Guide To The Common Symptoms Of Xeroderma Pigmentosum
Solar Keratoses
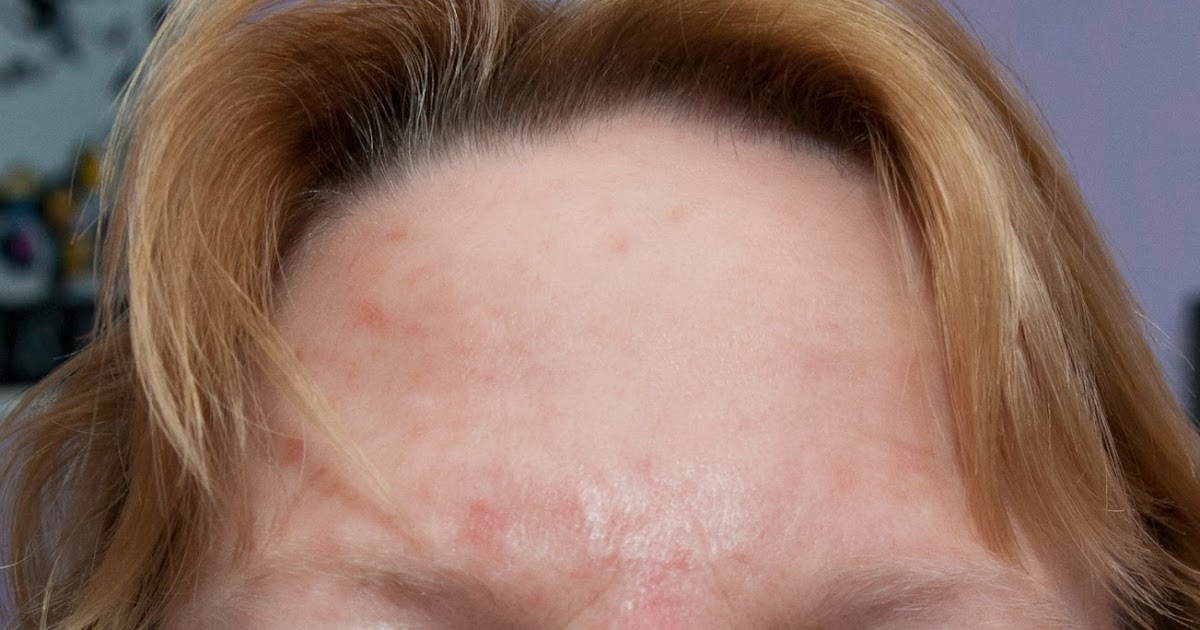
Solar keratoses are common among many individuals and present as bumps on the skin or scaly, rough patches on the skin. They are usually the result of prolonged exposure to the ultraviolet rays of the sun. However, individuals with xeroderma pigmentosum have an accelerated progression of any sun exposure. So, while it might take a person without xeroderma pigmentosum ten years to develop solar keratoses, it could take a person with the condition weeks to develop the lesions. In addition, they will develop more of the lesions than the average person. The danger with solar keratoses is the lesions can become cancerous. The lesions can be removed using various methods, like cryotherapy, topical chemotherapy, and laser surgery. If solar keratoses are removed, they will be tested to see if they are cancerous.
Read more about the various symptoms of xeroderma pigmentosum now.
Development Of Skin Cancer
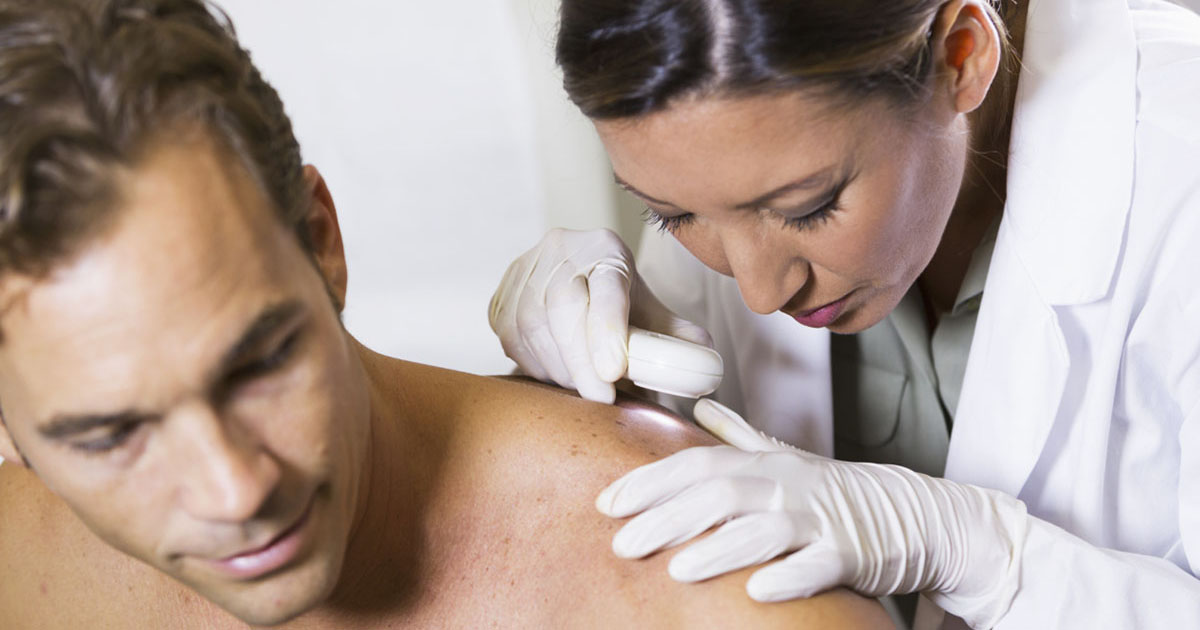
Patients with xeroderma pigmentosum have a high chance of developing skin cancer. For instance, solar or actinic keratosis is typically considered precancerous and can develop into squamous cell skin cancer. Therefore, it is important to get these lesions evaluated, usually through removal and examination. By getting the lesions removed and get treated if they come back as malignant, it can reduce the need for further surgery or other treatments. It is important to recognize skin cancer in these patients may present in childhood. There is a very high probability the xeroderma pigmentosum patient will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. This is why parents need to be very diligent with making sure all skin is treated with sunscreen or covered, perhaps even both. Patients can develop, not only skin cancer, but lip, eye, mouth, and eyelid cancer. Frequent skin inspections can help head off the progression of cancer.
Uncover details on more xeroderma pigmentosum warning signs.
