Guide To The Types Of Kidney Disease
Kidney Stones
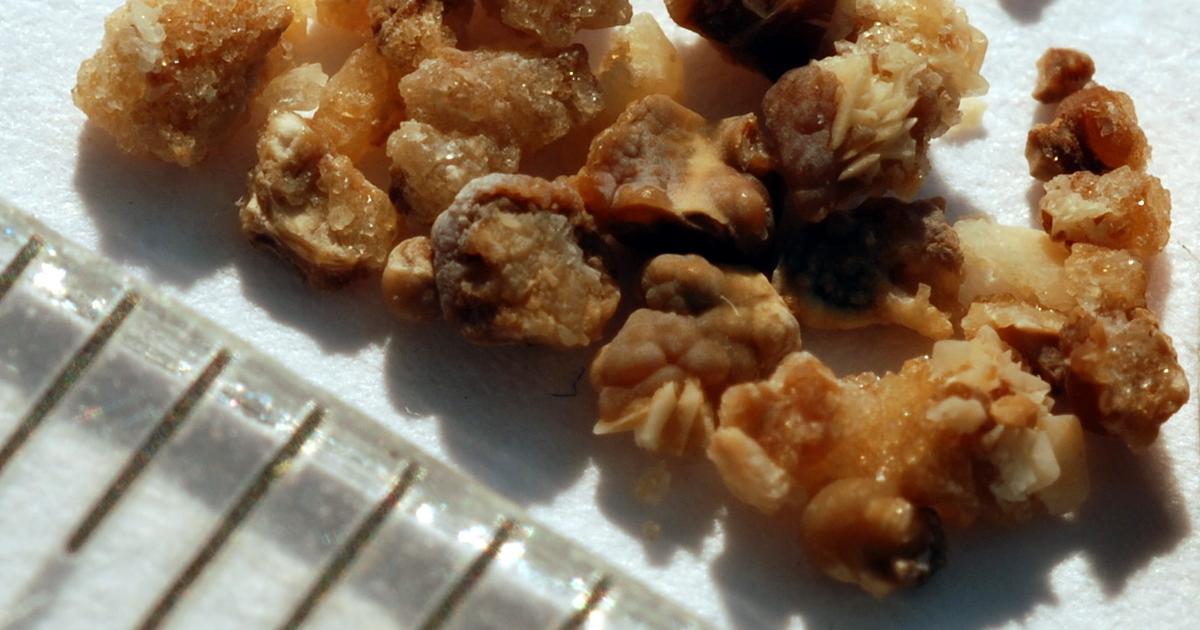

Kidney stones are hard deposits made up of minerals and salts. The stones can form inside the kidneys due to dehydration, kidney infections, and changes in diet or hormone levels. Patients with kidney stones often experience severe pain in the back and side of their abdomen. They may also have blood or pus in their urine. Some individuals could develop a fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting, and urinary output may be reduced. Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, inflammatory bowel disease, and hyperparathyroid conditions are associated with an increased risk of kidney stones. Patients who have had a gastric bypass operation also have an elevated risk.
Kidney stones can be detected with ultrasounds. Doctors may also perform computerized tomography scans, blood and urine tests, and an intravenous or retrograde pyelogram. If kidney stones are discovered, they may need to be treated in the hospital. A lithotripsy procedure can be performed to break up large stones. Doctors may choose to surgically remove them using percutaneous nephrolithotomy. This operation is used if a kidney stone is causing an obstruction and is also appropriate when kidney stones are causing unmanageable pain.
Learn more about kidney diseases and conditions that affect the kidneys now.
Kidney Cysts
Another condition that affects the kidney is kidney cysts. These are round fluid pouches that form in or on the patient's kidneys. In some instances, kidney cysts may be the result of serious conditions that impair the function of an individual's kidneys. However, kidney cysts are often simple kidney cysts, which do not have a clear cause. This means they are noncancerous and rarely trigger significant complications.
In most cases, patients only have one kidney cyst on the surface of a kidney. However, they can have multiple cysts, which can affect one or both of their kidneys. Of course, it is worth noting that simple kidney cysts are not the same type that form due to polycystic kidney disease. The majority of simple kidney cysts do not cause symptoms. However, if they grow large enough, they can trigger upper abdominal pain, fever, and dull back or side pain. Treatment may not be required, but options include draining the cyst and filling it with alcohol, as well as surgically removing the cyst.
Uncover information on more conditions that affect the kidneys now.
