How To Treat An Arrhythmia
Cardioversion
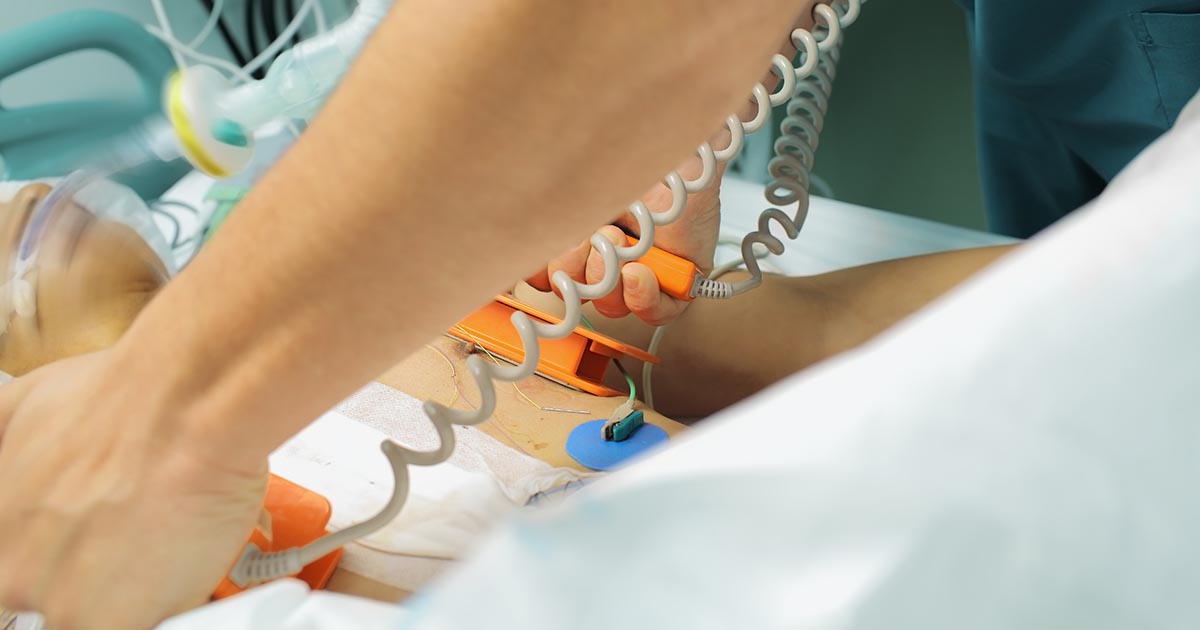

There are a variety of arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation that can be treated with a form of treatment known as cardioversion. The unique aspect of this treatment is it can be provided to patients as a medical procedure or through the use of certain medications. When this treatment is being administered to patients through a medical procedure, electric shocks will be sent to their heart, which can be done by placing electrodes directly on their chest. The procedure is a relatively simple one, and it can be completed in an hour or so. It also comes with very little recovery time. Whether the patient is suffering from a fast heartbeat or an irregular one, this treatment should help restore their heartbeat to a more normal rhythm. The reason an arrhythmia occurs in the first place is because electrical signals are unable to travel through the upper areas of their heart. The usage of this treatment allows patients to replace the damaged electrical signals with new ones. While medications can be used in the place of electric cardioversion, these medications will take longer to go into effect.
Uncover the next option for treating an arrhythmia now.
Catheter Ablation
Catheter ablation is a safe and straightforward treatment that can be used for several types of arrhythmia. During catheter ablation, patients will be provided with local anesthesia that will numb the area to keep them from experiencing pain during the procedure. Catheters are very flexible tubes sent through the patient's blood vessels and into their heart. The blood vessels used for sending the catheters to the heart can be located on the patient's neck, upper thigh, groin, or arm. These catheters are commonly equipped with wire electrodes that can identify where the abnormal heartbeat is located. These electrodes will then be used to damage a portion of the patient's heart tissue with a small amount of extreme cold, radio-frequency energy, or high heat. The development of scarring along the damaged tissue creates a barrier that keeps the abnormal electrical signals from reaching the healthy portions of the patient's heart, which means they will no longer suffer from arrhythmia.
Get the details on more ways to treat an arrhythmia now.
