15 Serious Warning Signs of Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially serious condition that occurs when serotonin levels in the body become excessively high, often as a result of medication interactions or dosage increases. This condition can also be triggered by certain dietary supplements or recreational drugs. While serotonin is essential for regulating brain and nerve function, an overabundance can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications if left untreated. In mild cases, symptoms may resolve on their own after discontinuing the offending substance, but more severe cases often require medical intervention, including the use of serotonin-blocking medications. Understanding the signs and risks of serotonin syndrome is crucial for early detection and treatment. Join us on this exploration of 20 warning signs that may be signalling serotonin syndrome—and how to recognize them.
1. Muscle Rigidity And Twitching

If an individual is going to develop serotonin syndrome, the symptoms tend to occur several hours after the first dose of a new drug or increased medication dosage. It's important for doctors and psychiatrists to be aware of symptoms to look for. They should also double check any new medications don't have potentially toxic interactions with other medicines the patient is already taking. While the risk of serotonin syndrome is relatively low if medication is carefully administered, patients taking serotonin-increasing drugs should be aware of the warning signs. It's important to self-monitor after new medication dosages. One of the most telling signs is unexplained muscle rigidity, loss of coordination in the muscles, or unexplained muscle twitches. If patients experience these muscular symptoms after a change in their medications, they should get in contact with their doctor right away. If the symptoms become more severe, seek emergency medical treatment.
2. Physiological Symptoms

Patients dealing with serotonin often experience strange physiological reactions, most commonly ones like goosebumps and shivering. Individuals do not, however, have to have every physiological symptom to be dealing with serotonin syndrome. Patients may also sweat heavily even in mild weather conditions, sometimes in conjunction with the chills. It may feel similar to having a bad case of the flu. Normally, the brain and spinal cord's nerve cells create serotonin that helps with attention regulation, body temperature management, and general behavior. An excess of serotonin causes these functions to go awry, which can explain the feelings of cold and excessive sweating. The body's ability to self-regulate its temperature is going haywire.
3. Restlessness, Agitation, And Confusion

There are a number of mental and cognitive symptoms caused by serotonin syndrome. Serotonin normally regulates mood, but an excess of the chemical causes the brain to lose its ability to regulate emotions. The cognitive symptoms may also be worsened by the pain and discomfort from symptoms in the rest of the body. Patients often experience restlessness and agitation. They may feel like they need to pace around or like their skin is crawling. Confusion is also fairly common. While mild confusion might not be an inherent sign of severe serotonin syndrome, serious confusion should be treated with concern. Any unusual, uncontrolled mood and cognitive changes are a sign of neurological issues. If individuals experience these following a new medication dose, they should contact their doctor or seek emergency medical care.
4. Rapid Or Irregular Heart Rate
Serotonin syndrome can cause a rapid or irregular heart rate, usually coupled with high blood pressure. Many of the cardiovascular symptoms are similar to the symptoms from taking a too-high stimulant dose. An unexplained and rapid heartbeat isn't always cause for concern, but it's absolutely a warning sign if it occurs after a medication adjustment. In addition, irregular heart rhythms are a sign of severe serotonin syndrome. High blood pressure occurs when the blood vessels are too constricted for the blood to pump adequately, causing increased pressure against the vessel walls. Chronic high blood pressure can lead to cardiovascular damage. Heart rate symptoms shouldn't be ignored, especially if they're accompanied by neurological or physiological symptoms. Serotonin syndrome can get worse before it gets better, particularly when the syndrome-causing medication is still working in the body. It's crucial to get medical help before severe and potentially life-threatening symptoms set in.
5. High Fever

A high fever is one of the most characteristic symptoms of severe serotonin syndrome. Fevers tend to occur because the overproduction of serotonin causes a loss of ability to regulate body temperature, which leads to an overall rise in core temperature. Any fever above 104 degrees Fahrenheit is generally considered high. Individuals with high fevers are often experiencing hyperthermia, an increase in body temperature that can potentially lead to organ damage. These patients need to seek emergency medical care immediately. It's important to tell the doctors about any medications they've taken, especially new doses. For doctors, one of the key signs that separates serotonin syndrome from other hyperthermic disorders is the shivering. If the condition isn't treated, the neurological conditions may progress to seizures and total unconsciousness.
6. Dilated Pupils
Dilated pupils, also known as mydriasis, can be one of the more visible signs of serotonin syndrome, signaling an overactive autonomic nervous system. Serotonin affects many involuntary bodily functions, and an excess can disrupt the delicate balance of these systems. When serotonin levels rise too high, the muscles controlling the pupils become overstimulated, causing them to expand. Dilated pupils can also increase sensitivity to light, making bright environments uncomfortable or even painful. This symptom is often accompanied by other neurological or physiological signs, such as restlessness, rapid heart rate, or muscle twitching. Although dilated pupils can result from a variety of causes, their presence alongside other symptoms of serotonin syndrome provides an important visual clue that serotonin levels may be elevated. If you notice persistently enlarged pupils and additional signs after a medication adjustment, consult a healthcare provider immediately to rule out serotonin syndrome.
7. Severe Headache

