Astonishing Ailments Prednisone Packs a Punch Against
7. Sjogren's Syndrome

Sjogren's syndrome is an autoimmune condition that impacts the body's ability to produce moisture. Patients with this condition typically have dry eyes and a dry mouth, and they could also experience dry skin, fatigue, numbness in the limbs, pain in the muscles and joints, and chronic coughing. Individuals with Sjogren's syndrome frequently have other autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus as well, and they may develop thyroid issues. Women are at a higher risk of Sjogren's syndrome, and the condition is typically diagnosed after the age of forty. Individuals with this health issue are more likely to develop tooth decay and yeast infections than others. To diagnose Sjogren's syndrome, doctors perform blood tests, and the Schirmer tear test can be performed to measure the tear production of the eyes. Some patients might need to have a sialogram, salivary scintigraphy, or a lip biopsy. In addition to prednisone, Sjogren's syndrome patients may need to use prescription eye drops to reduce symptoms associated with dry eyes, and antifungal medicines may be prescribed if yeast infections develop. Immunosuppressants like methotrexate could be considered for systemic treatment. Patients who have severely dry eyes could also benefit from a punctal occlusion procedure.
8. Psoriasis
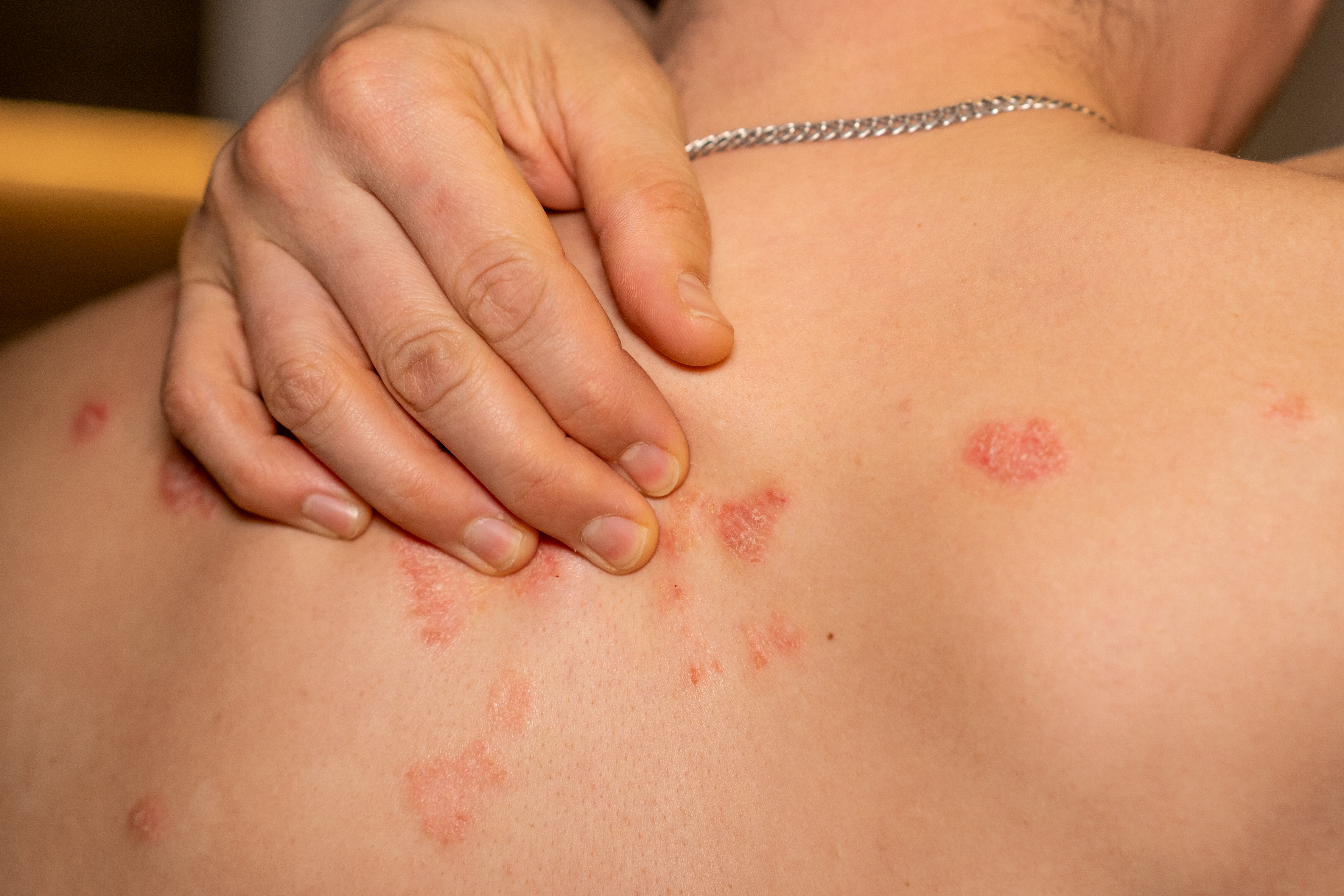
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that accelerates the typical life cycle of skin cells. This acceleration causes the cells to rapidly accumulate on the skin's surface, and this can create scales and red patches that may be itchy and painful. The skin could become so dry that it cracks and bleeds, and patients might notice their nails are thickened, pitted, or ridged. The joints could become stiff and swollen. Doctors are often able to diagnose psoriasis with a health history and a physical examination. A skin biopsy may be useful in determining the specific type of psoriasis the patient has, and it could also be used to rule out other conditions. Topical corticosteroids are frequently prescribed for mild to moderate psoriasis, and patients might need to use vitamin D analogs to slow down the growth of skin cells. Calcineurin inhibitors could be recommended to reduce both inflammation and scaling, and anthralin helps remove scales and smooth the skin. Light therapy sessions may be considered for certain patients, and patients with severe psoriasis typically need to take oral medications or injections to manage their symptoms. Methotrexate and cyclosporine can be taken orally, and patients may benefit from the use of injectable biologics such as etanercept or adalimumab. An oral biologic medication called apremilast might be recommended too.
