Guide To Diagnosing And Treating Cataracts
Comprehensive Eye Exam With Dilation
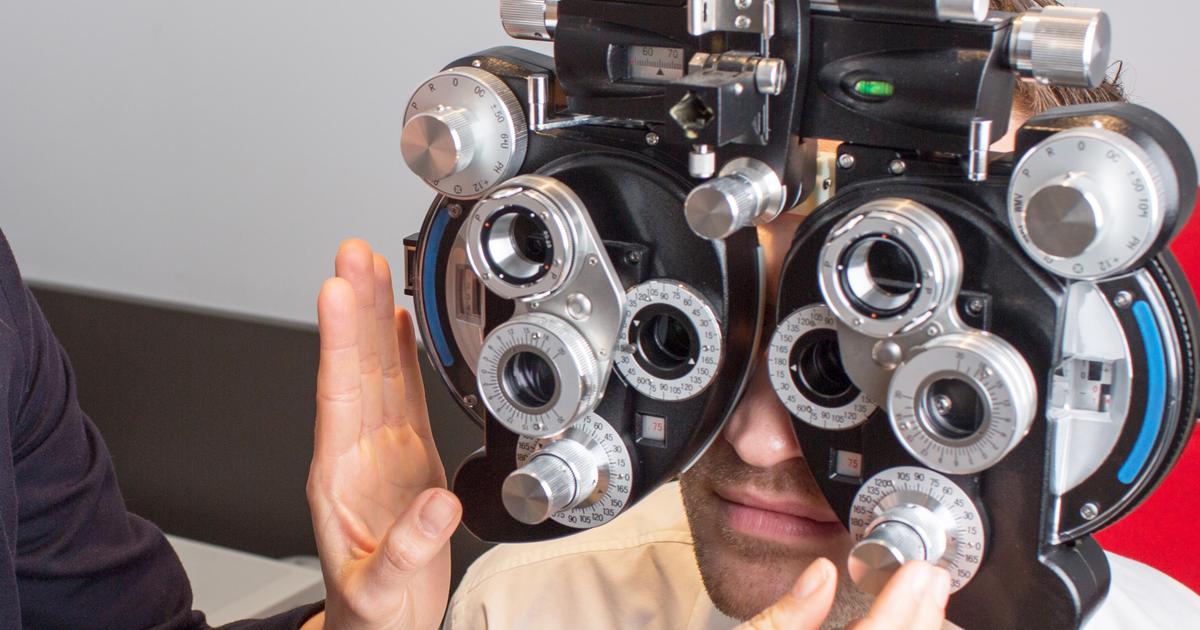
A comprehensive eye exam with dilation is a series of diagnostic tests that measure an individual's ability to see and identify any potential problems that can adversely affect the health and functionality of their eye. An optometrist assesses a patient's eye muscle movement and function, how light waves pass through the lens and cornea of the eye, color vision, the health of the retina, how clearly they can see, the degree to which an individual can see on both sides of them without changing the position of their eye, physical health of the eyelids and eyelashes, and a patient's risk of glaucoma. Because cataracts develop in individuals over forty years old, adults between forty and fifty-four years old are advised to have a comprehensive eye exam every two to four years. When an individual reaches between fifty-five and sixty-four years old, they are advised to have a comprehensive eye exam every one to three years. Individuals over sixty-five years old are advised to have yearly comprehensive eye exams.
Visual Field Test
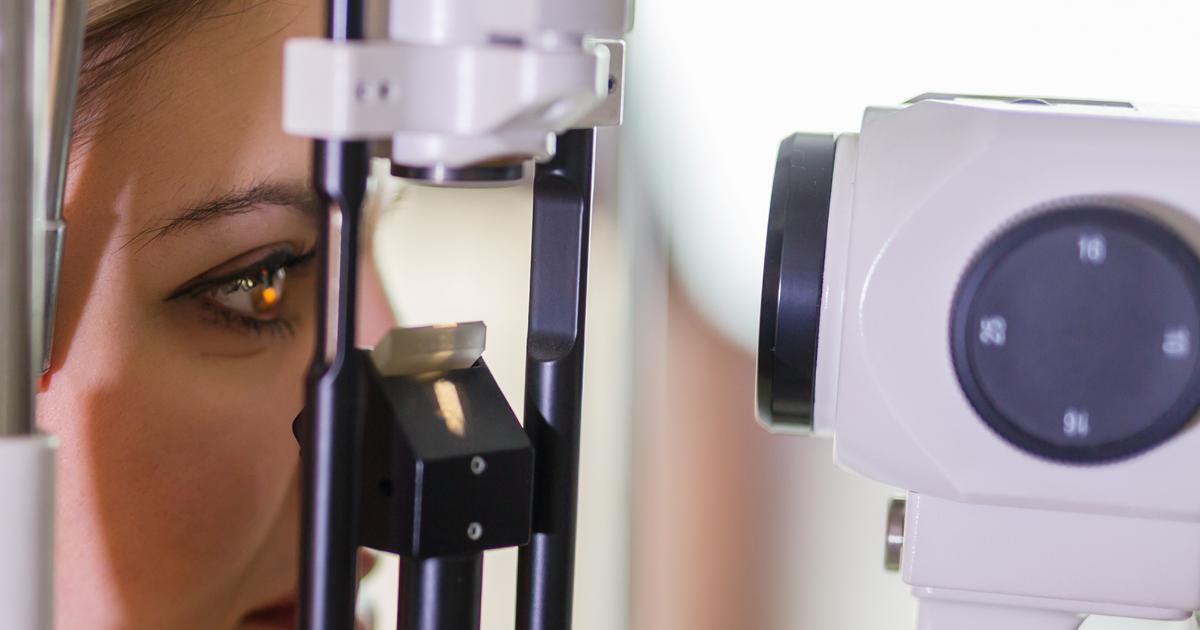

Cataracts can be detected with the use of a visual field test. As discussed, the width of an area that can be seen by the eye when it is focused on a central point is considered the visual field. A confrontation visual field test is the manual method used to test the accuracy of the patient's peripheral visual field. An automated perimetry test is a visual field test performed with the use of a machine called a perimeter that can show the provider a detailed map of where a patient can and cannot see. Cataracts can compromise a patient's ability to see clearly and accurately in certain parts of the eye. The peripheral vision is commonly affected by the development of cataracts in the eye, and a visual field test can pick up this type of compromised functionality.
