Beyond the Itch: The Infection Risks You Face When You Over-Scratch Bug Bites
Allergic Reactions and Secondary Skin Conditions

Beyond infections, over-scratching can lead to allergic reactions and secondary skin conditions. Continuous scratching can cause a condition known as lichen simplex chronicus, where the skin becomes thickened and leathery due to persistent irritation. This condition can exacerbate the itch-scratch cycle, leading to further complications. In some cases, individuals may experience allergic contact dermatitis, where the skin reacts to substances introduced through scratching. Recognizing these potential outcomes highlights the importance of managing bug bites promptly and effectively to prevent escalating skin issues.
Psychological Impacts: The Itch-Scratch Cycle
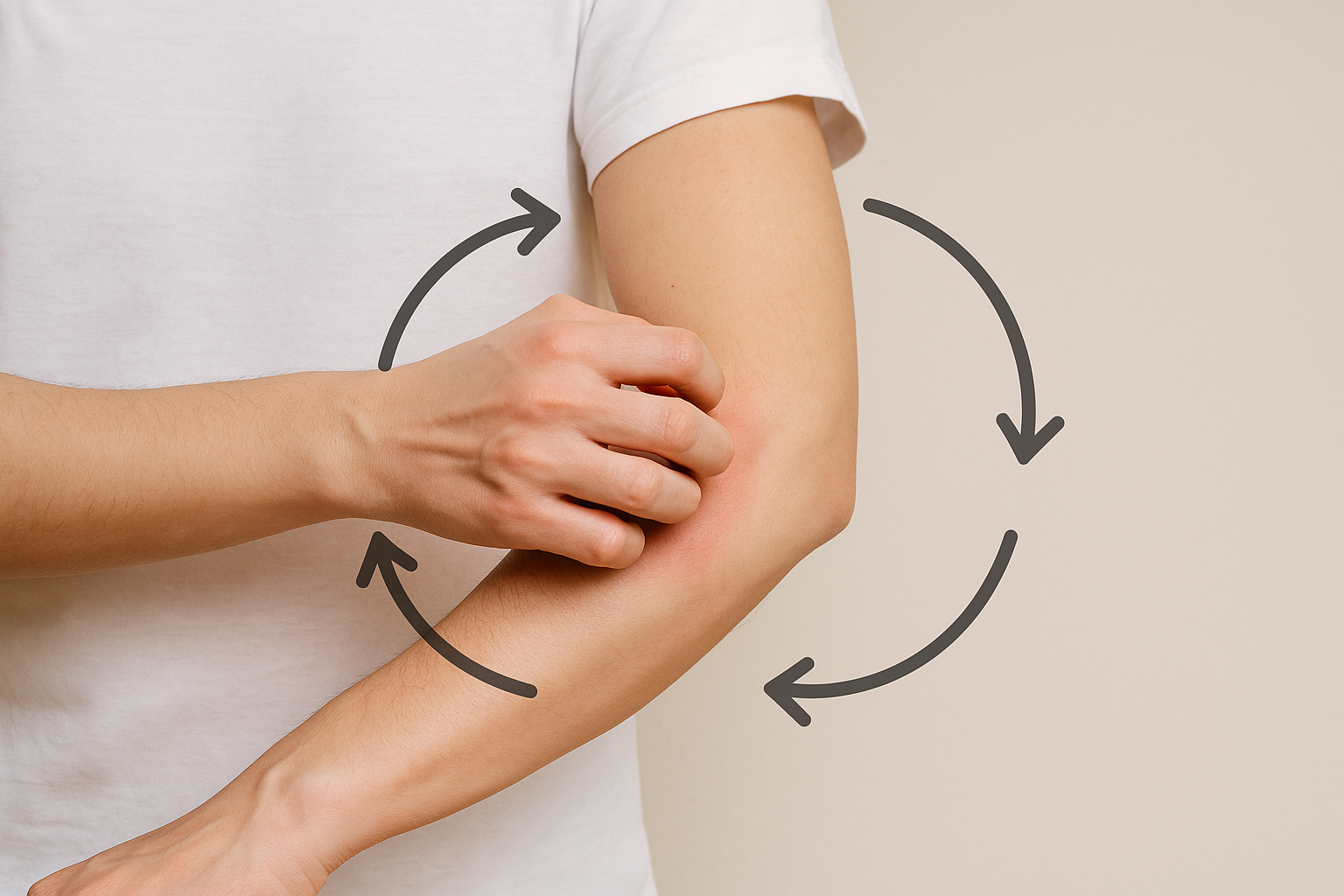
The itch-scratch cycle is not just a physical phenomenon; it has psychological implications as well. The persistent itch can lead to significant discomfort and distress, affecting sleep and overall quality of life. This discomfort can create a cycle of anxiety and stress, which in turn can exacerbate the perception of itchiness. Understanding the psychological aspect of scratching behavior is crucial for developing comprehensive strategies to manage bug bites. Techniques such as mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral approaches can help break the itch-scratch cycle, reducing both physical and emotional impacts.
