Guide To Lactic Acidosis Symptoms
Lactic acidosis is a condition in which the body has too much lactic acid circulating in the blood and tissues. It happens when lactic acid builds up faster than the liver and kidneys can remove it from the body. Lactic acidosis can occur due to underlying causes such as cardiac arrest, congestive heart failure, sepsis, acetaminophen usage, and chronic alcoholism. Temporary lactic acidosis can be caused by excessive, intense exercise and can usually be treated with rest and hydration. A fasting blood test is required to properly diagnose lactic acidosis. Treatment options are intended to treat the underlying cause, but center around increasing oxygen flow to the tissues and hydrating with electrolytes.
Get to know the details on symptoms associated with lactic acidosis now.
Problems With Breathing

With lactic acidosis, the body is trying to increase its oxygen levels so it can return to homeostasis. One way of doing this is to increase the breathing rate. Since the body is trying to lower lactic acid by increasing oxygen, patients with lactic acidosis often have problems with breathing resulting in rapid, shallow breathing. This condition is called tachypnea and can worsen conditions if left untreated. Normal respiration rates for adults is between ten and twenty breaths per minute, so anything over twenty is considered tachypnea. Some patients will notice feeling like they cannot take in enough air or they are short of breath, while others may not notice this symptom at all. Blue fingertips and lips often occur when an individual is suffering from tachypnea due to a lack of oxygen flow to the extremities.
Keep reading for more on the various symptoms of lactic acidosis now.
Fruity-Smelling Breath

Fruity-smelling breath is closely related to shallow, rapid breathing. With lactic acidosis, the body tries to release the excess acid any way it can. Should the liver and kidneys be unable to filter enough lactic acid to return the body to homeostasis, it will be released during regular breathing. These patients with lactic acidosis have fruity-smelling breath because the body is releasing lactate and hydrogen ions (acid) through respiration. This smell is usually very strong, and along with being fruity or sweet, can smell like acetone. Acetone is naturally occurring in the human body as a byproduct of the breakdown of fats.
Get the details on the next lactic acidosis symptom now.
Jaundice
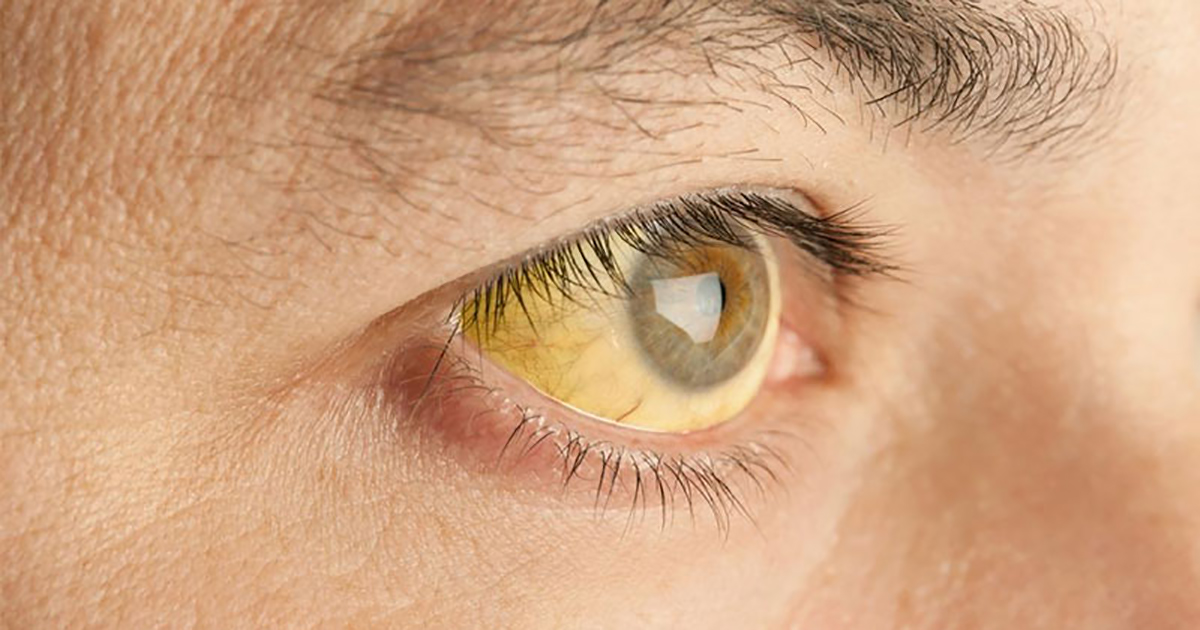
Jaundice occurs when the liver cannot break down bilirubin. It is not a disease, but a symptom of underlying conditions, and it is often a sign of lactic acidosis. Patients with jaundice have yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. Patients may also notice their urine is dark and their bowel movements are light and chalky. In lactic acidosis, a main underlying cause is the improper function of the liver or kidneys to filter lactate from the body, so it makes sense for them to also have this symptom. As lactic acid is removed from the body via medical intervention or naturally, the skin will return to its normal color.
Continue reading to discover more ways in which lactic acidosis can be spotted now.
Rapid Heart Rate

