What Are The Different Types Of Eczema?
Eczema is a condition in which skin becomes excessively dry, causing uncomfortable and painful symptoms. Eczema predominately occurs in individuals in their childhood, but anyone can develop it. Skin cells in healthy individuals are water abundant, which helps protect them from infection and damage. The skin contains oils and fats that help maintain body temperature, retain moisture, and prevent foreign substances from entering the body. Eczematous skin occurs because the skin is unable to produce enough of the oils and fats needed to hold in water. Due to this mechanism, the skin's barrier is impaired. Gaps between the skin cells allow the deeper skin layers to lose moisture, giving irritants and bacteria an easier way to penetrate and further strip it of its natural oils.
There are several types of eczema out there. Get to know them now.
Contact Dermatitis
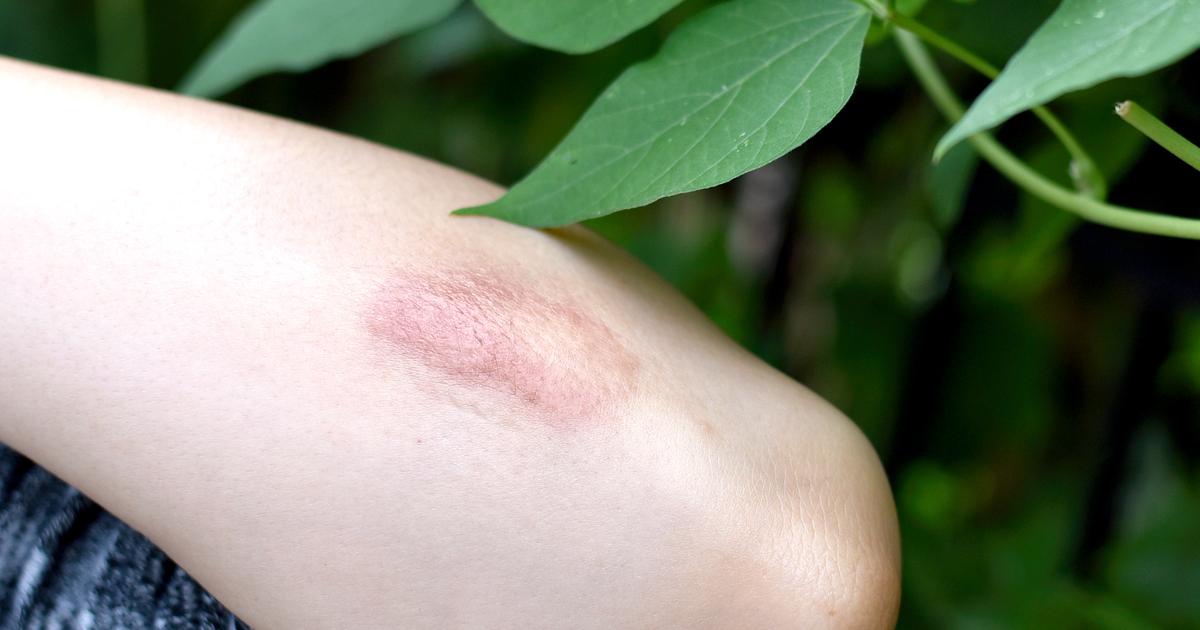
Contact dermatitis is a form of eczema where allergens and irritants in an individual's environment trigger an immune system reaction in their skin. There are three different subtypes in which an individual's contact dermatitis can fall. Irritant contact dermatitis forms quickly on the skin as soon as contact is made with an irritant, heat, or when it is rubbed too hard. Atopic dermatitis patients are at a greater risk of having irritant contact dermatitis. Allergic contact dermatitis develops between forty-eight and ninety-six hours following skin exposure to the allergen. The process an individual's immune system uses to recognize and react to the allergen is implicated in the delayed manifestation of allergic contact dermatitis. Contact urticaria, also referred to as hives, is a less common form of contact dermatitis. It is a rash on the skin that becomes red and swollen immediately following skin exposure to the irritating substance. This form of contact dermatitis does not stay on the skin for as long as the other two forms.
Read more about the different types of eczema now.
Atopic Dermatitis
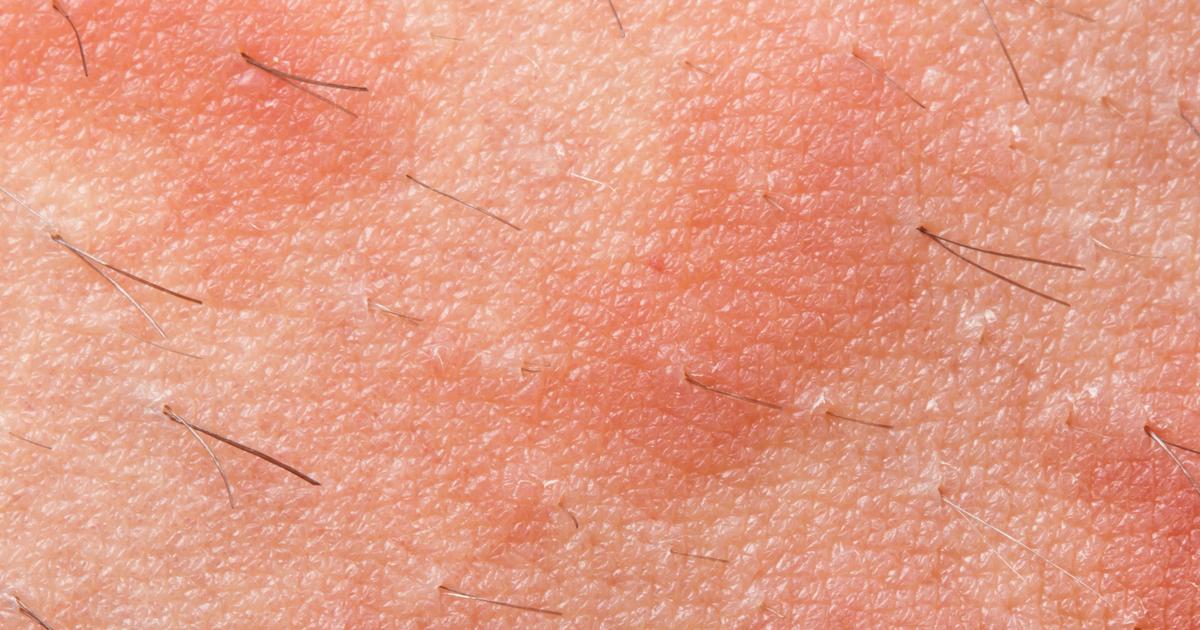
Atopic dermatitis is a form of eczema caused by a familial and personal predisposition to eczema because of an inherited defective skin barrier. It typically manifests within the first six months of an individual's life. Atopic dermatitis is known to be more severe than other types but tends to disappear as an individual grows older into their teen and adult years. Individuals affected by hay fever and asthma or have relatives with either condition are at a greater risk of developing atopic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis patients also have a genetic mutation that affects the way their bodies produce a protein called filaggrin, which is what creates the protective skin barrier that keeps water inside the cells and keeps the cells tightly packed together. Individuals with atopic dermatitis are more prone to developing skin infections, such as herpes or staph, because of the dysfunctional skin barrier. Atopic dermatitis tends to have a pattern of periodic outbreaks and flare-ups that alternate with periods of symptom reduction. Anti-inflammatory systemic drugs, antibiotics, medicated creams, medicated lotions, and biologic drugs are used to treat atopic dermatitis.
Continue reading to learn more about the different types of eczema now.
