Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Overview
White blood cells, also known as lymphocytes, are part of the immune system and are necessary to protect the body from foreign material and harmful microorganisms. White blood cells are made in the bone marrow, the tissues inside the bones, along with all other blood cells. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), also sometimes referred to as acute lymphocytic leukemia is the form of cancer that prevents the lymphocyte from doing its job properly.
Start reading now to learn the basics about the condition, along with details on symptoms and everything else patients need to know about ALL.
Condition Basics
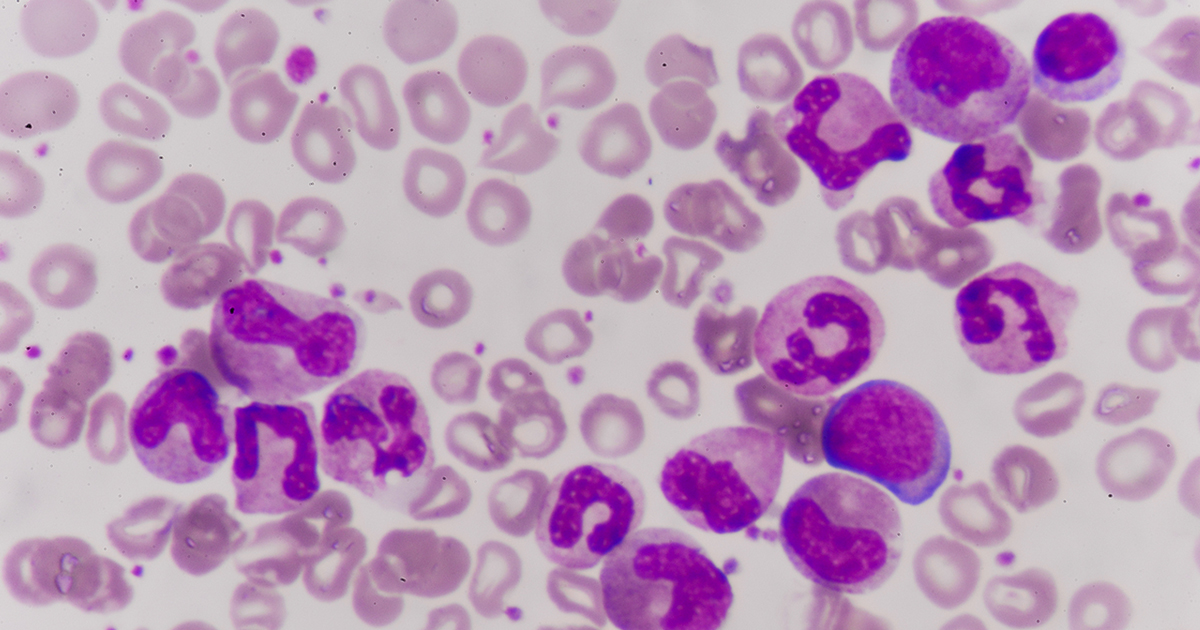
At the very beginning of a lymphocyte's life, it is called a lymphoblast. So, technically lymphoblast and lymphocyte are are both referring to a young white blood cell. This is why acute lymphoblastic leukemia is also occasionally called acute lymphocytic leukemia. The term ‘acute’ means quick. So, if not treated, this cancer spreads quickly and can be fatal within a few months.
This cancer affects the blood and bone marrow. In fact, the cancerous lymphoblasts are overproduced in the bone marrow, so they use up all the resources and then crowd and kill the normal lymphocytes. ALL spreads from the bone marrow through the blood to other parts of the body, a process called metastasis.
Continue reading to learn about the symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Symptoms

The beginning symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia can, unfortunately, be quite vague, at least in the beginning. These vague symptoms include fever, night sweats, fatigue, and loss of appetite or weight. If the patient has a shortage of red blood cells due to ALL, their symptoms can mimic those of anemia, and include shortness of breath, dizziness, feeling cold, lightheadedness, and weakness. A shortage of white blood cells in this condition causes an increase in the frequency of infections, and often fever as well. Other symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia include trouble breathing, joint or bone pain, blurred vision, headaches, issues with balance, and enlarged lymph nodes (e.g., in the groin, neck, or armpits). These symptoms vary based on where cancer spreads in the patient.
Continue reading to learn about who is most at risk for developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
