Guide To Rifampicin
Potential Side Effects

Patients have noticed headaches, nausea, upset stomach, and heartburn while taking this medication. Women taking it could develop changes in their menstrual cycles. This drug can cause urine, tears, saliva, or sweat to become brown, red, or orange. This discoloration resolves once the patient stops taking rifampicin. However, this medicine could permanently discolor the patient's teeth. This medication may cause changes in behavior and coordination. Some patients may experience diarrhea, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite during treatment.
Rifampicin can change the results of certain lab tests. For example, it could cause elevated liver function tests, low red blood cell counts, elevated BUN levels, and elevated serum uric acid levels. Some patients may develop liver disease as a result of taking this medication. Thus, patients should be aware of possible signs of liver damage. Individuals with liver damage may notice yellowing of the skin or eyes. They could also have dark urine, persistent nausea, or abdominal pain. They should report them to their doctor immediately.
Get the details on precautions to remember with this medication next.
Precautions To Remember
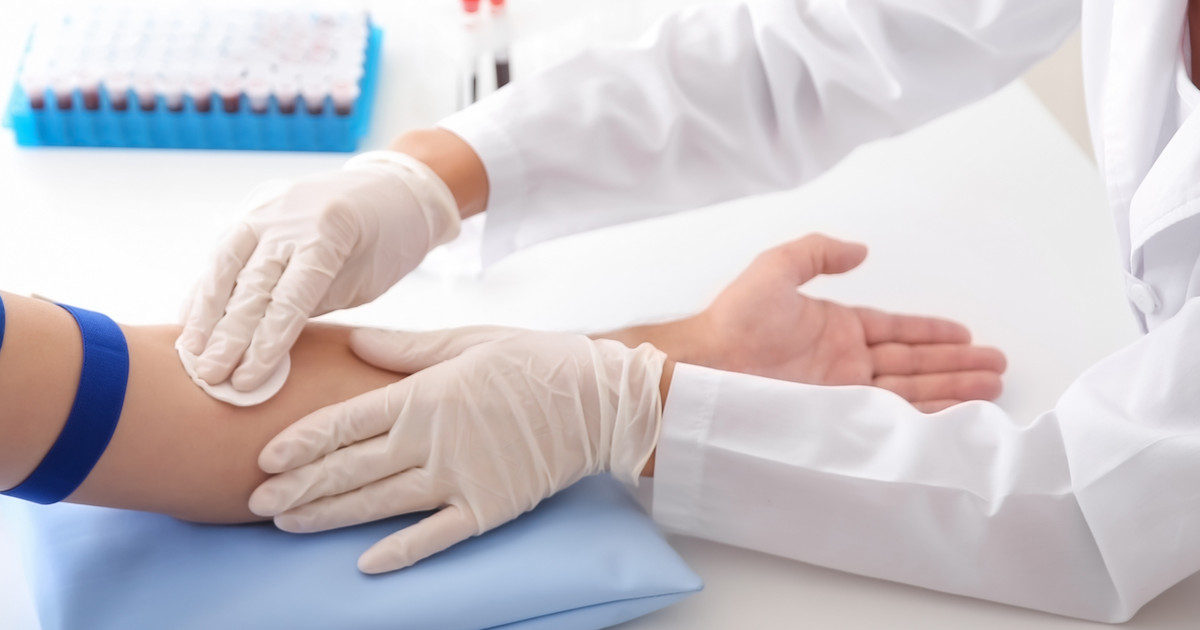
Before prescribing this medicine, doctors need to know about the patient's medical history. Rifampicin may not be safe for individuals with a history of diabetes, bleeding disorders, porphyria, or liver disease. Using this medicine during the last few weeks of pregnancy could cause bleeding in the mother or baby. Thus, patients should let their doctor know if they are pregnant. This medication is not safe for use in breastfeeding women. Since this medicine may reduce hormonal birth control's effectiveness, patients should use additional methods of contraception during treatment. Rifampicin could cause permanent staining of soft contact lenses. Thus, patients may need to wear glasses while taking this drug.
This medicine could cause inaccurate drug screening results. Thus, individuals having their urine tested should let the facility staff know that they take this medication. Patients may need frequent blood tests while they are on this medication. Specific tests are done to check for infection. Generally, patients continue taking this medication until tests indicate that the infection has cleared. When rifampicin is taken by mouth, patients should do so without food. They can choose to take it one hour before a meal or two hours after a meal. In both cases, they should do so with a full glass of water. It is important to take the entire course of this medication to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Reveal the potential medication interactions next.
