Strategies For Treating A Baker's Cyst
For those suffering from a baker's cyst, knowing what medications to use and where to find them is vital.
A fluid-filled sac that develops behind the knee and causes a sensation of tightness and a bulging appearance is called a Baker's cyst. This cyst can occur when the lubricant in the knee joint squeezes into the back of the joint and forms a cyst as a result of swelling. A Baker's cyst can also be caused by a knee injury, gout, and other types of arthritis. Some individuals with a Baker's cyst do not experience any noticeable symptoms. Cysts that grow to be large can manifest in symptoms like knee pain, swelling behind the knee, knee joint stiffness, and leg swelling. This type of cyst can be diagnosed with the use of an MRI or ultrasound. An untreated Baker's cyst has the potential to rupture. A ruptured cyst can cause bruising, pain, and swelling on the back of the knee and calf.
There are numerous methods used to treat symptomatic Baker's cyst. Uncover them now.
Fluid Drainage
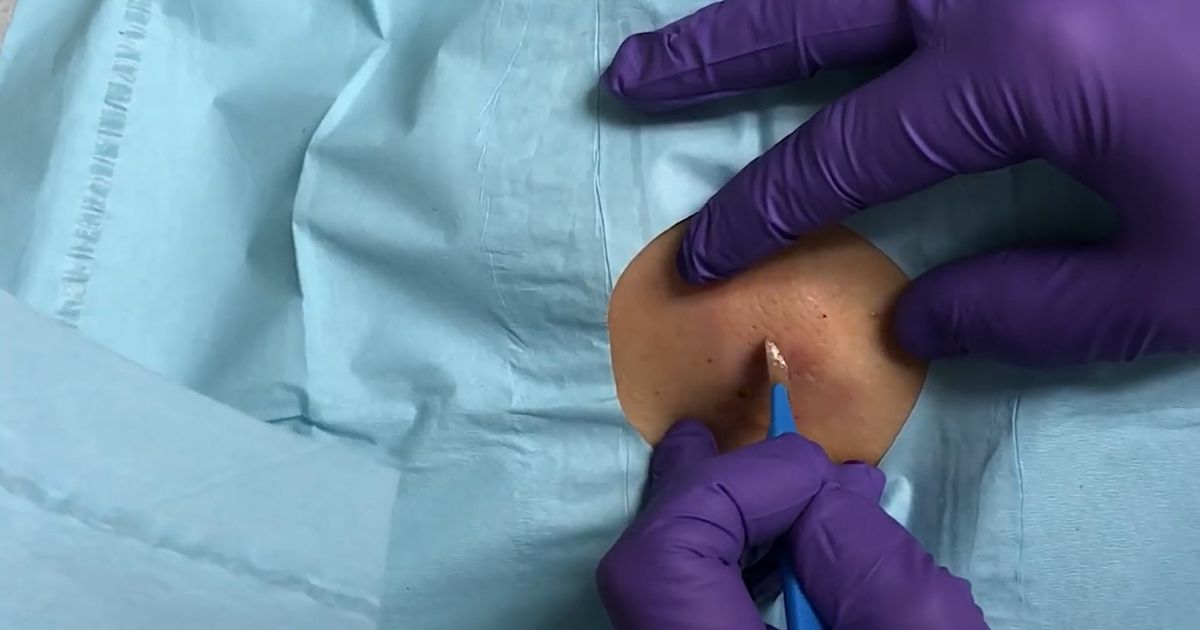
An individual experiencing symptoms as a manifestation of their Baker's cyst may need fluid drainage as part of their treatment. Fluid drainage or aspiration is typically administered on an outpatient basis and does not require any special preparation. During the procedure, a topical or injection of local anesthetic is delivered to the skin around the cyst. A device with a large screen called an ultrasound machine is used to locate the precise location of the patient's cyst. A small needle is inserted into the tissue behind the knee and the cyst. The vacuum mechanism of a syringe is used to draw out the fluid inside of the cyst. This treatment should shrink the cyst to reduce the symptoms the patient is experiencing as a result of the cyst growth. This method of treatment is often used for individuals who cannot undergo surgery to remove the cyst but still need symptomatic relief. The recovery from this aspiration procedure is short and allows the affected individual to resume their regular daily activities the day of or after. Most patients who undergo an aspiration for a baker's cyst do not feel pain during their fluid drainage procedure. Fluid drainage is an effective way to alleviate Baker's cyst symptoms, but there is a possibility the cyst will grow back.
Uncover more options for treating a Baker's cyst now.
