The Most Lethal Viruses Known To Mankind
Measles
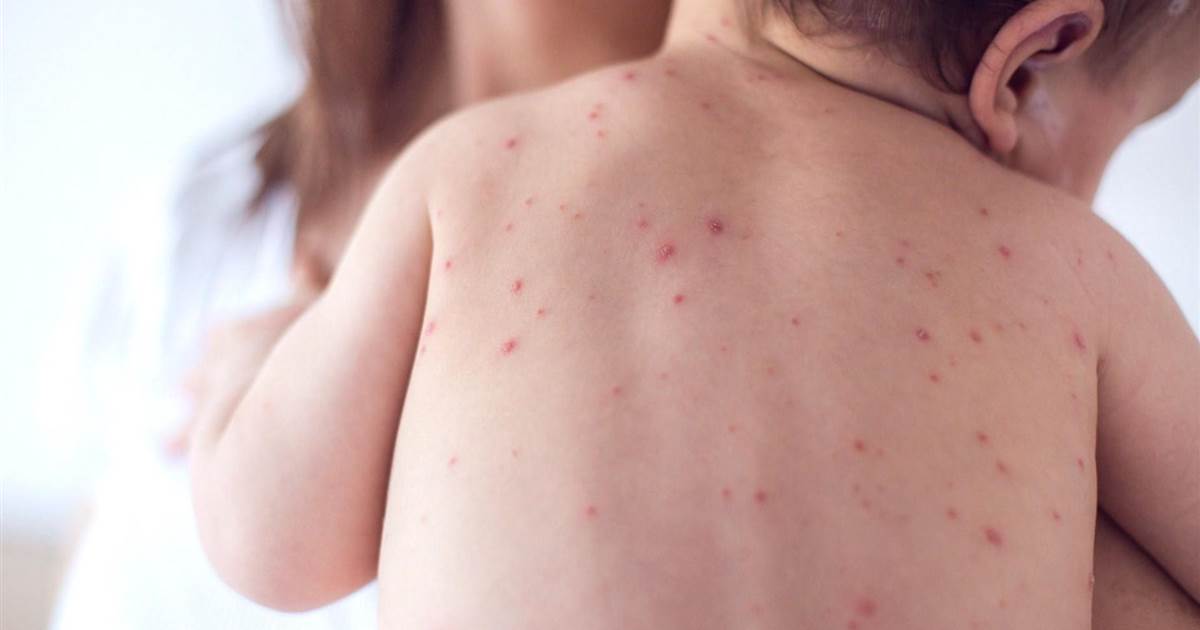
Also known as rubeola, measles is a highly contagious virus that can be prevented through vaccination. Symptoms of measles include runny nose, fever, conjunctivitis, and a rash. The rash associated with this condition typically begins on the face, and it consists of tiny red blotches that occur in clusters. The rash gradually spreads across the torso and arms, eventually spreading to the thighs, legs, and feet. When the rash is present, the patient's fever will often rise, and it could be as high as 104 to 105.8 degrees Fahrenheit.
A blood test can be used to diagnose measles, and treatment consists of post-exposure vaccination and the use of immune serum globulin. Fever reducers and antibiotics may also be used. Even with treatment, measles can cause serious complications, including ear infections, bronchitis, pneumonia, and encephalitis. If contracted during pregnancy, the virus may trigger early labor, and it is associated with low birth weight in the newborn. To prevent measles, two doses of vaccine are required, and these are normally given before a child enters elementary school. Without the vaccine, measles can be incredibly dangerous and often results in death.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a type of viral infection that can become chronic. The virus triggers liver inflammation, and it can lead to liver disease. Signs of hepatitis C include fatigue, easy bruising or bleeding, jaundice, reduced appetite, itchy skin, and swelling in the legs. Some patients may also deal with weight loss, spider angiomas, dark-colored urine, and fluid accumulation in the abdomen. Hepatitis C can be diagnosed through a blood test. Patients born between 1945 and 1965 have an increased risk of this condition, and doctors recommend that they consider being screened for hepatitis C.
Individuals who received a blood transfusion prior to 1992 may also wish to be screened. If hepatitis C is diagnosed, doctors may perform MRI scans and special ultrasounds to assess the patient's liver health and plan treatment. A number of oral medications are available for treatment, and doctors typically recommend that patients receive vaccinations for hepatitis A and hepatitis B to protect the liver as much as possible.
