The Complete Guide To Cord Blood Banking: Pros, Cons, Costs And Basics
Banking a child' s cord blood has become an increasingly popular practice over the past two decades, giving families access to life-saving treatments later on in life. A variety of family banks across the world offer cord blood banking services for a reasonable fee. The stem cells stored can be used in the future for emerging treatments for the family. Public banks offer a similar service for free, but this doesn't always mean that one will have access to their baby's stem cells in future.
What Is Cord Blood Banking?
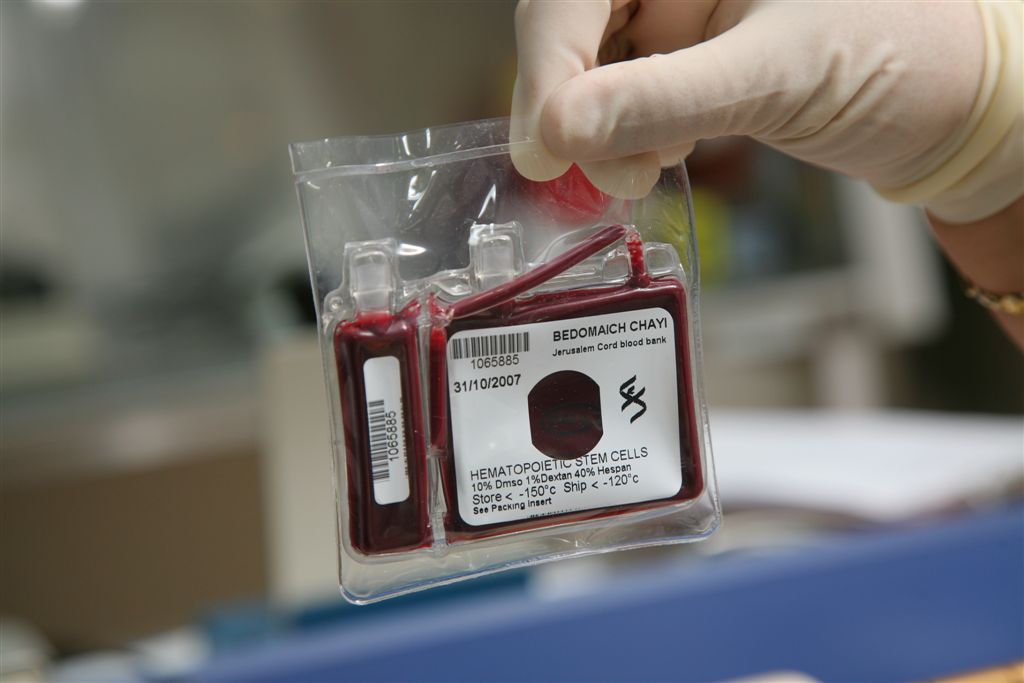
Cord blood banking is a practice that involves preservation of a newborn's stem cells found in the placenta and umbilical cord. There is a certain amount of blood with valuable stem cells that remain in the placenta and umbilical cord when a baby is born, even in cases of delayed cord clamping.
The umbilical cord and placenta are rich sources of newborn stem cells. The stem cells found in the placenta and cord tissue are mesenchymal while those in the cord blood itself are hematopoietic. New parents have the option of dispensing that blood, preserving it with either a family bank or donating it to a public bank. The whole process of collecting the cord blood and storing it for future medical purposes is what is known as cord blood banking.
How Cord Blood Is Collected
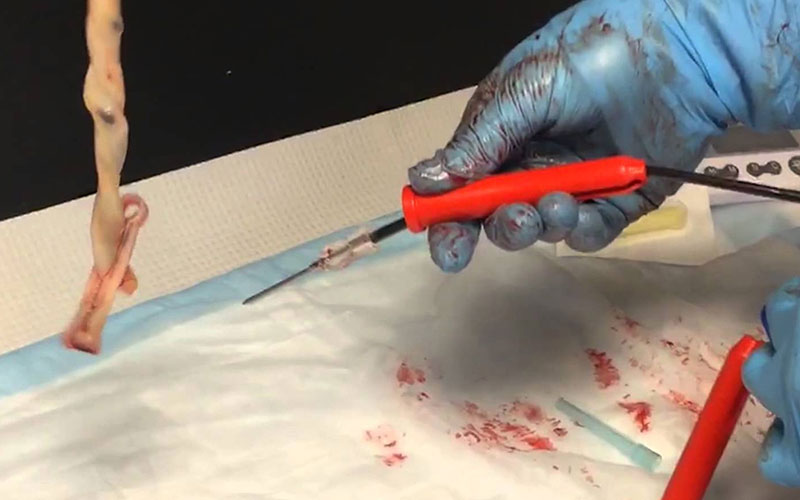
Whether one has a C-section or a vaginal birth, the process of collecting cord blood is painless and non-disruptive for both mother and baby. Once the baby is born, the doctor clamps the umbilical cord before cutting it, then a nurse or assigned caregiver inserts a needle into the umbilical cord to extract any remaining blood.
Cord blood has to be harvested immediately after birth because delaying the procedure will give it time to clot. The device used is kept away from the baby for safety purposes. Doctors often collect cord blood into heparin free bags. Once collected, the blood is shipped to a bank of the family's choice. Upon arrival at the bank, the cord blood is tested for usability and then cryogenically frozen.