Corticosteroid Injection Medication
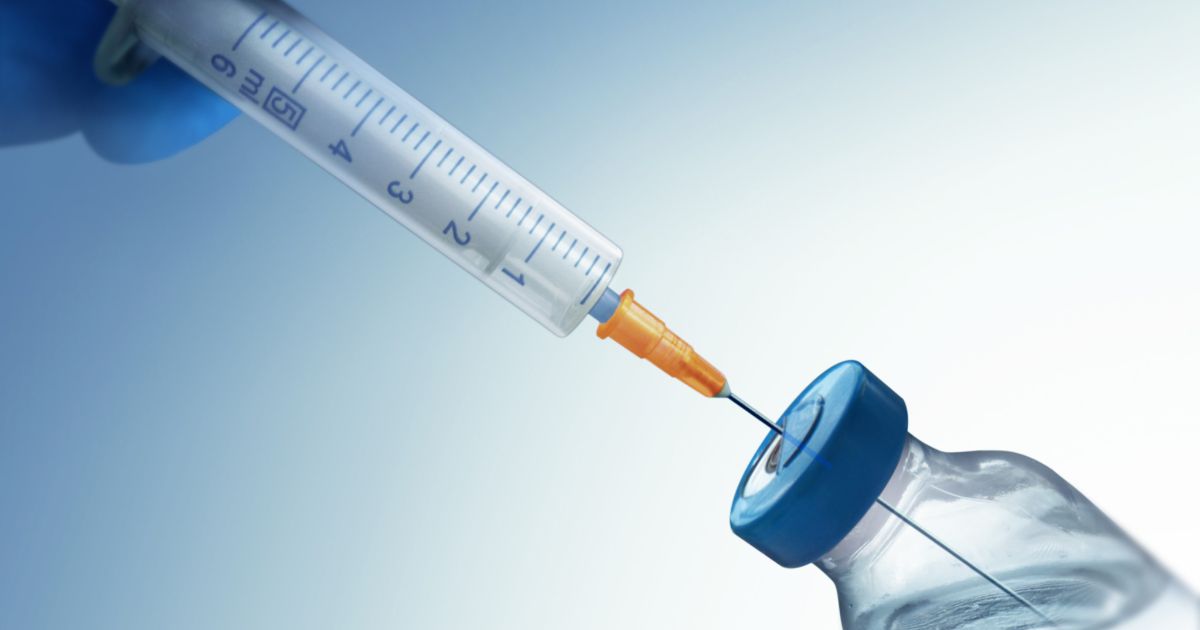
An individual who has a Baker's cyst and is experiencing significant pain as a result of the cyst may require corticosteroid medication. Baker's cyst causes damage and compression of surrounding tissues and structures. The patient's immune system reacts to this compression and injury with an inflammatory response. An inflammatory response includes blood vessel dilation to increase blood flow to the area. The increased circulation is so a rush of oxygenated blood and immune system components can effectively reach the site of the damage. This response causes the area around the cyst to swell up, become red and warm to the touch, and experience sensations of pain. While the inflammatory response has the intention of mediating and repairing cellular damage caused by the cyst, not all of its effects are beneficial in terms of a patient's symptoms. In such cases, medication may be required to inhibit the action of the inflammatory response to help with the reduction of pain and swelling. This type of treatment can be accomplished with the delivery of a type of medication called a corticosteroid through a syringe to the affected region. Corticosteroids work to put the brakes on an affected individual's immune system temporarily so they will not experience so much pain and swelling from the benign cyst.
Discover more ways to treat a Baker's cyst now.
