Severe Complications With Eustachian Tubes
Hearing Loss
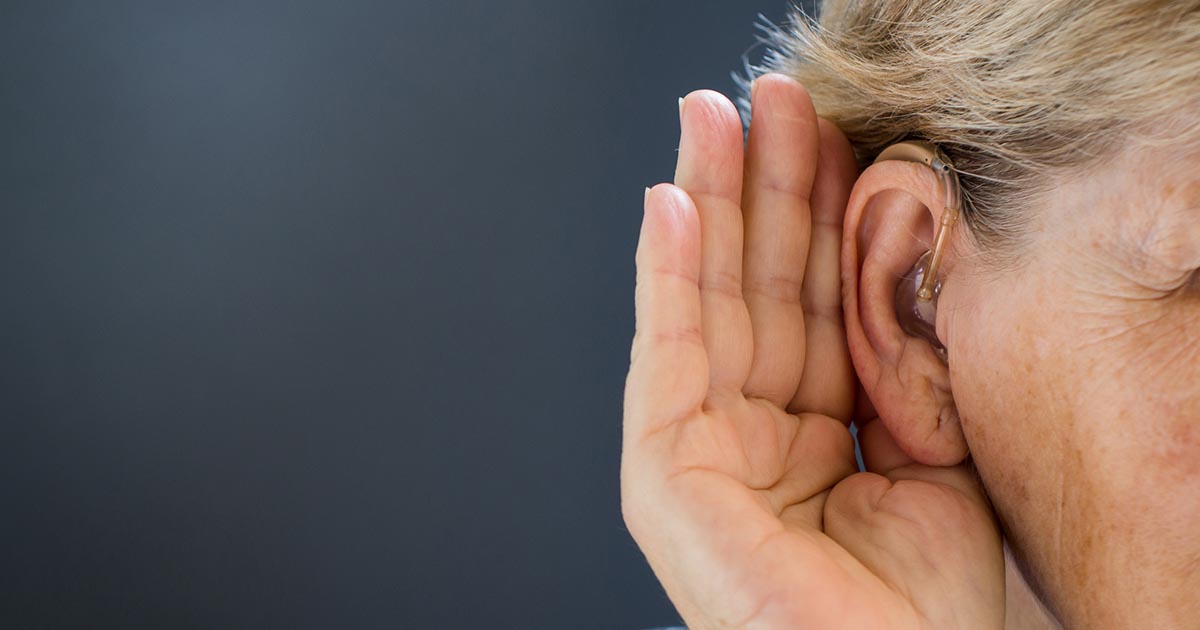

A blocked eustachian tube can lead to hearing loss. Unless the condition causes damage to structures within the ear, the hearing loss tends to be temporary. Many individuals are familiar with the feeling of having their ears 'pop' during air pressure changes, especially if they're in an airplane. The difference in pressure can make sounds seem muffled. Swallowing and yawning are both ways to open the eustachian tubes and help the air pressure outside equal the air pressure inside. Sometimes the problems with pressure aren't related to altitude changes, though. Patients might experience hearing loss from a blocked eustachian tube if there's negative pressure or fluid trapped inside the middle ear.
Impacted Earwax
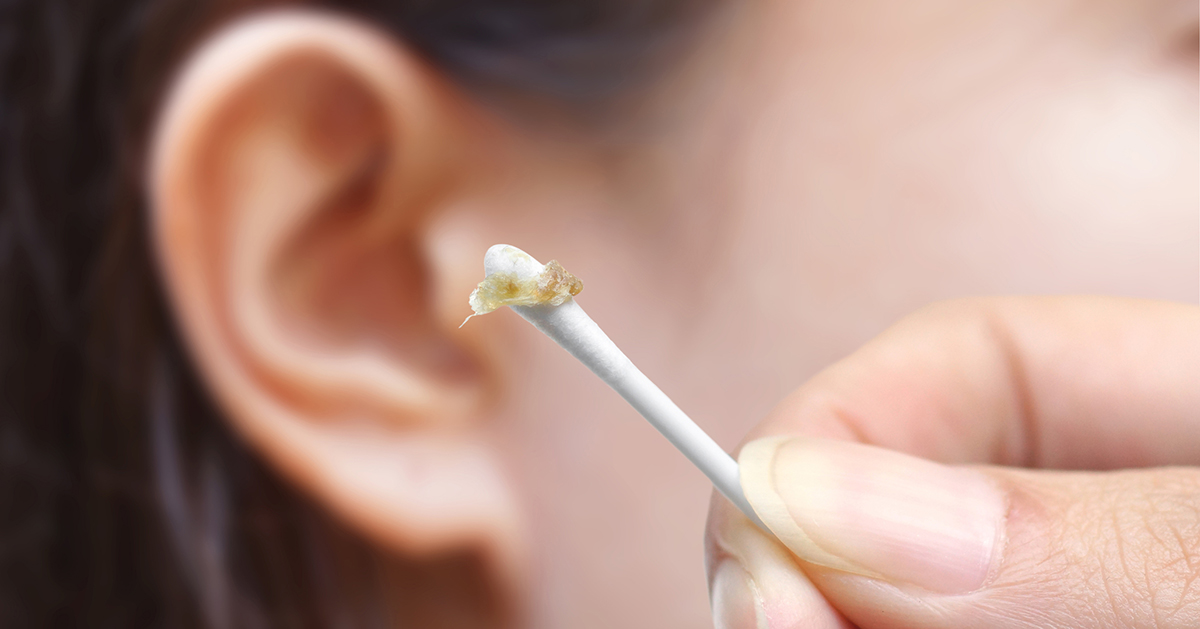
Earwax is a yellowish and waxy substance lining the inside of the ear canal. Wax is used to protect the ear from foreign objects, injury, infection, and water. But when there's too much wax built up, it can cause problems. The buildup is referred to as impacted earwax. Impacted earwax can be related to eustachian tube dysfunction when it blocks the eustachian tube, or when the eustachian tube is too narrow to cope with the amount of earwax in the ear. The ear contains glands that make secretions which combine with dead cells to make earwax. Over time, earwax migrates from the inner ear canal to the outer portion of the ear. But if the ear canal is blocked, the wax may build up without naturally migrating to the outside of the ear. Impacted earwax may also occur due to individuals sticking things into their ears, such as cotton swabs, which is why this should not be done.
