Symptoms, Risk Factors, And Causes Of Congenital Heart Diseases
Heart Murmurs
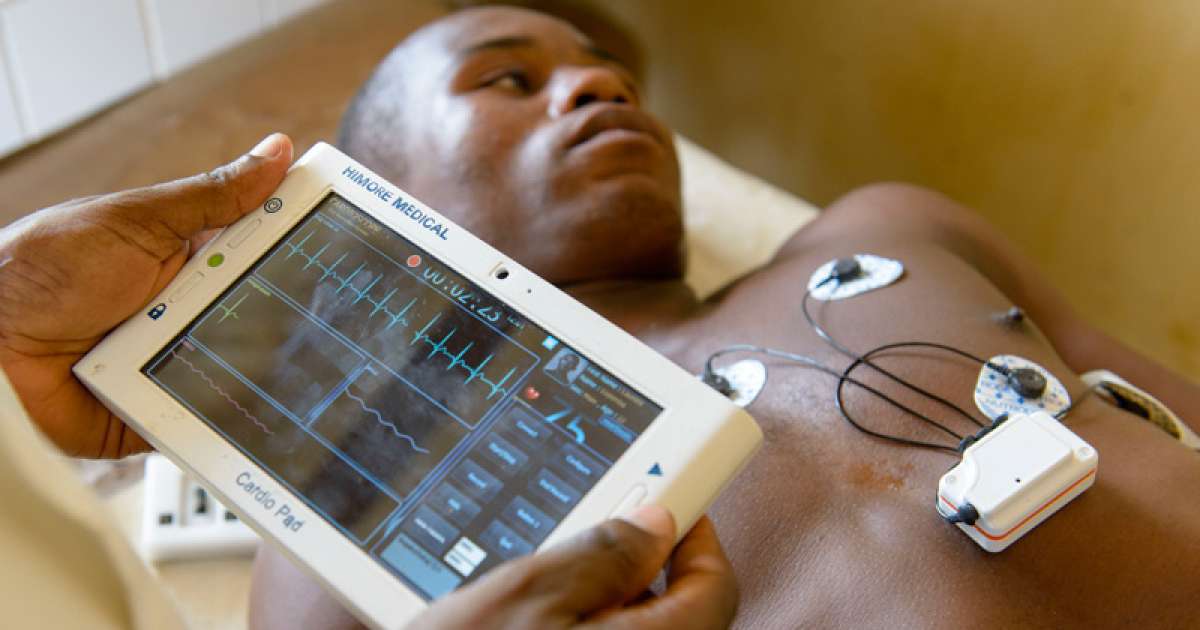
Heart murmurs are one of the primary indicators of latent congenital heart diseases or defects. A heart murmur is what medical professionals call the rushing sound of blood through the heart, and can indicate some kind of fault in the heart valves, which can lead to leaking or inefficient blood flow. For that reason, individuals should undergo routine physical examinations conducted by a doctor at least once a year. Non-invasive cardiovascular exams including auditory analysis of one's heartbeat with a stethoscope can often identify murmurs associated with congenital heart diseases. In some cases, these heart diseases are only identified after blood samples are analyzed, which is a common aspect of many annual examinations.
Cyanosis
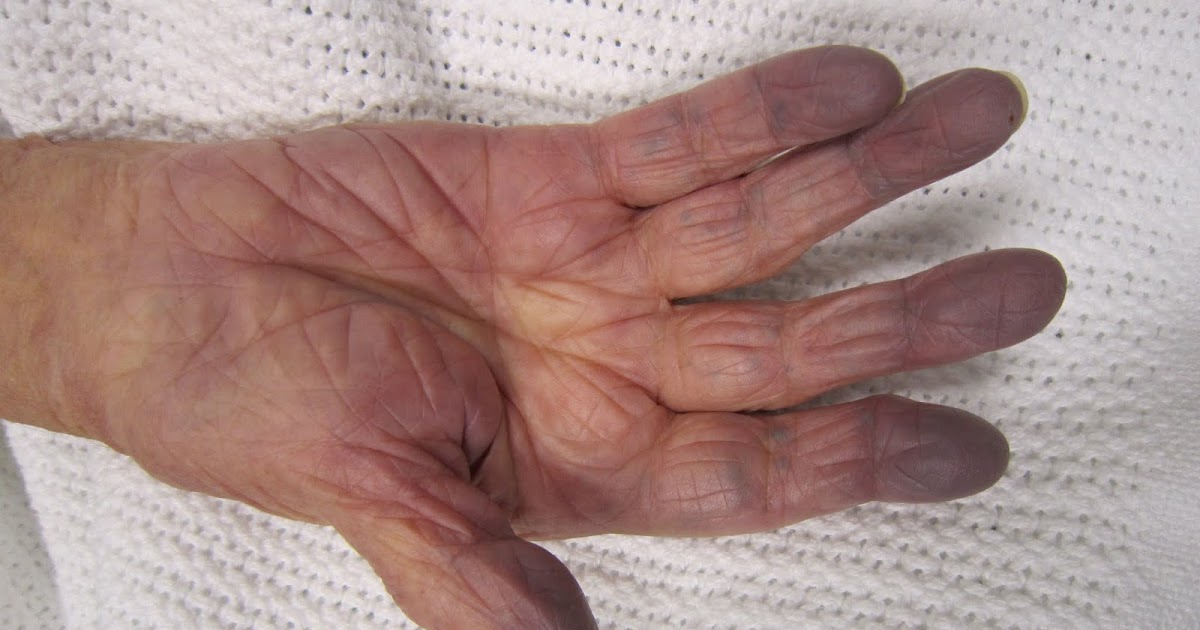
An individual who experiences cyanosis may be affected by a congenital heart disease. Cyanosis is a medical term used to describe a blueish hue to the mucous membranes or skin. Cyanosis caused by congenital heart diseases develops slowly over time. The mechanism behind cyanosis has to do with the way light reflects off the blood through the skin. Poorly oxygenated blood is a very dark red color. Blood rich with oxygen appears as a bright red color in the body. It is this difference in the color of the blood that causes light to reflect off oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood through the skin differently. While oxygen-rich blood yields a healthy pink skin color, the way light reflects off the dark color of oxygen-poor blood yields a grey-blue skin color.
An individual who has a congenital heart disease has a heart that does not work as it should because of structural or functional abnormalities. These abnormalities can make it difficult for the heart to pump oxygen-rich blood to all distant regions of the body. As a result, the blood inside of the small capillaries that run through the mucous membranes, to the tips of the fingers, and to the toes may have a near-constant low blood oxygen content. This malfunction causes cyanosis in an affected individual.
