Strange Medical Conditions You Won’t Believe Are Real
Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis: Tree Man Syndrome
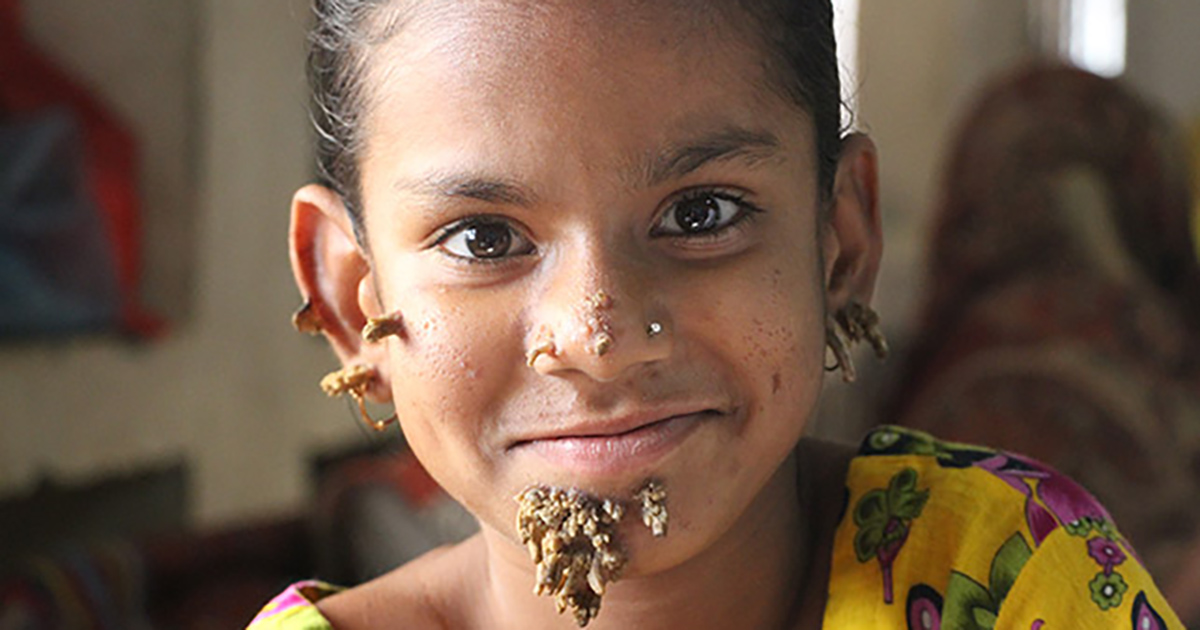

Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV) - also known as the tree man syndrome - is a rare, hereditary disease causing tumor growth on the patient's skin that resembles the bark from a tree. EV can occur during any time of the patient’s life, but it generally occurs in children between the ages of five and eleven. The symptoms of EV include flat or bumpy lesions, small bumps known as papules, patches of inflamed skin, and brown lesions resembling tree roots or tree bark. Approximately six-hundred cases of EV have been reported since the disease was first identified in 1922. Two-thirds of patients with EV are diagnosed with skin cancer between the ages of twenty and thirty.
Keep reading to learn all about fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, or stone man syndrome.
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: Stone Man Syndrome
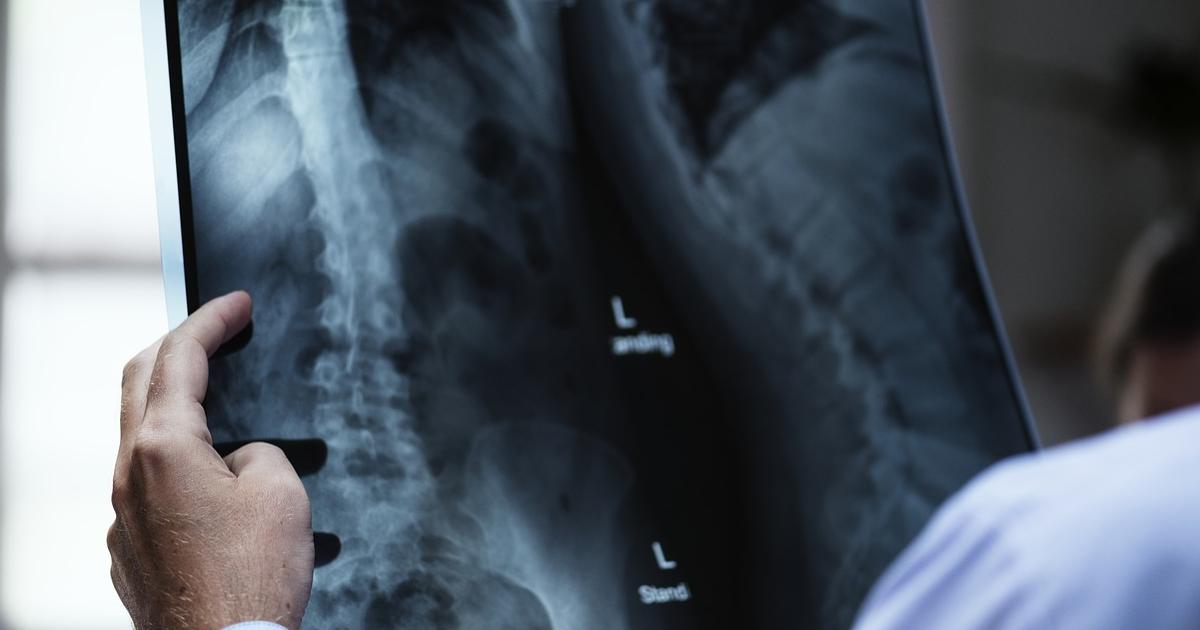
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) - more commonly known as stone man syndrome - is a genetic disorder that turns tissue, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage into bone over time. FOP is quite rare, affecting approximately one to two million patients worldwide. The condition commonly becomes noticeable in childhood, beginning in the neck and shoulders and working its way down the body and into the limbs. As FOP progresses, patients lose mobility. In some cases, they are unable to fully open their mouth and have a difficult time speaking and eating. Any trauma to muscles and joints such as a hit or a fall can trigger muscle swelling and inflammation that often leads to more ossification to the area. Often children born with FOP have larger, malformed toes, shorter thumbs, and other skeletal deviations.
Now that you know about fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, keep reading to learn about hypertrichosis, the werewolf syndrome.
