Can Immunotherapy Treat Other Conditions?
Multiple Sclerosis

Multiple sclerosis is a disease that affects an individual's central nervous system or their brain, spinal cord, and associated nerves. Multiple sclerosis is considered an autoimmune disease because it is a result of the patient's immune system attacking the protective myelin sheath that covers their nerve fibers. This malfunction causes difficulty with nerve communications, widespread nerve damage, and deterioration of the nerves. Treatment aims at reducing the frequency of multiple sclerosis flare-ups and attempting to slow the progression of the disease. Immunotherapy has proven useful for multiple sclerosis patients through a number of mechanisms. Laboratory manipulation of activated T-cells can stop them from commanding immune system macrophages to attack the central nervous system.
Laboratory manipulation of class II major histocompatibility complex-bearing cells can prevent the immune system from tagging its own nerve tissues for immune cell attack. Disruption of immune lymphocyte traffic can stop lymphocytes from reaching their target nerves. Manual removal of immune white blood cells and other serum factors through a machine outside of the body can reduce the inflammatory response on the myelin sheathing. Additionally, laboratory manipulation of antigen-specific cells can reduce the production of antibodies that also attack the central nervous system of an individual with multiple sclerosis.
Other Immune Conditions
Inflammatory bowel disease is among the other immune conditions that can be treated with the use of immunotherapy. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are forms of inflammatory bowel disease where the patient's immune system incorrectly targets and attacks the digestive system lining. This malfunction causes inflammation characterized by debilitating pain and severe diarrhea. Because the immune system abnormalities associated with inflammatory bowel disease have been identified, the immune system can be modulated in several ways to reduce its attacks on the digestive system lining.
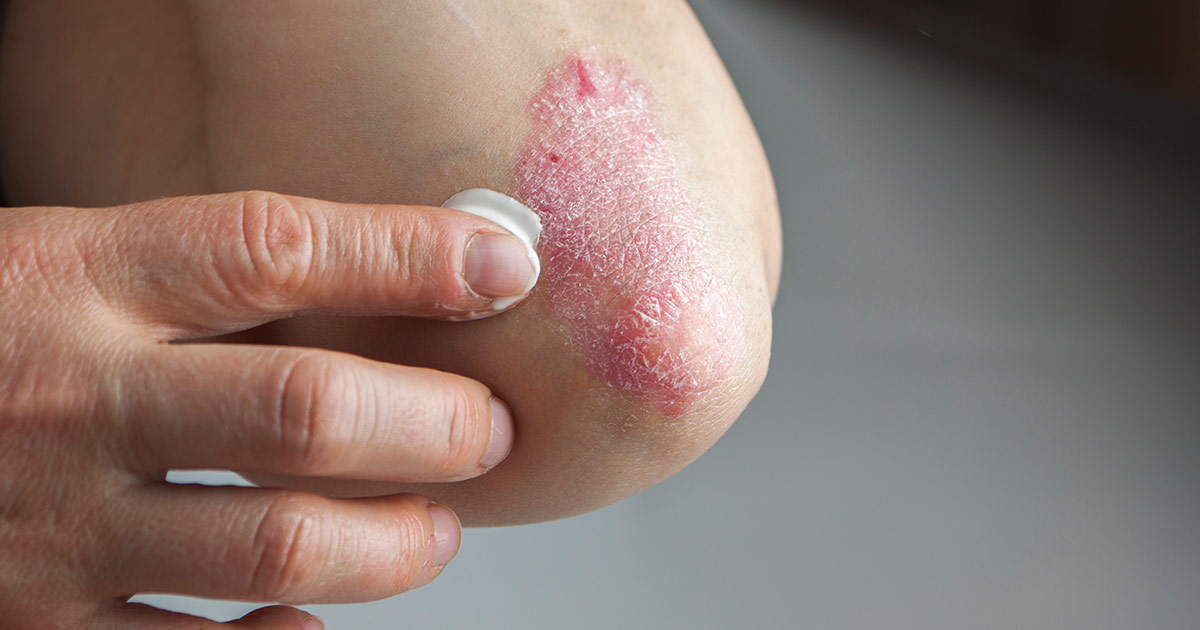
Psoriasis is another inflammatory disease that has been treated with the use of immunotherapy. Psoriasis occurs when the patient's immune system attacks healthy cells of the skin. This malfunction causes an overproduction of skin cells and white blood cells that result in scaly hard skin lesions. Immunotherapy for psoriasis involves the use of the immune system to target the particular inflammatory cytokines abnormally upregulated in individuals affected by psoriasis.
