Health Dangers And Risks Associated With Turpentine
Convulsions

Convulsions are one of several nervous system effects that may develop with exposure to turpentine. At first, patients could feel dizzy, and they might also feel drowsy or nervous. Some patients become very excited and euphoric after short-term exposure. As the patient is exposed to more turpentine, they could develop more advanced neurological signs, including tremors, walking difficulties, and weakness. These signs could then progress to convulsions, and the patient might lose consciousness. If someone is observed having a seizure, bystanders should call an ambulance, and a pillow should be placed under the individual's head. Furniture or any other objects near the patient should be moved aside, and nothing should be placed in the patient's mouth. If possible, bystanders should note the duration of the seizure. Once the ambulance arrives, bystanders should let the paramedics know the patient has been exposed to turpentine, and they should also inform them of the duration of the patient's seizure, if known. Doctors will give anticonvulsant medications via injection to stop seizures, and the patient may need to have a brain scan and an electroencephalogram to be assessed for epilepsy and other potential causes of convulsions.
Get more information about the health risks linked to turpentine now.
Lung Damage
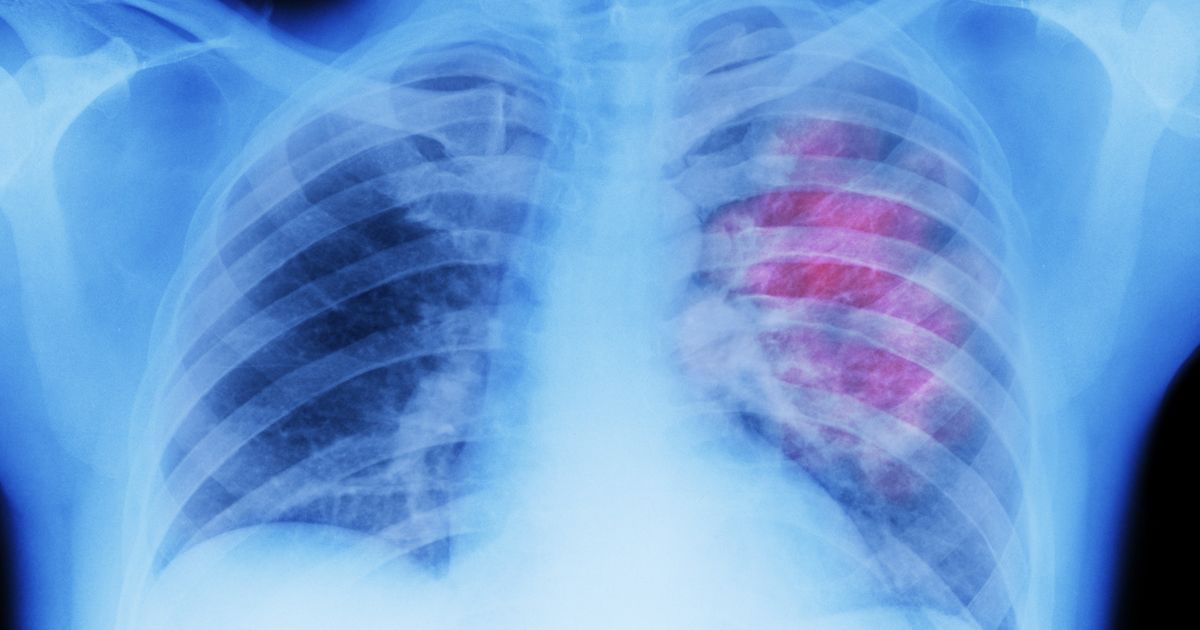
Longer-term exposure to turpentine is linked to lung damage, and patients often develop a chronic form of bronchitis. Individuals who have worked with turpentine regularly for more than five years are at an increased risk of lung cancer. Patients exposed to turpentine at their workplace need to follow proper safety precautions, including the use of face masks and protective clothing, to reduce the potential for lung damage from this chemical. Individuals who work with turpentine regularly may want to have more frequent checkups with a physician to monitor their lung health. To assess the lungs, doctors will begin by listening to the patient's breathing with a stethoscope. They will check for any wheezing, coughing, or other abnormal sounds. Patients might need to have a chest x-ray, CT scan, pulmonary function tests, and a sputum test as part of an evaluation for chronic bronchitis. Individuals with this condition will often be treated with bronchodilators (inhaled medications that open the airways), and theophylline (an oral medicine that relaxes muscles in the airways) may be needed to relieve shortness of breath. Steroids are sometimes required, and patients are typically offered pulmonary rehabilitation to help improve their breathing overall.
Uncover more health dangers of turpentine now.