A normal resting heart rate for adults is between sixty and one hundred beats per minute. A rapid heart rate, or tachycardia, is anything above one hundred beats per minute. It is normal for the heart rate to rise during exercise or activity, but it can be a symptom of lactic acidosis when the patient is at rest. It is also tied to rapid breathing because increased breathing will also increase the heart rate. Some patients will not experience any symptoms from a rapid heart rate, but others will experience pressure or tightness in the chest, pain, fatigue, and even fainting. In extreme cases, tachycardia can lead to a heart attack or unconsciousness.
Read more about the major symptoms of lactic acidosis now.
Weakness And Confusion

Weakness and confusion are a common pair of symptoms sometimes associated with lactic acidosis and can be tied to tachycardia and tachypnea. Both tachycardia and tachypnea can further exacerbate the effects of weakness and confusion. Weakness is defined by a lack of muscle strength. Fatigue can also be felt in the muscles and can make performing simple activities like walking or taking care of oneself difficult or even painful. Confusion and dizziness can also occur leaving a patient with lactic acidosis feeling unclear or uncertain about what is going on. Other complications of confusion can include a lack of focus and the inability to make decisions. Panic may also set in if a patient is disturbed by their confusion.
Read more about the symptoms linked to lactic acidosis now.
Abdominal Discomfort And Muscle Cramps

Individuals affected by lactic acidosis may present with abdominal discomfort and muscle cramps. Many symptoms of lactic acidosis are based on the underlying cause of the condition. An individual's acid-base homeostasis is strongly influenced by disturbances in their normal gastrointestinal function. Numerous factors can contribute to this mechanism, including surgical complications, acquired diseases, infection, and hereditary diseases. Abdominal discomfort is common in individuals who have a short small intestine or have undergone jejunoileal bypass surgery. Glucose within the food the affected individual has consumed is not digested when passing through the stomach and small intestine. This malfunction provides a rich source of food for the bacteria that populate an individual's colon. The gut bacteria produce lactic acid when they consume the undigested glucose, resulting in a build-up of this lactic acid in the colon. This process irritates the large intestine and its neighboring muscular tissues. This irritation can manifest in the form of abdominal discomfort and muscle cramps in the affected individual.
Keep reading for more information on the warning signs of lactic acidosis now.
Loss Of Appetite

Lactic acidosis patients may present with a loss of appetite due to their condition. Numerous factors contribute to an affected individual's appetite loss. Lactic acidosis causes the acidity of the blood to become too high, inducing vascular constriction. Blood vessel constriction can cause issues all around the body, but particularly in the digestive tract. The lack of blood supply due to constricted vessels causes food to move through the gastrointestinal tract slower than usual. When the food stagnates or moves slowly, the affected individual will not feel hungry from one meal to the next. Lactic acidosis can be the result of bacteria growth and colonization in the colon as a result of a short small intestine that cannot fully digest glucose. The bacteria in the large intestine overproduce due to the abundance of glucose and may invade into the small intestine. Bacterial infection of the small intestine causes inflammation of these tissues. This type of inflammation and toxicity in the small bowel often induces nausea and vomiting in affected individuals, effectively reducing their appetite. Pancreatitis, the inflammation of the pancreas, has been implicated as a cause for the development of lactic acidosis, which also produces nausea, vomiting, and appetite loss.
Keep going to discover more lactic acidosis symptoms now.
Diarrhea

An individual affected by lactic acidosis may present with diarrhea as a symptom of their condition. Diarrhea is a symptom often attributed to the underlying causes of lactic acidosis. Infections that affect the gastrointestinal tract can cause diarrhea and subsequent dehydration. Dehydration can cause the development of lactic acidosis, implicating diarrhea as a symptom of the condition. Diarrhea is also a common result of bacterial overgrowth into an affected individual's small intestine. Lactic acidosis can be caused by a patient's inability to digest glucose fully from the food that they consume. This allows undigested glucose to proceed into the large intestine, where the good gut bacteria consume it and begin to grow out of control. Glucose consumption by the gut bacteria causes an accumulation of lactic acid because it is a byproduct of the process. This bacteria becomes unmanageable and grows into the small intestine where it causes inflammation and damage to the intestinal lining. The bacteria can also metabolize bile salts into compounds that cannot be reabsorbed by the intestines. This absorption impairment causes the patient to experience diarrhea.
Read more about the different symptoms associated with lactic acidosis now.
Extreme Fatigue

