What Is Tramadol?
Uses For Tramadol
Tramadol is used to treat both acute and chronic pain. For instance, it is often prescribed for patients experiencing acute pain while recovering from surgery. The medication is also prescribed to patients coping with chronic pain caused by accidents and injuries and by illnesses such as cancer. Some doctors may prescribe tramadol for moderate to severe lower back pain and pain from arthritis. The medicine is sometimes considered as a treatment option for pain from autoimmune conditions, including lupus.
In certain instances, it might be recommended as one of several medications to control pain from migraines. Patients who have been prescribed tramadol for any reason should always let their doctors know if they feel the medication is not relieving their pain or if they experience any changes in their symptoms.
Side Effects Of Tramadol
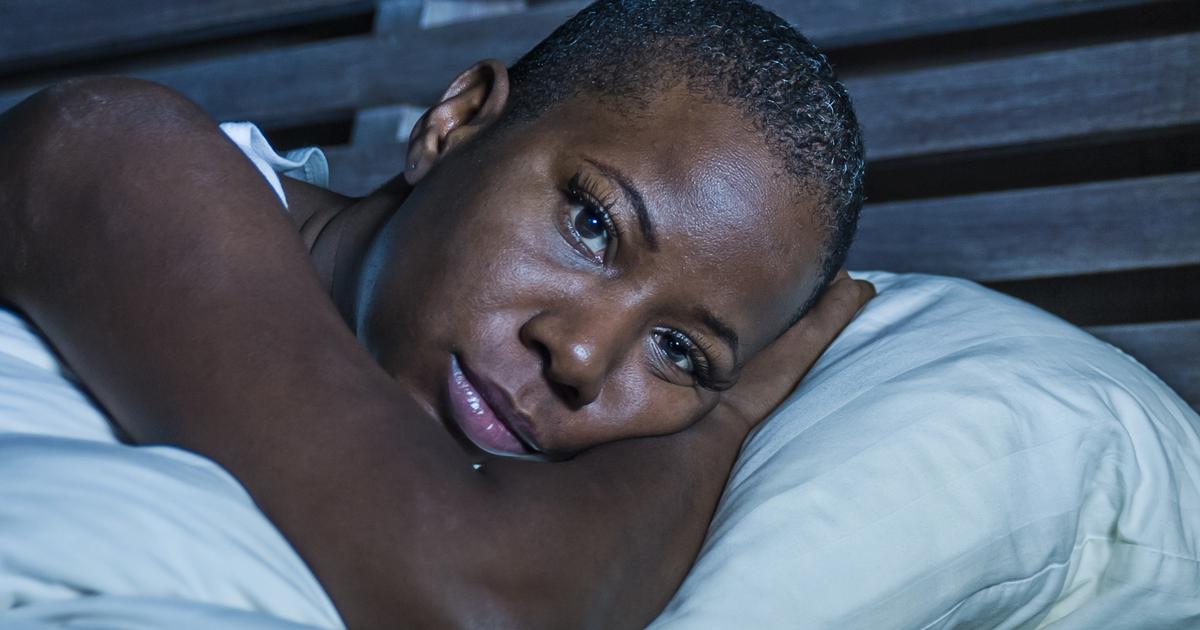

Tramadol can affect sleep, and patients could experience sleepiness or difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Headaches, dry mouth, heartburn, and muscle tightness have been reported, and some patients have noticed mood changes, nervousness, and uncontrolled shaking of a limb. Tramadol could also lead to flushing, congestion, sore throat, and itching.
Serious side effects may develop as a result of using tramadol, and patients are most at risk of these during the first seventy-two hours of using the medicine and at any time their tramadol dose is increased. Seizures, breathing and swallowing difficulties, hives, confusion, agitation, and hallucinations are among the most serious side effects that could occur. Some patients lose consciousness after taking tramadol. Patients should mention all side effects to their doctor, and any serious side effects should be treated in an emergency room.