Physical Therapy
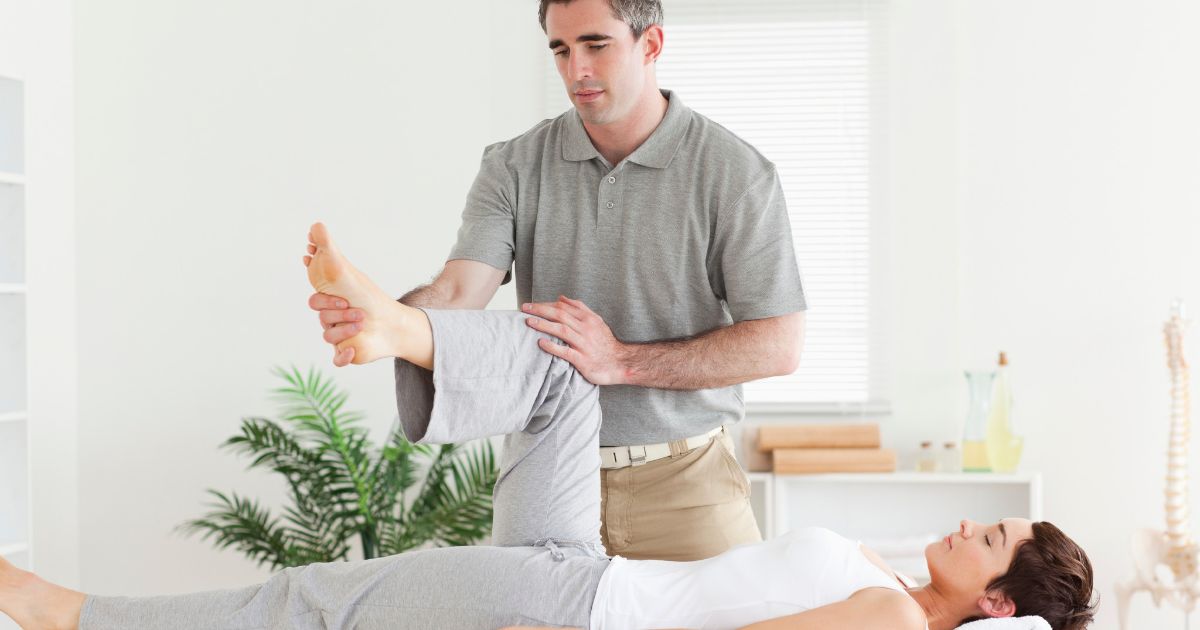

An individual experiencing symptoms from their Baker's cyst may be advised to have physical therapy as part of their treatment. When a patient's Baker's cyst grows large enough, it can easily cause them to have difficulty with joint movement. The cyst can cause the individual to be unable to mobilize the joint physically, or it can cause them to experience severe pain upon attempting to mobilize the knee joint. By the time the cyst has grown large enough to cause such symptoms, the muscles of the knee have become weak as a result of reduced muscle use. This mechanism can lead to problems with an individual's overall balance and stability when standing or walking because the muscles that move the knee can no longer support it. Physical therapy can help a patient learn how to do exercises, strengthening moves, and manipulations to rebuild the muscle strength in the knees. The exercises and movements are also effective at improving an individual's range of motion in the knee. With consistent physical therapy, a patient can prevent and even reverse any effects on their balance and stability caused by their Baker's cyst.
Learn more about effectively treating a Baker's cyst now.
Pain Relief Medication
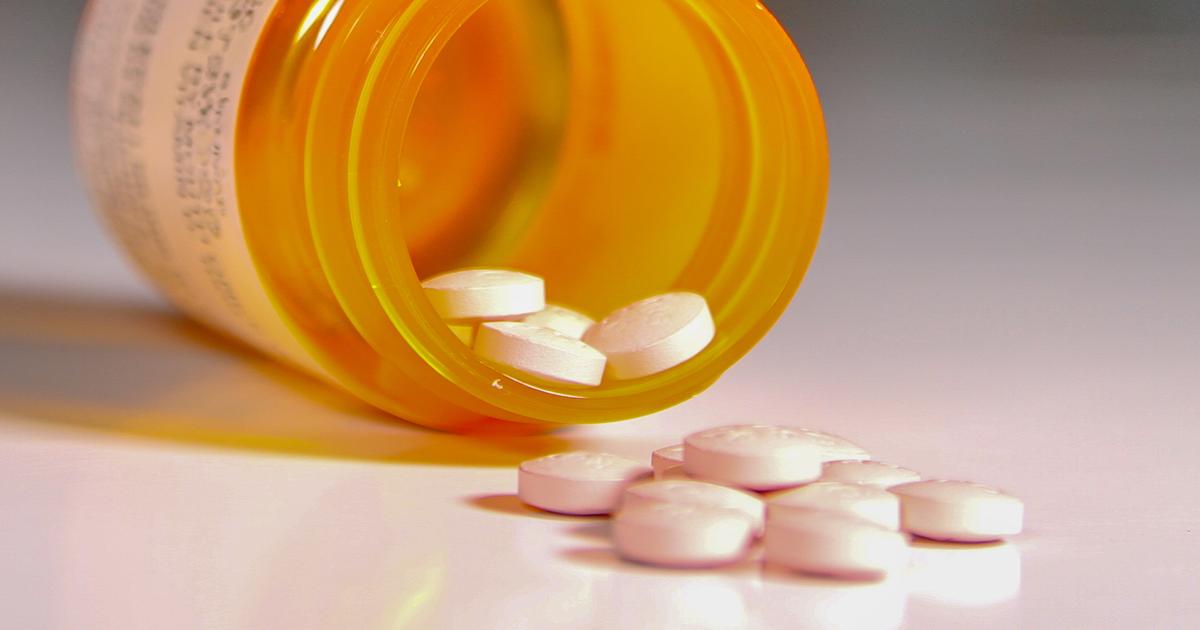

Pain relief medication may be recommended or prescribed for patients experiencing significant pain from their Baker's cyst. In most cases, over-the-counter medicines such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, acetylsalicylic acid, and naproxen sodium are all that is needed to help alleviate the pain from a cyst. Corticosteroid medications can also help with pain relief when they are injected into the site of the cyst because they reduce inflammation. In more severe cases where a patient cannot undergo a surgical procedure to remove an extremely painful cyst, their physician may prescribe stronger painkillers such as narcotic opioids to manage their pain. In circumstances where a patient's Baker's cyst ruptures, they may be prescribed a short round of narcotic painkillers. Some individuals may be prescribed systemic steroids if they are experiencing an excessive amount of inflammation from the cyst itself or the rupture of their cyst. Oral steroids help stop the response of the immune system that causes excessive swelling and pain. Both over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription painkillers may be necessary during recovery for an individual who undergoes surgery to remove their cyst.