A sudden, severe headache can be a distressing symptom of serotonin syndrome, indicating that the brain is struggling to manage excessive serotonin levels. Unlike a typical tension headache, this type often appears suddenly and may resemble a migraine in its intensity. The pain can be throbbing and localized, frequently accompanied by sensitivity to light, sound, or both. Serotonin plays a vital role in blood vessel regulation, and an excess can lead to vasodilation (widening of blood vessels), which may contribute to the onset of a severe headache. Patients experiencing a headache caused by serotonin syndrome may also notice additional symptoms, such as nausea, restlessness, or visual disturbances. Although headaches are common and can have numerous causes, a severe headache in conjunction with other serotonin-related symptoms—like fever, muscle rigidity, or confusion—should not be ignored. Seek medical evaluation promptly, as this may be an early warning sign of a developing condition.
8. Nausea and Vomiting

Nausea and vomiting are classic symptoms of serotonin syndrome, stemming from the critical role serotonin plays in the digestive system. In fact, the majority of the body's serotonin is produced and stored in the gut, where it regulates bowel movements and communication with the brain. When serotonin levels spike due to medication interactions or overdose, the gut becomes overstimulated, leading to nausea, vomiting, and general digestive distress. This symptom is often an early warning sign of serotonin syndrome and can range from mild queasiness to severe and persistent vomiting. In more advanced cases, patients may also experience diarrhea, which further exacerbates fluid and electrolyte imbalances. If nausea or vomiting is accompanied by other symptoms, such as agitation, sweating, or muscle twitching, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Left untreated, these symptoms can escalate, leading to dehydration and worsening the overall condition.
9. Seizures

Seizures are among the most severe symptoms of serotonin syndrome and indicate that the condition has progressed to a critical stage. They occur when excessive serotonin in the brain disrupts the normal electrical activity of neurons, leading to uncontrolled and abnormal bursts of energy. These seizures can range from short, mild convulsions affecting a specific area of the body to full-body seizures accompanied by unconsciousness. Patients who experience seizures as part of serotonin syndrome are at significant risk of further complications, including permanent neurological damage or death if untreated. Seizures are often preceded by other symptoms, such as high fever, rapid heart rate, and confusion, making these earlier signs critical for timely intervention. If a seizure occurs, immediate medical attention is required to stabilize the patient and address the underlying cause. Treatment may involve serotonin-blocking drugs and supportive care to prevent further complications.
10. Uncontrollable Shaking or Tremors

Tremors, or involuntary shaking, are a hallmark symptom of serotonin syndrome and often one of the first noticeable signs of nervous system overstimulation. These tremors are caused by an overabundance of serotonin triggering hyperactivity in the muscles and nerves. While mild shaking might initially appear localized—such as in the hands—it can spread to other areas of the body as the condition worsens. The severity of tremors can vary widely, from subtle twitching to pronounced and uncontrollable shaking that interferes with daily activities. These tremors are often accompanied by muscle stiffness, agitation, or restlessness, further compounding discomfort. For individuals experiencing tremors following medication changes, prompt medical evaluation is essential. Uncontrolled shaking that persists or worsens without treatment can escalate into more severe symptoms, such as muscle spasms or seizures, making early recognition and intervention critical.
11. Clenched Jaw or Jaw Tightness

A clenched jaw, also known as trismus, is another symptom linked to serotonin syndrome. This involuntary muscle tension occurs due to the overstimulation of muscles and nerves in the face. Patients may find their jaw muscles feel unusually tight, sore, or difficult to relax. In severe cases, this can interfere with eating, speaking, or even breathing comfortably. Jaw clenching often accompanies other muscle-related symptoms, such as rigidity or tremors, and is typically part of the broader neuromuscular effects of excessive serotonin. While jaw tightness might seem minor compared to other symptoms, it can be a significant warning sign when paired with agitation, sweating, or other indicators of serotonin syndrome. Promptly addressing this symptom and its underlying cause can prevent progression to more severe complications, such as muscle spasms or seizures.
12. Diarrhea

