and alcohol use should be avoided.
Hydrocolloid Dressings
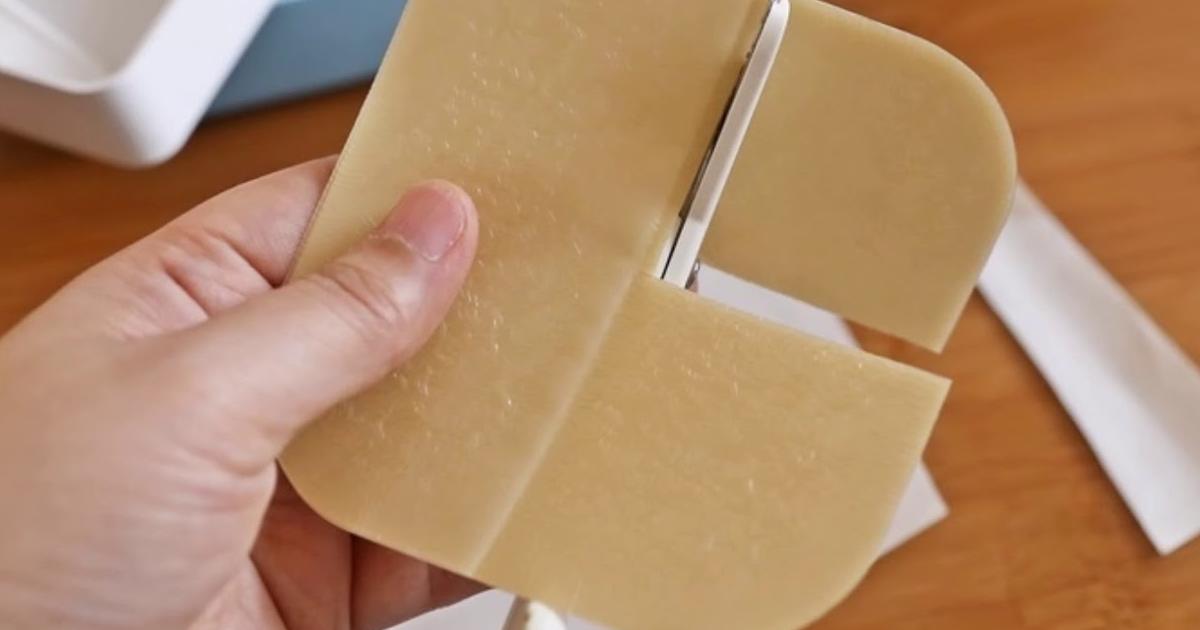

Hydrocolloid dressings can improve healing and are appropriate for non-infected wounds. For patients with urticaria pigmentosa, hydrocolloid dressings can be particularly helpful if hives or blisters have formed at the site of a rash. The dressings are normally opaque and need to be changed every three to seven days. The dressings are impregnated with a layer of a gel-like substance that keeps the wound moist and encourages faster healing. They can be used on both dry and moist wounds. Unlike other kinds of wound dressings, hydrocolloid dressings are flexible, waterproof, and impermeable to bacteria. Patients who wear these dressings often report they can be more active than with other bandages, and they also report less pain than with other dressings. To apply the dressing, patients should warm it between their hands for a few seconds before peeling off the back layer. Then, press it gently onto the affected area for a few seconds, starting from the center of the wound and working toward the outside edges.