Keep reading to discover more options for the treatment of Baker's cysts now.
RICE Treatment
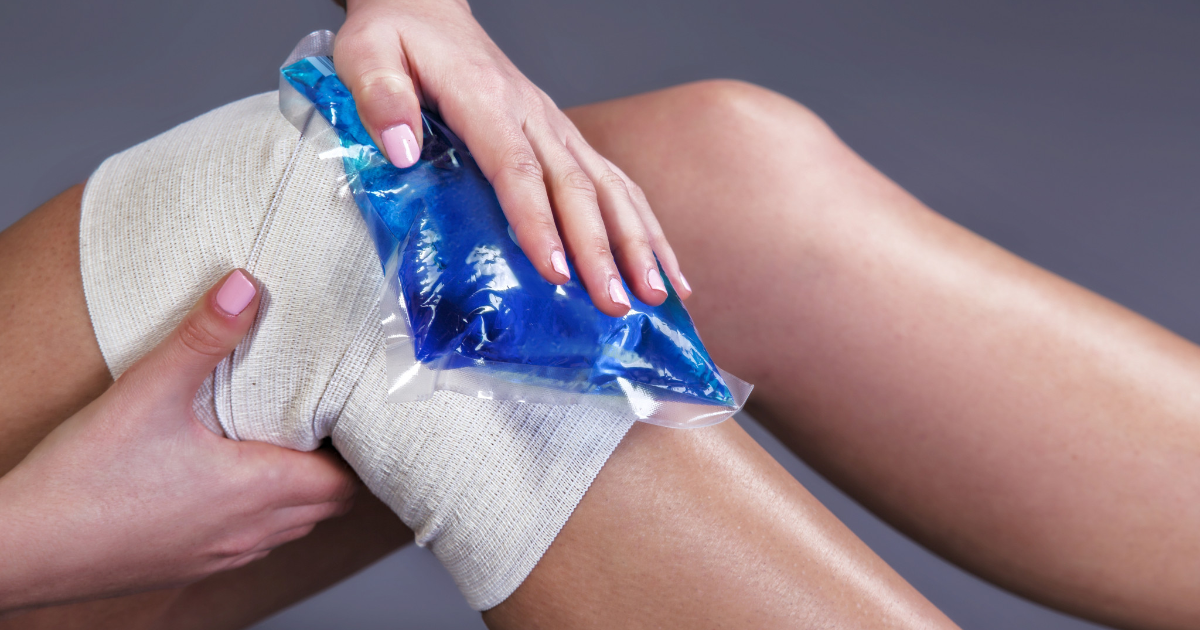

Individuals with a Baker's cyst may be advised to follow the RICE protocol as part of their treatment. RICE stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Rest means the affected individual should stop engaging in any movements or activities that irritate their Baker's cyst and cause increased inflammation. Ice means the patient should use a cold compress in intervals of ten to twenty minutes on the Baker's cyst at a frequency of more than three times a day. This part of the regimen also states if the swelling goes down after forty-eight to seventy-two hours, heat can be applied to help with the pain. Compression is the part of the RICE regimen that means wrapping up the knee around the cyst with an elastic type bandage to help reduce swelling in the area. The bandage should not be wrapped too tight is to obstruct blood flow, as it can result in swelling in the lower leg. Sensations of tingling, numbness, increased pain, swelling, or coolness in the lower leg can indicate the bandage is wrapped too tight. Elevation means to lift the leg when sitting or lying down to a level higher than the elevation of the heart to mediate swelling. The RICE treatment method is typically included in the treatment plan for all symptomatic Baker's cysts.