Diarrhea is a common gastrointestinal symptom of serotonin syndrome, often appearing as one of the earliest indicators. Serotonin’s role in the digestive system includes regulating gut motility, but an overproduction can lead to hyperactivity in the intestines, resulting in frequent and watery bowel movements. This can cause significant discomfort and may quickly lead to dehydration if left unchecked. When diarrhea is accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, or abdominal cramping, it becomes an even more concerning sign of serotonin syndrome. If diarrhea occurs after starting a new medication or adjusting a dosage, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Addressing this symptom early can help prevent complications like severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and worsening of the syndrome.
13. Excessive Sweating
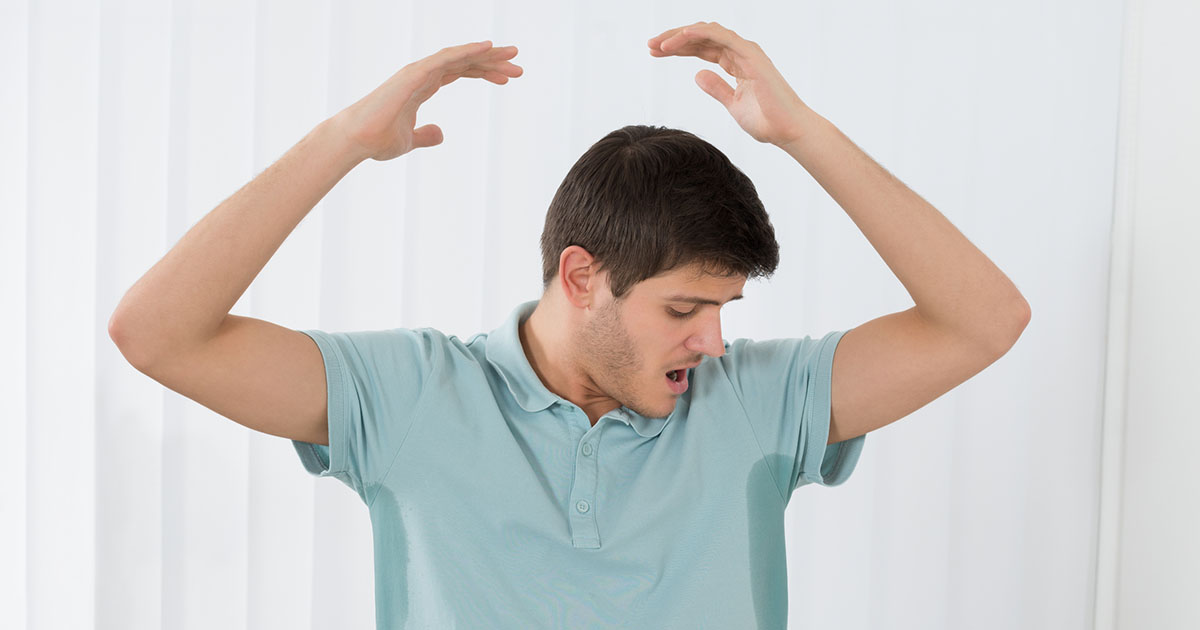

Excessive sweating, also called hyperhidrosis, is a classic symptom of serotonin syndrome caused by the body’s inability to regulate temperature effectively. The overstimulation of serotonin receptors disrupts the hypothalamus, the brain’s temperature control center, leading to sweating that can be profuse and unrelated to environmental conditions. This symptom is often paired with other signs of dysregulation, such as fever or chills. Excessive sweating can quickly result in dehydration, further complicating the condition. If heavy sweating occurs alongside neurological symptoms, such as agitation, tremors, or confusion, it may signal that serotonin syndrome is progressing. Medical attention is essential to prevent the condition from becoming more severe.
14. Hyperreflexia (Overactive Reflexes)
Hyperreflexia, or exaggerated reflex responses, is a telltale neuromuscular symptom of serotonin syndrome. This occurs when serotonin overstimulates the spinal cord and peripheral nerves, causing reflexes to become overly sensitive. For example, a slight tap on the knee during a reflex test may result in an unusually forceful or prolonged response. This heightened reflex activity often coincides with other muscle-related symptoms, such as twitching, rigidity, or tremors. While hyperreflexia may seem less alarming than other symptoms, it’s a clear indication that the nervous system is in overdrive. Recognizing this sign early, especially after a recent medication change, can prompt timely medical intervention to address the underlying serotonin imbalance.
15. Loss of Consciousness

Loss of consciousness is a grave symptom of serotonin syndrome and signals that the condition has reached a critical stage. This can occur due to a combination of high fever, seizures, and severe cardiovascular strain caused by excessive serotonin levels. When unconsciousness develops, the body’s vital functions, such as breathing and heart rate, may also become unstable. This symptom is often preceded by warning signs like confusion, agitation, or seizures, making early detection of these indicators vital. If someone loses consciousness and serotonin syndrome is suspected, immediate emergency medical care is required. Treatments such as cooling measures, serotonin-blocking drugs, and intensive monitoring can help stabilize the patient and prevent further complications.
Recognizing and Responding to Serotonin Syndrome

Recognizing the signs of serotonin syndrome is crucial for preventing the condition from escalating into severe or life-threatening complications. From mild symptoms like dilated pupils and excessive sweating to critical indicators such as seizures and loss of consciousness, the spectrum of serotonin syndrome symptoms underscores the importance of early detection and intervention. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms after starting or adjusting a medication, seeking medical attention promptly is essential. Awareness of serotonin syndrome not only empowers individuals to take control of their health but also ensures that healthcare providers can act swiftly to address the underlying cause. By understanding the risks, staying informed, and acting quickly, we can reduce the dangers associated with this condition and ensure safe and effective treatment for those affected.