Serious Causes Linked To Poor Circulation
Atherosclerosis
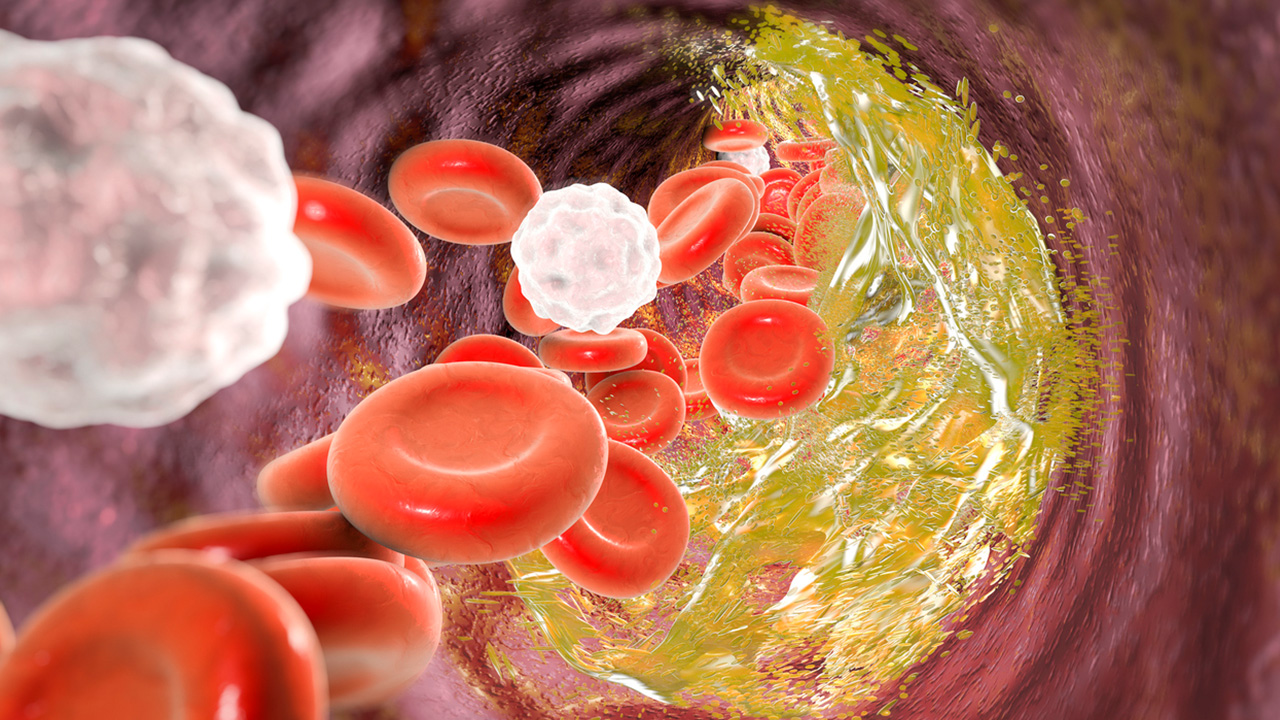
Atherosclerosis is a condition that causes plaque accumulation in the arteries. This contributes to a narrowing of the arteries that reduces blood flow. In the initial stages of atherosclerosis, most patients do not have symptoms. Symptoms generally begin in middle age, and they vary depending on which arteries are affected. When the coronary arteries are affected, patients could experience shortness of breath, angina, and heart rhythm irregularities. These may be symptoms of ischemic heart disease, one of the major complications associated with atherosclerosis. If the carotid arteries become narrowed as a result of atherosclerosis, patients are at risk of a stroke. Stroke symptoms include sudden weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, trouble speaking or understanding speech, loss of coordination, breathing problems, and a sudden, severe headache.
When atherosclerosis leads to plaque accumulation in the peripheral arteries, patients could notice numbness or pain in their arms or legs. Many patients with atherosclerosis do not know they have it until they experience a medical emergency such as a heart attack or a stroke. Patients with high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, or high cholesterol, may be given medication to control these risk factors. Treatment methods for atherosclerosis focus on weight loss and other lifestyle changes, and doctors may prescribe medications to reduce the patient's blood glucose and blood pressure and prevent blood clots. Patients with severe atherosclerosis might need to have surgical intervention such as a coronary artery bypass procedure.
Smoking

Individuals who smoke tend to have reduced circulation, and they are at an increased risk of heart disease, lung cancer, and stroke compared to non-smokers. Smoking makes blood vessels thicker, and it causes the inside of the blood vessels to narrow. As a result, smokers typically have increases in blood pressure and heart rate. Smokers have a thirty to forty percent higher chance of getting type two diabetes compared to non-smokers, and they are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis and cataracts as well.
In general, smoking increases inflammation throughout the body and reduces the function of the immune system. Due to the significant health risks associated with smoking, patients are advised to quit smoking to improve their health. Since it can be difficult to quit smoking without support, patients should ask their healthcare provider about resources to help. Prescription and over-the-counter medicines are available, and patients might be able to attend a local smoking cessation class or support group too.
