Common Causes And Risk Factors For Gingivitis
When plaque accumulates on the teeth and under the gums, it hardens into a substance called tartar that extends below the gum surface and causes the development of a bacterial infection. This bacterial infection causes the inflammation of the gums, or what is referred to as gum disease and gingivitis. Symptoms of gingivitis include red gums, bleeding when brushing the teeth, loose teeth, gums that have pulled away from the teeth, tender gums, pain when chewing, swollen gums, bleeding when flossing, pus between the teeth and gums, foul-smelling breath, malocclusion, poorly fitting partial dentures, and sensitive teeth. Diagnosis of gingivitis is made with gum measurements, mouth x-rays, and an oral examination. Treatment of gingivitis may include deep cleaning the teeth with the use of scaling, root planing, and laser techniques. Treatment may also include the use of antiseptic and antibiotic medications.
There are several risk factors and causes of gingivitis. Get familiar with them now.
Accumulation Of Plaque
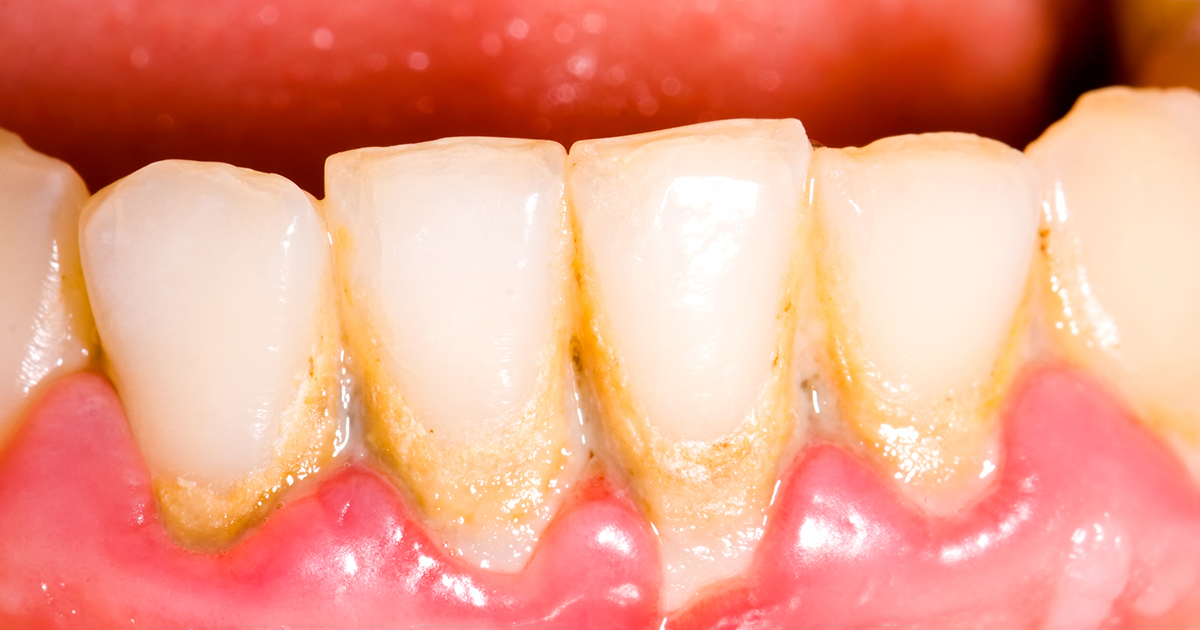
The main cause of gingivitis is the accumulation of plaque on the teeth. Plaque, which is comprised of bacteria, is a sticky film that naturally develops on teeth. The bacteria that live in the plaque on the teeth utilize sugars from the food an individual consumes to make acids that are corrosive to the tooth enamel. These corrosive acids break down the enamel of the tooth. When plaque is not removed from the teeth, it hardens into tartar, a substance that is more difficult to remove from the teeth. The bacteria and plaque continue to build off of the existing tartar on the teeth. The bacteria in the plaque produce byproducts that are toxic and irritating to the gum tissues. The gums can become puffy, red, and inflamed when tartar and plaque accumulate on the teeth and are not removed properly. Accumulation of plaque can occur in an individual who brushes their teeth every day, as it is easy to miss plaque around the gumlines. An individual can floss regularly, attend regular dental cleanings, and use products that help illuminate plaque on the teeth to ensure they are removing all of it regularly.
