Causes And Symptoms Of Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is a life-threatening condition characterized by high blood pressure in the arteries leading to the lungs and heart. Unlike regular hypertension or high blood pressure, pulmonary hypertension occurs when the arteries in the lungs become blocked or narrow, making it harder for the heart to pump blood through them. This raises blood pressure in the lungs and causes the heart to weaken, which may eventually lead to heart failure. Here are the symptoms and causes to watch out for.
Causes
Pulmonary hypertension is caused by a rise in blood pressure due to changes in cells lining the pulmonary arteries, which causes artery walls to become thick and stiff. In some cases, excess tissues may form, making blood vessels tight and inflamed. The right ventricle of the heart is responsible for pumping blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery. When this becomes clogged, the heart has to work extra hard to transport oxygen and blood to the lungs, which weakens the heart and raises blood pressure in the lungs.
Idiopathic Pulmonary Hypertension
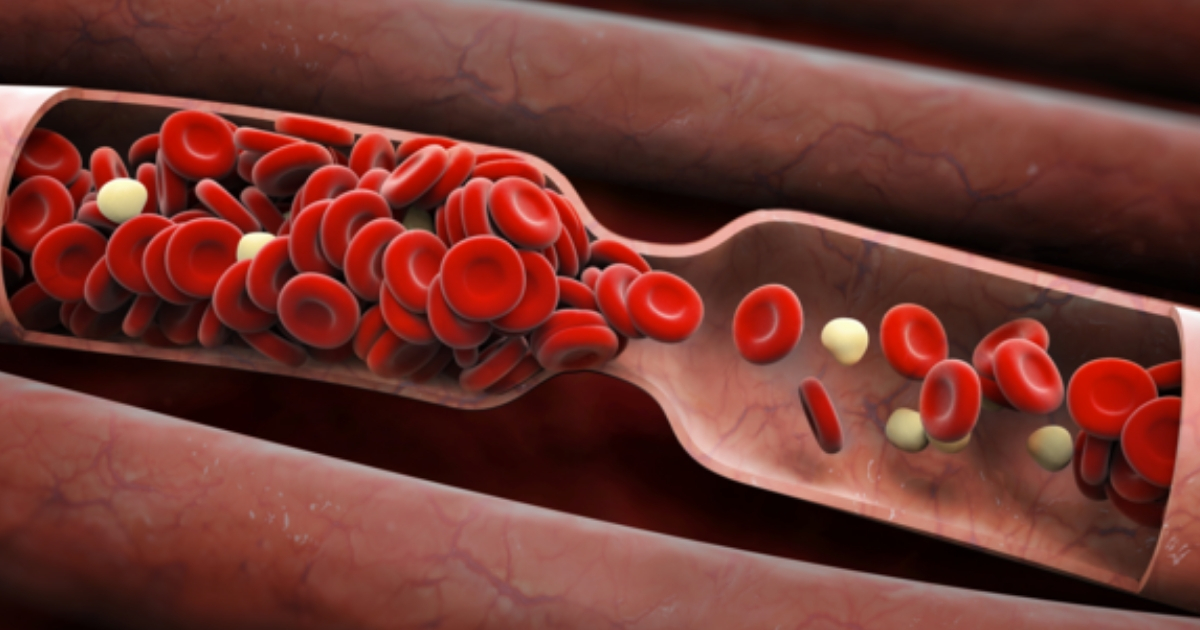
Sometimes pulmonary hypertension occurs for no apparent reason. Idiopathic pulmonary hypertension is the term used to describe the development of pulmonary hypertension when no underlying illnesses are causing it. Genetics and lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise habits may play a role in pulmonary hypertension. Eating lots of fruits and vegetables that are high in antioxidants may help reduce inflammation associated with the narrowing or blocking of the arteries. Antioxidants also support cardiovascular disease to reduce the risk of heart failure.