Extreme fatigue can be a symptom indicative of lactic acidosis. Lactic acidosis, we know, is a condition directly associated with the production of cellular energy throughout the body. The best way for the cells to produce usable energy is a process that requires an adequate amount of oxygen. The cells have a backup method of energy production when oxygen is scarce in the tissues. This backup process does produce cellular energy, but it does not do as good of a job as the normal energy production process. Lactic acidosis in an individual indicates their tissues are deprived of a sufficient amount of oxygen because it is a byproduct of the backup energy production process. Even with the activation of this backup process, there is still an energy shortage. Fatigue is a feeling of tiredness or sluggishness due to the body adaptively responding to the low energy conditions. The body modulates and distributes cellular energy to the essential tissues of vital organs by taking it away from tissues not essential to survival. The redistribution of energy in the body as a part of this process is what produces the feeling of fatigue in affected individuals.
Discover additional lactic acidosis symptoms now.
Headache
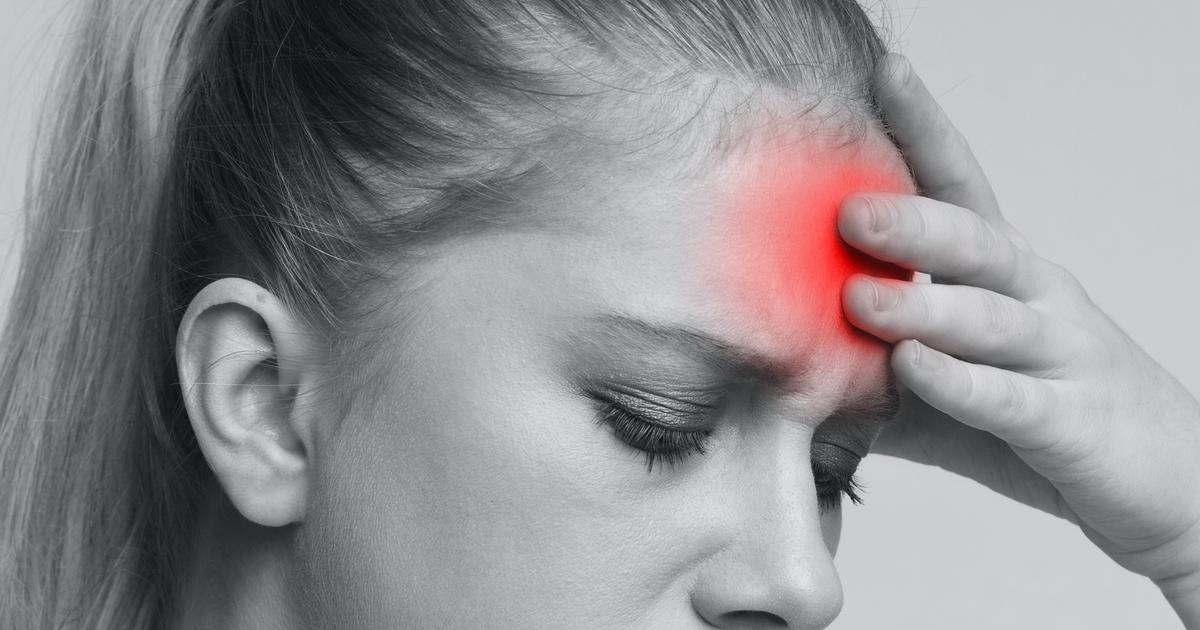

A headache can be a symptom in an individual affected by lactic acidosis. Lactic acid is a byproduct of a process that makes energy for the cell that is typically only activated when tissues are in a state of oxygen deprivation. Mitochondria are the organelle inside of a cell responsible for metabolizing glucose into usable cellular energy. Oxygen deprivation causes an impairment in the transport chain the mitochondria use in this process. This type of impairment occurs most often in the cells that make up the brain tissues and muscular tissues around the body since they have a higher demand for oxygen than other tissues. When some mechanism causes oxygen deprivation in the brain like excessive exercise or an underlying medical condition, the cells have to produce energy without it. The process the cells use to accomplish this causes an increased level of lactic acid as a byproduct. The lactic acid can accumulate in the affected individual's blood as a result. The higher acidity of the blood causes the blood vessels around the brain to constrict, reducing blood flow and oxygen delivery further. Vessel constriction and oxygen deprivation cause the affected individual to feel a headache.