Read more about the risk factors and causes linked to gingivitis now.
Poor Oral Hygiene
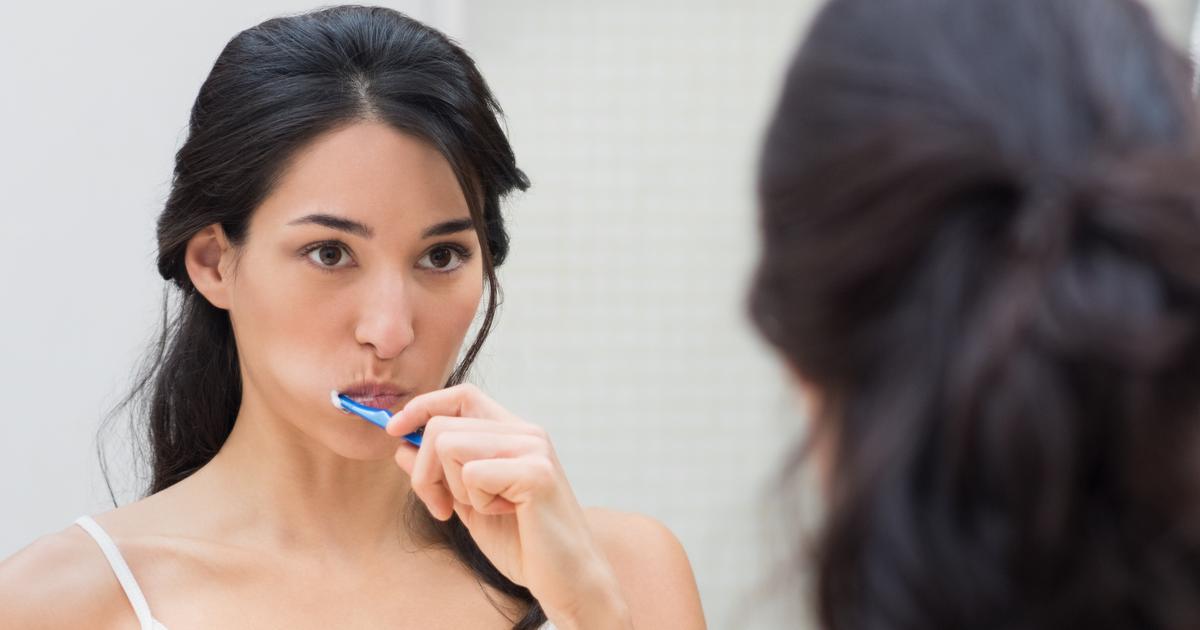

An individual who has poor oral hygiene habits can develop gingivitis. Oral hygiene refers to the practice of keeping the teeth and mouth clean to avoid painful dental issues. Poor oral hygiene occurs when an individual fails to form good oral hygiene habits, like regular flossing and brushing of the teeth to remove any tartar and plaque stuck to them. Poor oral hygiene can also be caused by an individual's habits of using tobacco products, whether it is smoking cigarettes, using chewing tobacco, or any other method of consumption involving the mouth. There are thousands of chemicals in tobacco and cigarette smoke that throw off the entire balance and natural cleaning processes of the mouth. Poor oral hygiene can also occur when an individual consumes a diet high in acidic and sugary foods. Proper oral hygiene and the prevention of gingivitis can be accomplished by quitting smoking, consuming a healthy diet, brushing and flossing the teeth twice per day, using mouthwash twice per day, and getting annual cleanings by a dentist.
Get more details on the causes and risk factors of gingivitis now.
