Guide To Diagnosing And Treating Cataracts
Retinal Exam
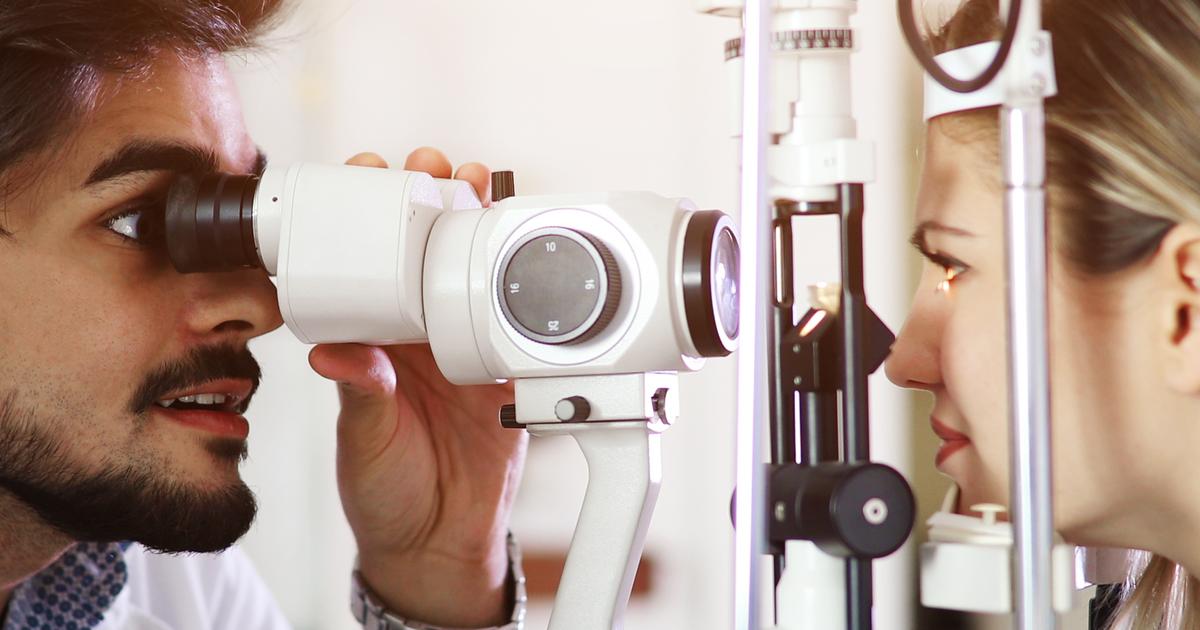
A patient's cataracts can be detected and diagnosed with a retinal exam or retinal imaging. A retinal exam allows an ophthalmologist or optometrist to see a patient's retina, blood vessels, and optic disk. The digital retinal imaging technique commonly used to carry out a retinal exam in modern-day medicine enables specialists to take a digital photo of the inside of a patient's eye. This photograph contains the macula, blood vessels, optic nerve, and retina. If signs of cataracts are present on a digital retinal imaging test, the ophthalmologist or optometrist will carry out the same test with the use of higher resolution and higher quality imaging referred to as fundus photography. Some characteristics of diseases that affect the eye may not be able to be seen with the use of a comprehensive eye exam with dilation. Certain subtle changes in the characteristics of a patient's eye can be seen better with the use of a digital retinal exam.
Visual Acuity Test
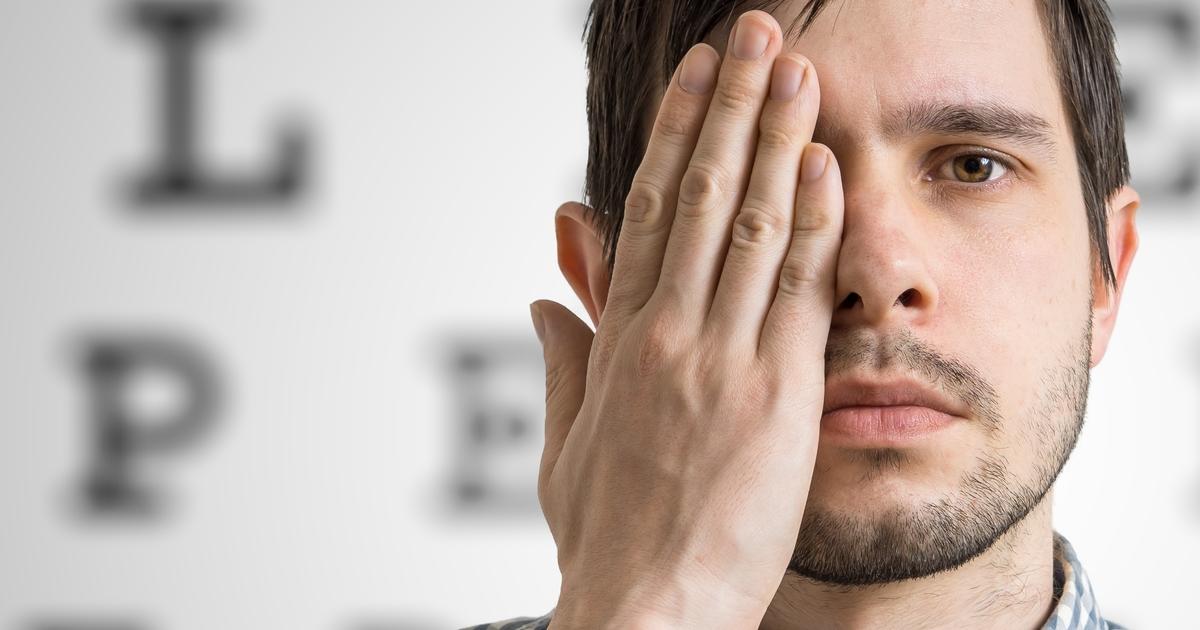

Optometrists will regularly employ visual acuity tests to determine the accuracy of a patient's vision using an eye chart with a series of letters of varying sizes printed on it. They will test the patient's eyes one at a time, often asking the patient to either close one eye or using a viewing device to block out one eye. This can help them determine if the patient has 20/20 vision or if their vision is exhibiting any indicators of impairment. If the patient's vision does show some decline, it can help optometrists determine what tests may be required from there, including further testing for cataracts.
