11 Common Symptoms Linked To Liver Cancer
The liver may not get as much attention as the heart or lungs, but this football-sized organ plays a crucial role in keeping you alive and well. Nestled above the stomach and beneath the diaphragm, the liver filters toxins from your blood, aids in digestion, and supports dozens of vital processes. Unfortunately, it can also be the site of serious disease—including cancer. While hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of primary liver cancer, other forms like hepatoblastoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma also occur. In fact, liver cancer is often diagnosed after it has spread from another part of the body. Because early symptoms can be subtle or easily mistaken for other conditions, liver cancer often goes undetected until it’s more advanced. That’s why recognizing the early warning signs is so important. In this updated guide, we’ve expanded our list to highlight 11 common symptoms linked to liver cancer—so you can spot the signals early and seek help when it matters most.
1. Jaundice
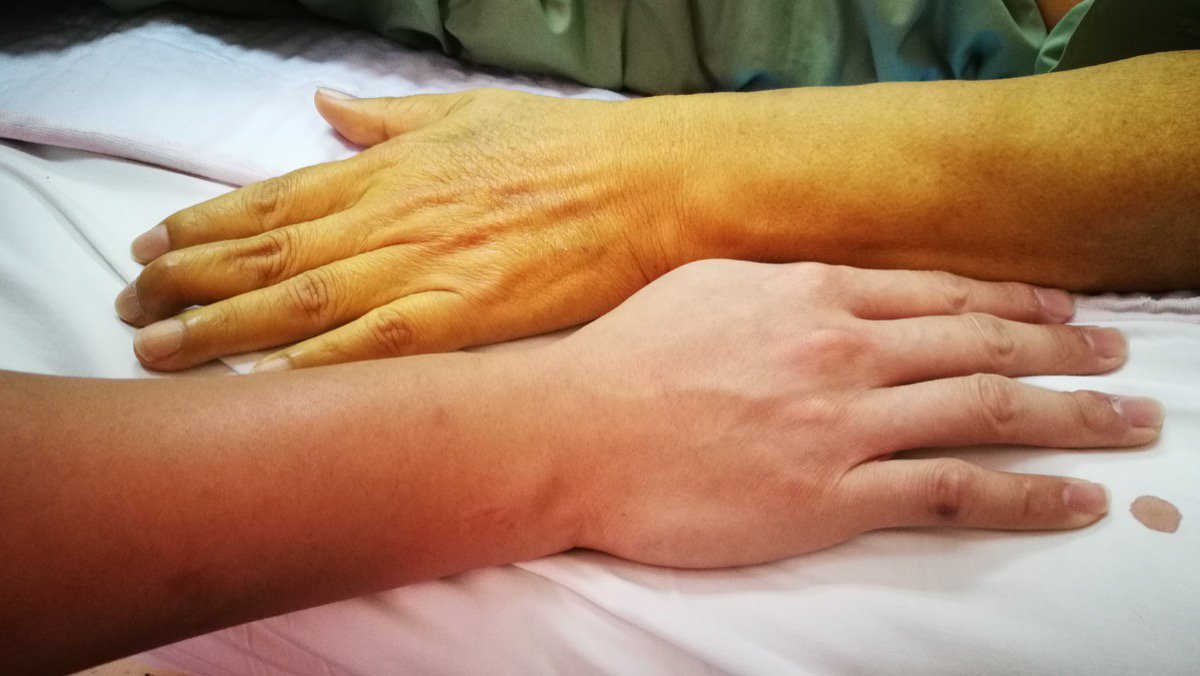
Jaundice is a condition where an individual's skin or the white part of their eyes turn yellow. Bilirubin is a resulting compound of the process of red blood cell breakdown. When bilirubin is broken down by the liver, it produces a compound called urobilin with a potent yellow pigment. Urobilin is excreted from the body through the urine and gives it the yellow coloring. Bilirubin is also responsible for the yellowing that occurs in the last stages of the bruise healing process. Bilirubin in healthy individuals is removed through the stool and the urine after being processed in the liver. The cells that make up a cancerous tumor in the liver can eventually crowd out and replace the healthy, functional liver cells. Malignant tumors also cause liver tissues to become damaged, producing cirrhosis. Rarely, a tumor can grow into or large enough to obstruct the flow of bile from the liver into the small intestine. It is a combination of these factors that results in the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood that leeches into the skin and white of the eye.
2. Unexpected Weight Loss

An individual affected by liver cancer can experience unexpected weight loss. Over two-thirds of all individuals diagnosed with cancer have wasting of the body tissue (cachexia). Body fat and skeletal muscle are the types of tissue most commonly affected by wasting. The first mechanism that causes weight loss and wasting in affected individuals is associated with the liver's role in fat digestion. The liver produces bile, which is secreted into the small intestine to assist with breaking fats and other substances down into units the intestine can absorb. Liver cancer stops the liver from being able to produce enough bile for this process. Less commonly, a tumor can block the bile duct and inhibits bile from reaching the small intestine. Fats that aren't digested are not absorbed and are excreted in the stool. Fats also cannot be transported throughout the body when the liver can no longer produce fat transporting proteins. The malfunctions in fat absorption and deposition result in weight loss. Other symptoms such as appetite loss and feeling full easily also produce unexpected weight loss in liver cancer patients.
